Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including PsA – Treatment Poster III: Psoriatic Arthritis II (1801–1835)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Guselkumab (GUS), an anti-interleukin-23p19 subunit monoclonal antibody, is approved to treat psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Post hoc analyses of DISCOVER-1&2 suggested that GUS may be effective in improving symptoms of axial manifestation of PsA. This study evaluated the efficacy of GUS across components of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) in improving symptoms of axial manifestations of active PsA patients using data from phase-3, randomized, placebo (PBO)-controlled studies.
Methods: In DISCOVER-1&2, patients with active PsA were randomized to subcutaneous injections of GUS 100 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W) or at Week 0, 4, and Q8W, or PBO. These post hoc analyses included patients who were identified by the investigator as having axial symptoms and sacroiliitis (prior X-ray or MRI or screening X-ray). BASDAI scores were assessed at Weeks 0, 8, 16, 24, and 52. Mean BASDAI component scores through Week 52 are reported by treatment group. Pooled data from the two studies are reported. Mean BASDAI component scores are reported using observed data; total BASDAI scores with missing components were set to missing. The proportion of patients achieving ≥50% improvement in BASDAI (BASDAI 50) was also determined; patients with missing data or who met the treatment failure criteria (discontinued study agent or used prohibited medications) were considered nonresponders at all subsequent timepoints.
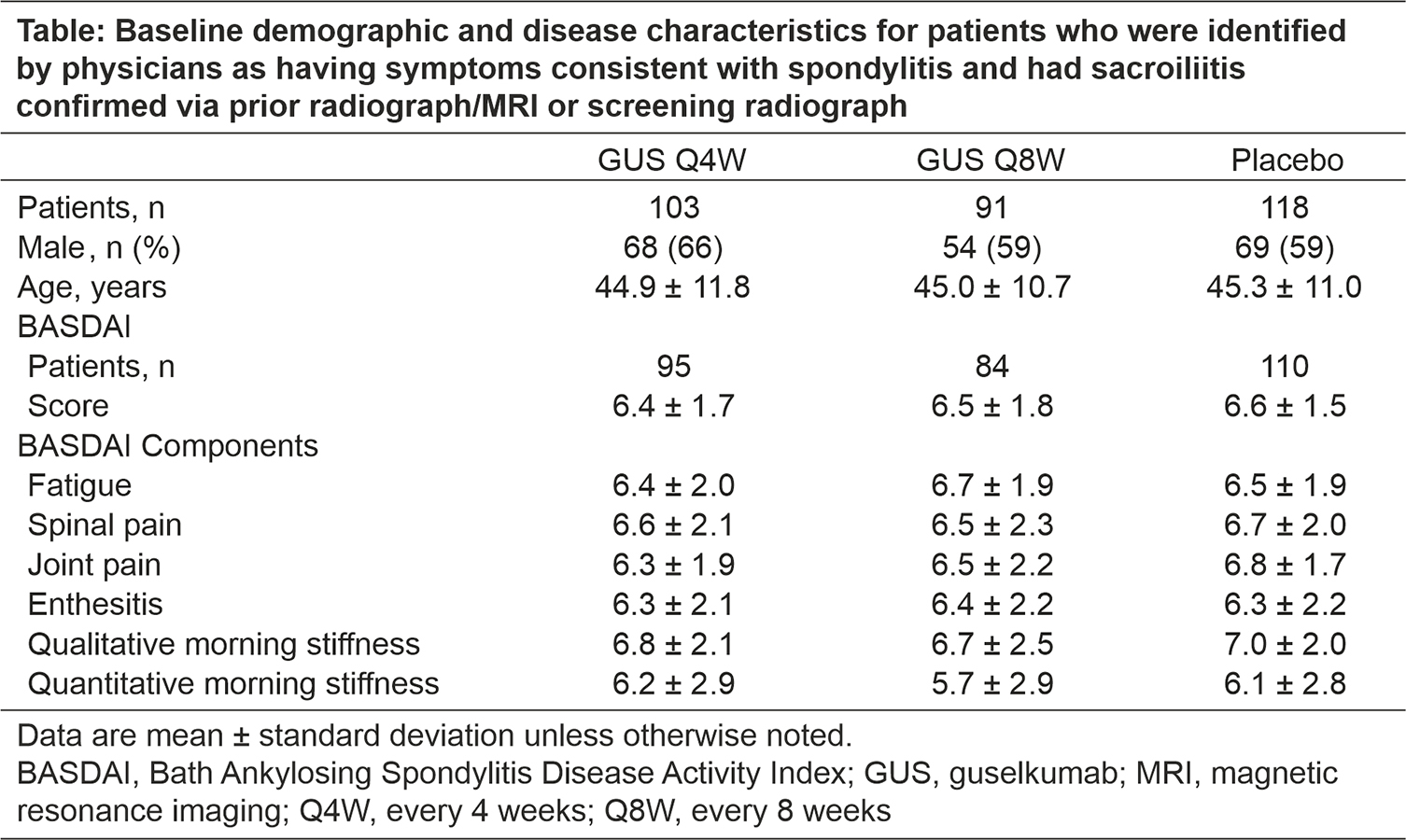
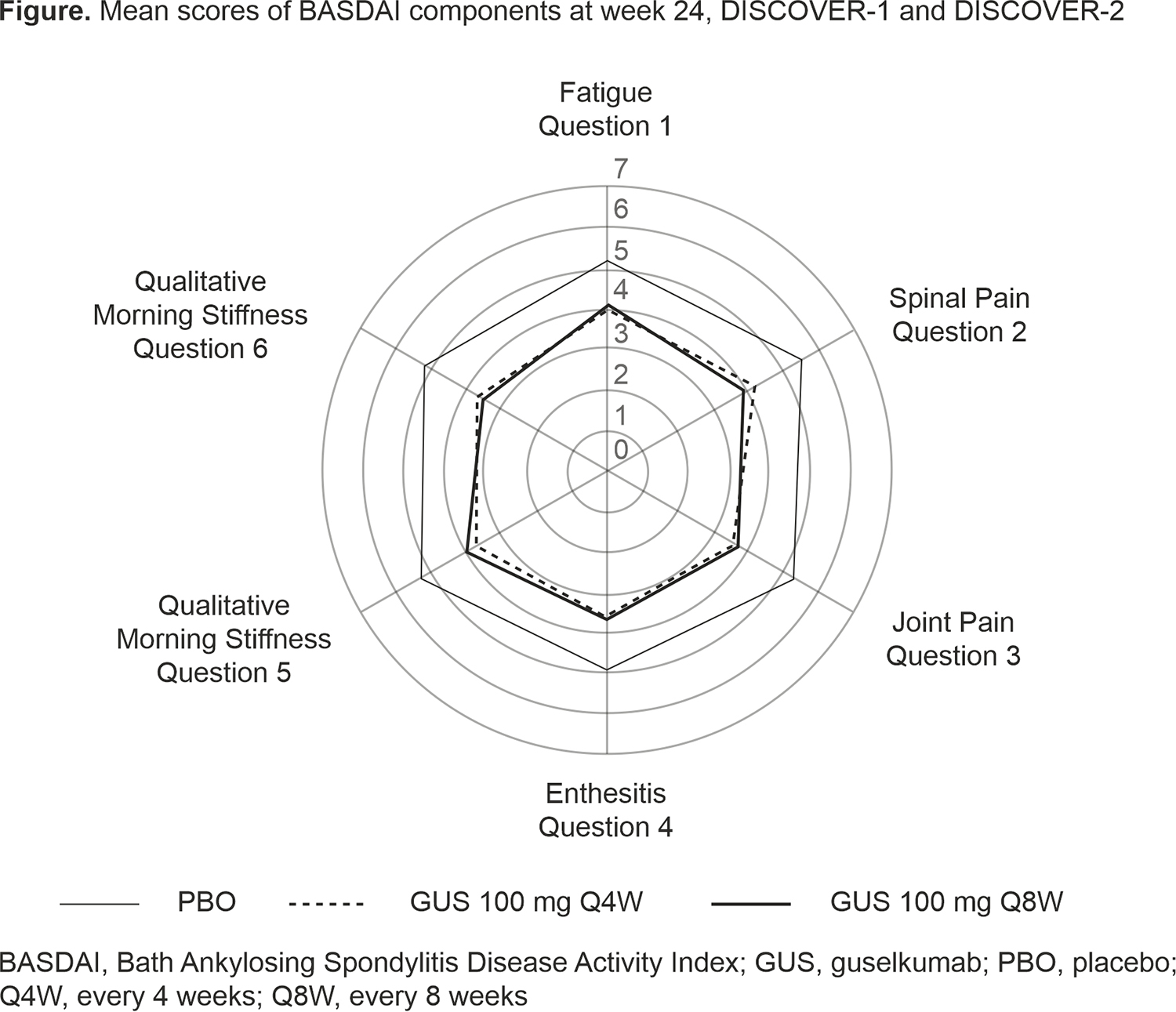
Results: These analyses included 312 patients from DISCOVER-1&2 (103 GUS Q4W, 91 GUS Q8W, 118 PBO); mean total BASDAI scores at Week 0 were 6.4, 6.5, and 6.6, respectively. Demographics and mean baseline BASDAI component scores (ie, fatigue, spinal pain, joint pain, enthesitis, qualitative morning stiffness, and quantitative morning stiffness) were similar across treatment groups (Table). In comparison with the total study population, this subgroup of patients had a higher mean C-reactive protein level at baseline and a higher proportion of patients with enthesitis and included a slightly higher proportion of males. Mean scores for all six BASDAI components, including spinal pain, decreased through Week 24 in GUS-treated patients, with separation from PBO observed as early as Week 8; improvements were maintained at Week 52. At Week 24, BASDAI 50 response rates were higher in the Q4W and Q8W groups versus PBO (38% and 40% versus 19%).1 At Week 52, mean BASDAI component scores for PBO patients who crossed over to GUS Q4W at Week 24 were similar to those for patients who were randomized to GUS.2 A similar trend was observed for BASDAI 50 response.
Conclusion: Among PsA patients with axial symptoms and sacroiliitis (via investigator-confirmed imaging) in the DISCOVER-1&2 trials, GUS treatment resulted in lower mean scores for all six BASDAI components compared with PBO as early as Week 8 and through Week 24, with mean scores maintained at Week 52.
References:
1Helliwell P, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020; 79; Suppl 1.
2Mease PJ, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72; Suppl 10.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Behrens F, Mease P, Helliwell P, Shawi M, Noel W, Chakravarty S, Kollmeier A, Xu X, Xu S, Wang Y, Baraliakos X. Efficacy of Guselkumab Across BASDAI Components in Treating Axial-Related Symptoms of Psoriatic Arthritis: Results from Two Phase 3, Randomized, Placebo-controlled Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-guselkumab-across-basdai-components-in-treating-axial-related-symptoms-of-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-two-phase-3-randomized-placebo-controlled-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-guselkumab-across-basdai-components-in-treating-axial-related-symptoms-of-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-two-phase-3-randomized-placebo-controlled-studies/