Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 12, 2022
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster I: AxSpA
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Since the 2016 recommendations for axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) management, new evidence emerged regarding axSpA treatment. The aim of this work was to update the evidence on efficacy and safety for non-pharmacological and non-biological treatments to inform the update of ASAS-EULAR recommendations for the management of axSpA.
Methods: Systematic literature review (SLR) from 2016 (previous SLR), up to 1st January 2022 (PROSPERO registration CRD42021261959). The research question was formulated according to the PICO format: Population: adult patients with r-axSpA or nr-axSpA;
Intervention: non-pharmacological and non-biological treatments; Comparator: active comparator or placebo; Outcomes: all relevant efficacy and safety outcomes; Type of studies: randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies (the latter for efficacy of non-pharmacological treatments and safety only). Cohen’s effect size (ES) was calculated for non-pharmacological and risk ratio (RR) for pharmacological treatments. Risk of bias (RoB) was assessed using the Cochrane tool for RCTs and the Hayden tool for cohort studies.
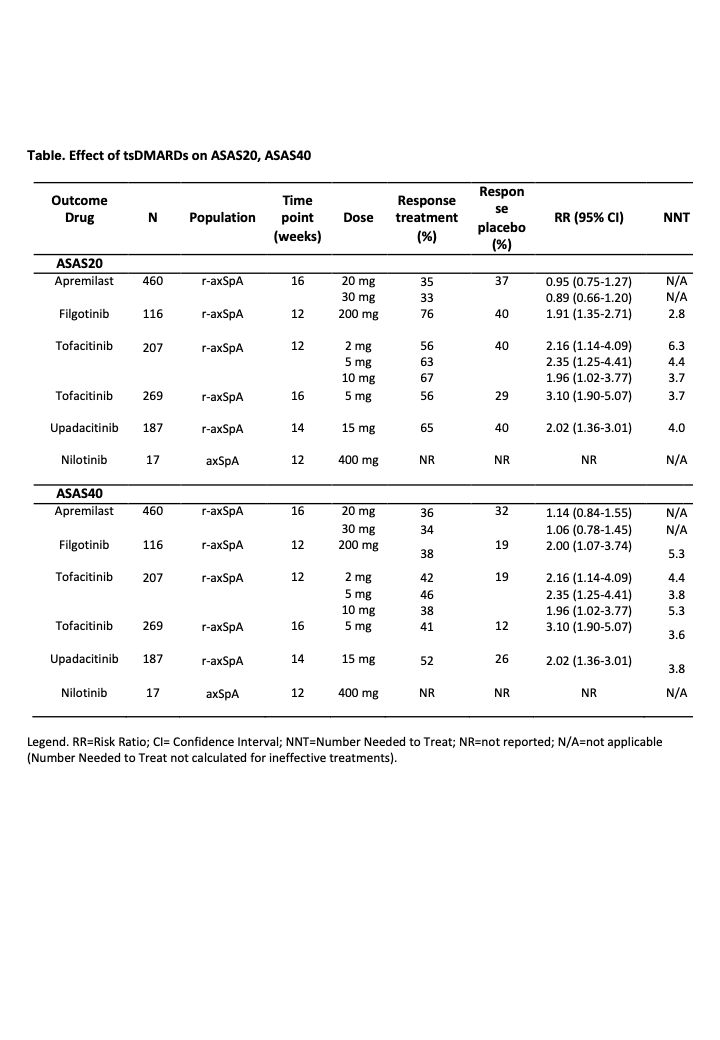
Results: After title/abstract screening and full-text reading, 117 publications were included in the present SLR. Studies on non-pharmacological interventions addressed education (n=8), exercise (n=20) and other treatments (n=16). The majority of these studies were conducted on r-axSpA, and were with high RoB, except 6 RCTs at unclear RoB. The ES for education on disease activity, function, and mobility were small to moderate (ES min/max for BASDAI: -1.2/0.59, BASFI: -0.25/0.58, BASMI: 0.07/0.54). The ES for exercise regarding the same outcomes were moderate to high (ES min/max for ASDAS: 0.29/0.94, BASDAI: 0.14/1.43, BASFI: 0.04/0.92, BASMI: 0.06/1.14). Studies describing other types of non-pharmacological interventions (e.g. ultrasound therapy, moxibustion, diet) were very heterogeneous in the type, duration, and frequency of the treatments. Studies on conventional synthetic DMARDs (n=3), NSAIDs (n=8) and other drugs (n=12) did not provide new relevant evidence on efficacy or safety. Among 12 studies addressing other pharmacological interventions, one at unclear RoB showed limited efficacy of short-term glucocorticoids in axSpA (ASAS20 RR 1.80; 95%CI: 0.87-3.70; ASAS40 RR 2.47, 95%CI 0.98-6.22). One RCT at unclear RoB has shown that alendronate is not efficacious in r-axSpA. Six RCTs on 5 targeted synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARDs) showed efficacy of tofacitinib, upadacitinib and filgotinib, only in r-axSpA (Table). Two RCTs showed that apremilast and nilotinib are not efficacious in r-axSpA (BASDAI 50 more often reached in placebo -33%- than nilotinib -0%).
Conclusion: New evidence on education and exercise confirms their efficacy in axSpA. Within the new class of tsDMARDs tofacitinib, upadacitinib and filgotinib were those which have shown efficacy in r-axSpA.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ortolan A, Webers C, Sepriano A, Falzon L, Baraliakos X, Landewé R, Ramiro S, van der Heijde D, Nikiphorou E. Efficacy and Safety of Non-Pharmacological and Non-Biological Therapy: A Systematic Literature Review Informing the 2022 Update of the ASAS-EULAR Recommendations for the Management of Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-non-pharmacological-and-non-biological-therapy-a-systematic-literature-review-informing-the-2022-update-of-the-asas-eular-recommendations-for-the-management-of-axial-spondyloar/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-non-pharmacological-and-non-biological-therapy-a-systematic-literature-review-informing-the-2022-update-of-the-asas-eular-recommendations-for-the-management-of-axial-spondyloar/