Session Information
Session Type: Late-Breaking Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-11:15AM
Background/Purpose: COVID-19 vaccines have robust immunogenicity in the general population. Data on individuals with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases who are taking immunosuppressants remains limited. Our cohort study showed that methotrexate but not targeted biologics impaired functional humoral immunity to a single dose of COVID-19 vaccine BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech), while cellular responses were comparable. We sought to assess immune responses following a second dose.
Methods: Individuals with the common inflammatory skin disease psoriasis receiving methotrexate or biologic monotherapy (TNF, IL-17, or IL-23 inhibitors) were recruited from a national specialist psoriasis centre serving London/South-East England. Healthy volunteers without psoriasis, not receiving immunosuppression, were recruited as controls. Immunogenicity was assessed immediately before, on day 28 after the first BNT162b2 dose and on day 14 post-second dose (administered according to an extended interval regimen). Immune responses following the second dose are reported. Primary outcomes were humoral immunity to the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein, defined as neutralising antibody responses to wild-type, Alpha and Delta SARS-CoV-2, and spike-specific T cell responses (IFNγ, IL-2, IL-21).
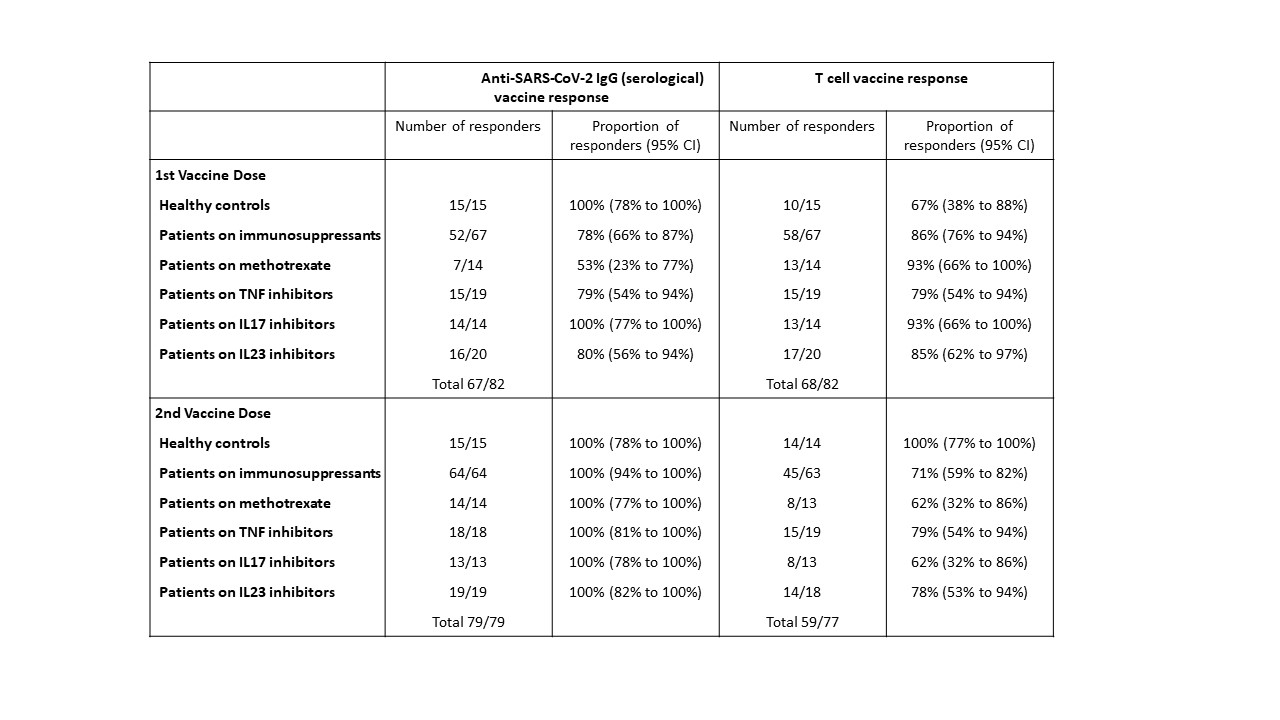
Results: The study population (n=82) included patients with psoriasis receiving methotrexate (n=14), TNF inhibitors (n=19), IL-17 inhibitors (n=14), IL-23 inhibitors (n=20) and healthy controls (n=15), who had received both vaccine doses. The median age of the study population was 44 years (IQR 33–52), with 43 (52%) males and 71 (87%) participants of white ethnicity. All participants seroconverted at 14 days following the second vaccine dose. All study groups (healthy controls, methotrexate, targeted biologics) demonstrated comparable neutralising antibody titres against wild-type, Alpha and Delta variants. In contrast, a lower proportion of participants on methotrexate (62%, 95%CI 32-86) and targeted biologics (74%, 95%CI 60-85) had detectable T cell responses following the second dose, compared to controls (100%, 95%CI 77-100) (p=0.022). Overall, there was no difference in the magnitude of T cell responses between all patients receiving methotrexate (median log-cytokine-secreting cells per 106 cells 2.2 [IQR 1.0–2.8]), targeted biologics (2.2 [IQR 1.4–2.7], p=0.5578) and controls (2.3 [IQR 2.1–2.5], p=0.4093).
Conclusion: Functional humoral immunity at 14 days following a second dose of BNT162b2 is not impaired by methotrexate or targeted biologics. A proportion of patients on immunosuppression do not have detectable T cell responses following the second dose. The longevity of vaccine-elicited antibody responses is uncertain in this population.
A threshold EC50 value of 25 was used for anti-SARS-CoV_2 IgG titres, at which serological responses were classified as positive.
A threshold value of 30 cytokine secreting cells per million PBMCs was established for total T cell responses (IFNγ and/or IL_2 and/or IL_21), at which the T cell response was classified as positive.
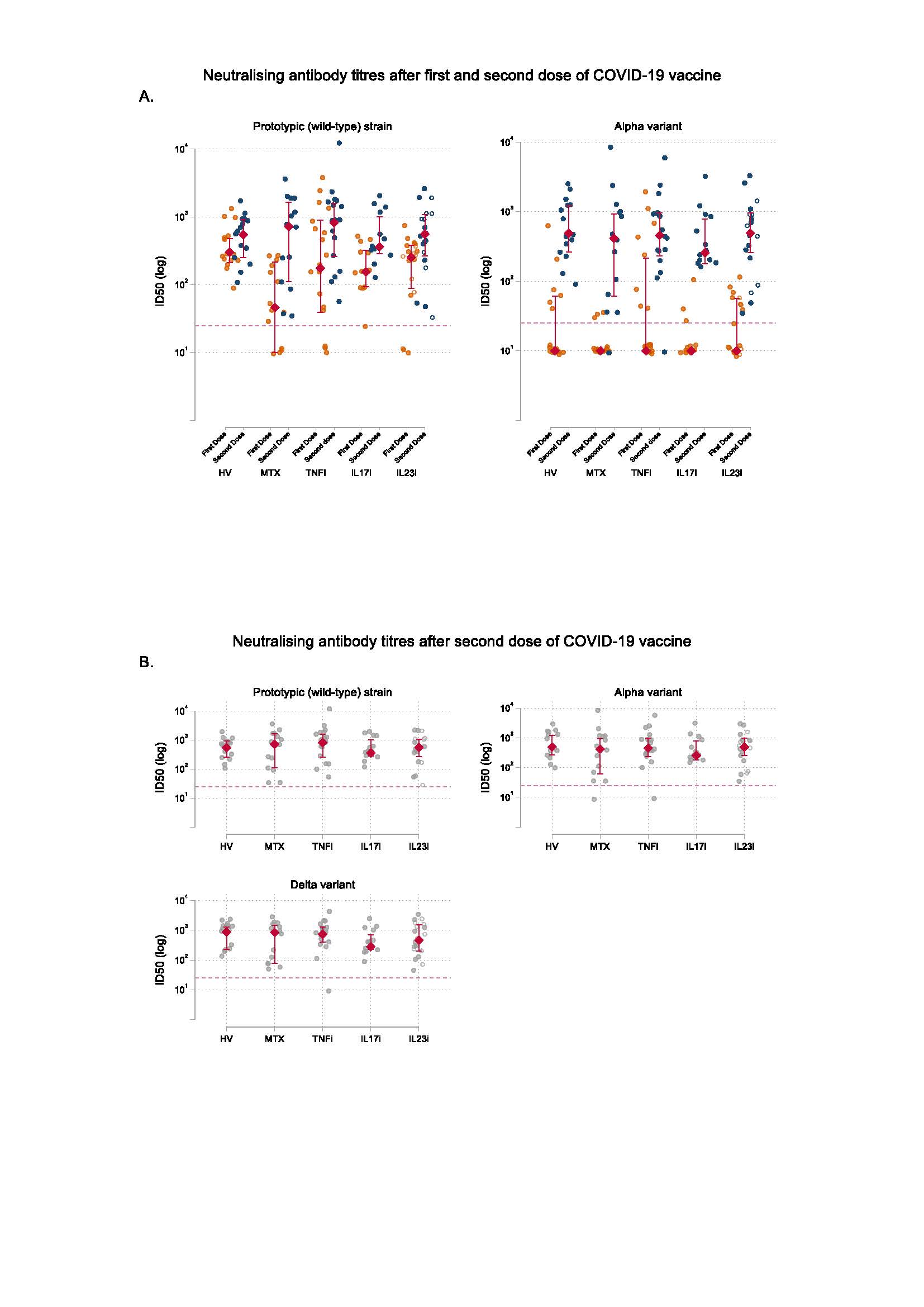
A. Neutralising antibody titres against prototypic (wild-type) strain and Alpha variant at day 28 following the first dose and at day 14 following the second dose of COVID_19 vaccine BNT162b2. The circles represent individual values. The red diamonds and range lines indicate the median and interquartile range (IQR), respectively. In the IL23i group, filled circles represent participants receiving IL_23p19 inhibitors and hollow circles represent participants receiving IL_23p40/IL_12 inhibition. Horizontal dashed line indicates neutralisation activity threshold.
B. Neutralising antibody titres against wild-type SARS-CoV_2, Alpha variant, and Delta variant at day 14 following the second dose of COVID_19 vaccine BNT162b2. The circles represent individual values. The red diamonds and range lines indicate the median and interquartile range (IQR). In the IL23i group, filled circles represent participants receiving IL_23p19 inhibitors and hollow circles represent participants receiving IL_23p40/IL_12 inhibition. Horizontal dashed line indicates neutralisation activity threshold.
HV, healthy volunteers; MTX, methotrexate; TNFi, TNF inhibitors; IL17i, IL_17 inhibitors; IL23i, IL_23 inhibitors; ID50, 50% inhibitory dilution.
A. Fold change in total T cell response, as determined by IFNγ and/or IL_2 and/or IL_21 responses to stimulation with peptides from total Spike peptide pools between the first dose and second dose of COVID_19 vaccine. The red diamonds and range lines indicate the median and interquartile range (IQR).
B. Total T cell response, as determined by IFNγ and/or IL_2 and/or IL_21 responses to stimulation with peptides from total Spike peptide pools, reported as number of cytokine secreting cells per 106 PBMCs at day 28 following the first dose and at day 14 following the second dose of COVID_19 vaccine. The circles represent individual values. The red diamonds and range lines indicate the median and interquartile range (IQR), respectively. Horizontal dashed line indicates total T cell response threshold. In the IL23i group, filled circles represent participants receiving IL_23p19 inhibitors and hollow circles represent participants receiving IL_23p40/IL_12 inhibition.
HV, healthy volunteers; MTX, methotrexate; TNFi, TNF inhibitors; IL17i, IL_17 inhibitors; IL23i, IL_23 inhibitors.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mahil S, Bechman K, Raharja a, domingo-Vila c, Baudry d, Brown m, Cope A, Dasandi t, Khan h, Lechmere t, Malim m, Meynell f, pollock e, Sychowska k, Barker J, Norton S, Galloway J, Doores k, Tree t, Smith c. Humoral and Cellular Immune Responses to a Second Dose of COVID-19 Vaccine BNT162b2 in People Receiving Methotrexate or Targeted Immunosuppression: A Cohort Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/humoral-and-cellular-immune-responses-to-a-second-dose-of-covid-19-vaccine-bnt162b2-in-people-receiving-methotrexate-or-targeted-immunosuppression-a-cohort-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/humoral-and-cellular-immune-responses-to-a-second-dose-of-covid-19-vaccine-bnt162b2-in-people-receiving-methotrexate-or-targeted-immunosuppression-a-cohort-study/