Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Adalimumab (ADA) was approved in the European Union for the treatment of severe non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA) in patients with objective signs of inflammation (elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) or positive MRI) and inadequate response or intolerance to NSAIDs. We aimed to evaluate effects of long-term ADA treatment on patient-reported outcomes (PROs) and work productivity in nr-axSpA patients with elevated CRP or positive MRI.
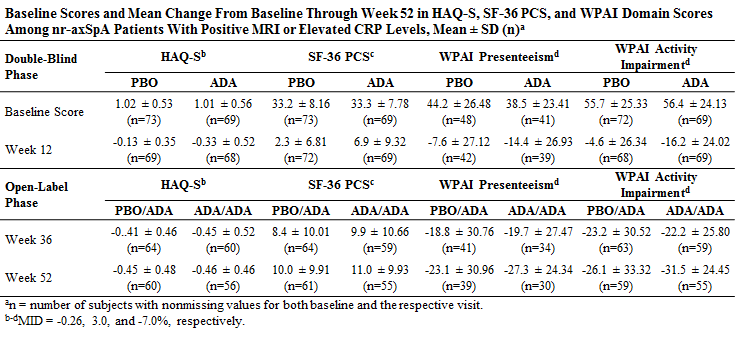
Methods: ABILITY-1 is an ongoing Phase III, multicenter, randomized, controlled trial of ADA vs. placebo (PBO) in patients with nr-axSpA (fulfilling Assessment of Spondyloarthritis international Society axial SpA criteria but not modified New York criteria for ankylosing spondylitis). After the 12-week double-blind phase, all patients switched to open-label ADA (represented as ADA/ADA and PBO/ADA groups) for 144 weeks. This post-hoc analysis evaluated productivity and PROs until Week 52 among 142 patients with elevated CRP or MRI evidence of inflammation (spine or SI joints) at baseline. Physical function was assessed using the disability index of the Health Assessment Questionnaire for Spondyloarthropathies (HAQ-S) and health-related quality of life using the Short Form 36 Health Survey (SF-36) Physical Component Summary (PCS) score. Productivity was assessed using the Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire (WPAI). Changes from baseline to Week 12 were compared between groups using ANCOVA with adjustment for baseline scores and with treatment as a factor.
Results: No significant differences between treatment groups were observed in baseline HAQ-S, SF-36 PCS, or WPAI domain scores. After 12 weeks of therapy in the double-blind period, the ADA group experienced significant improvements from baseline compared with PBO in mean HAQ-S (P=.007) and SF-36 PCS (P<.001) scores, and in 3 of 4 WPAI domain scores (P=.017, 0.041, 0.128, and 0.005, for absenteeism, presenteeism, overall work impairment, and activity impairment, respectively). By Week 52, PBO patients who switched to open-label ADA demonstrated improvements comparable to those in patients who received ADA during the double-blind period. Patients in both groups achieved SF-36 scores (43.2 and 44.3 for the PBO/ADA and ADA/ADA groups, respectively) approaching the US general population norm of 50 at Week 52.
Conclusion: Among patients with elevated CRP or positive MRI, ADA therapy was associated with significant improvement in PROs and productivity compared with PBO during the double-blind phase of the ABILITY-1 trial. Patients who continued on ADA therapy and those who switched to ADA in the open-label period experienced comparable meaningful improvements in PROs and productivity through Week 52.
Disclosure:
D. M. van Der Heijde,
AbbVie,
5,
Amgen,
5,
Aventis Pharmaceuticals,
5,
Bristol-Myers Squibb,
5,
Centocor, Inc.,
5,
Pfizer Inc,
5,
Roche Pharmaceuticals,
5,
Schering-Plough,
5,
UCB,
5,
Wyeth Pharmaceuticals,
5;
P. J. Mease,
AbbVie, Amgen, BiogenIdec, BMS, Celgene, Crescendo, Genentech, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Vertex,
2,
AbbVie, Amgen, BiogenIdec, BMS, Celgene, Crescendo, Genentech, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, UCB, Vertex,
5,
AbbVie, Amgen, BiogenIdec, BMS, Crescendo, Genentech, Janssen, Lilly, Pfizer, UCB,
8;
A. L. Pangan,
AbbVie,
1,
AbbVie,
3;
S. A. Rao,
AbbVie,
1,
AbbVie,
3;
N. Chen,
AbbVie,
3,
AbbVie,
1;
M. Cifaldi,
AbbVie,
3,
AbbVie,
1.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/improvement-in-physical-function-health-related-quality-of-life-and-work-productivity-with-adalimumab-treatment-in-non-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis/