Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Tocilizumab (TCZ) for treatment of severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pneumonia decreases the probability of progression to invasive mechanical ventilation (CORIMUNO-TOCI) or death (REMAP-CAP, RECOVERY). Standard doses of 400-800 mg or 8 mg/kg of body weight have been used in previous studies; however, determining the optimal dose is critical given the possibility of increased rates of infection in higher doses and limited global supplies. The COVIDOSE study evaluated the pharmacodynamic and clinical efficacies, safety and dose response of low-dose TCZ in COVID-19.1 With the emergence of “long COVID” sequelae, we present follow up to COVIDOSE with analysis of 90-day mortality.
Methods: This was an adaptive phase 2 study of low-dose TCZ in hospitalized, non-mechanically ventilated adult patients with COVID-19 pneumonitis, C-reactive protein (CRP) ≥ 40 mcg/mL, and at least 1 epidemiologic risk factor for increased risk of COVID-related death (e.g. underlying medical conditions). Dose cohorts were determined by a trial Operations Committee, with the initial doses of 80 or 200 mg. Doses were decreased to 40 mg and 120 mg after interim assessment. Pre-specified secondary objectives included 28-day mortality; 90-day mortality was a later addendum given the emergence of “long COVID.”
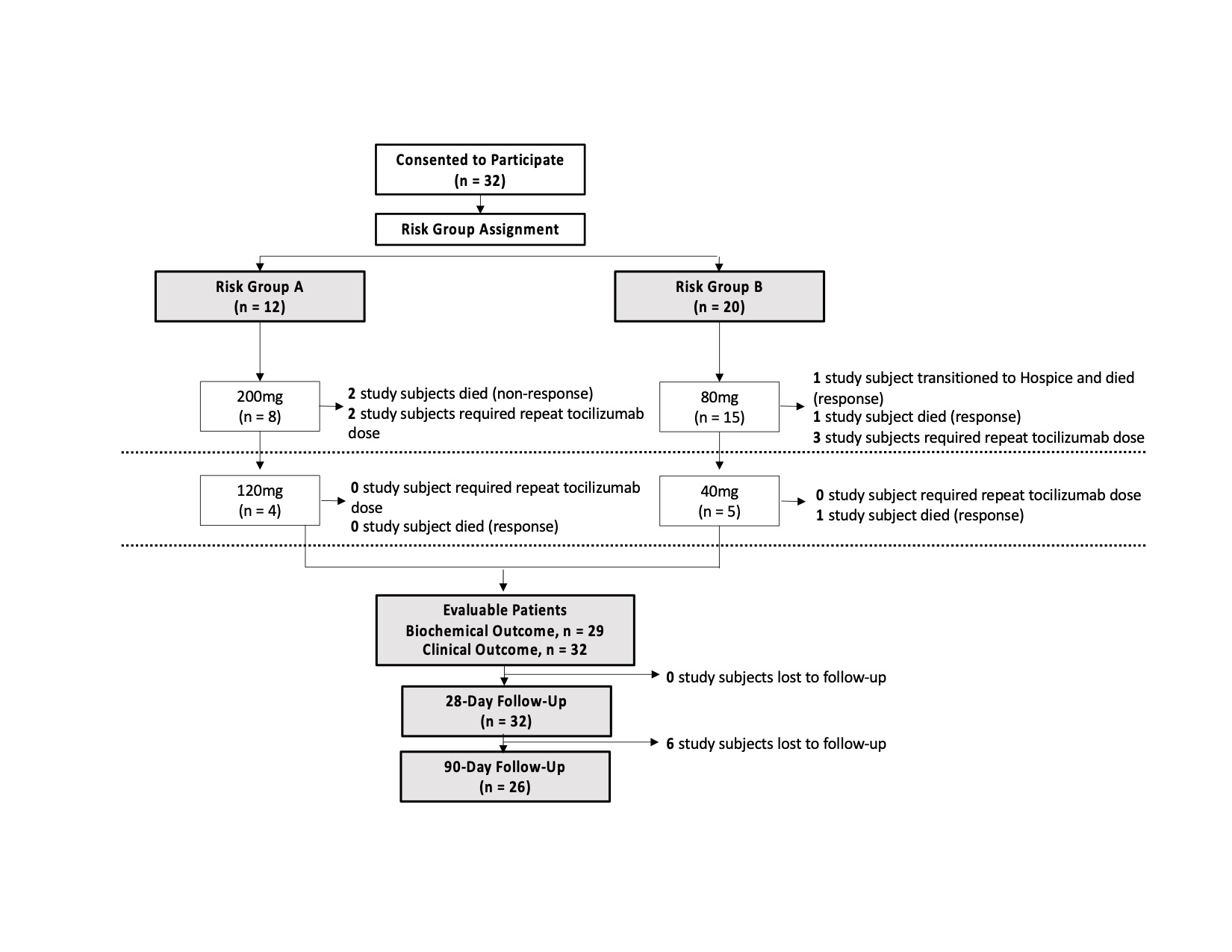
Results: Thirty-two patients received low-dose TCZ (Figure 1). Within the 28-day follow up period, 5 (16%) patients died. Within the 90-day follow up period, 6 participants were lost to follow up, and 6 (23%) had died (including 5 who died within the 28-day period). Four out of 6 died during index COVID-19 hospitalization. Mean baseline CRP did not differ between patients who died versus those alive at 90 days (158 ± 96 mcg/mL vs 158 ± 83 mcg/mL). Mean CRP decrease in the 24 hours following first TCZ dose did not differ between patients who died vs those alive at 90 days (38 ± 11% vs 34 ± 15%).
Conclusion: Ninety-day mortality rate in this small phase 2 study was 23%, with 1 out of 26 patients dying between the 28-day and 90-day mark. Previously reported 90-day mortality rate of similar patients with elevated CRP receiving usual care has been reported at 35%.2 These findings support our actively enrolling randomized controlled trial of low-dose tocilizumab versus standard of care in hospitalized, non-invasively ventilated patients with COVID-19 pneumonia, COVIDOSE2 (ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04479358). (ClinicalTrials.gov COVIDOSE Identifier: NCT04331795)
References
1. Strohbehn GW, Heiss BL, Rouhani SJ, et al. COVIDOSE: A Phase II Clinical Trial of Low-Dose Tocilizumab in the Treatment of Noncritical COVID-19 Pneumonia. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2021;109(3):688-96. doi: 10.1002/cpt.2117 [published Online First: 2020/11/20]
2. Mariette X, Hermine O, Tharaux PL, et al. Effectiveness of Tocilizumab in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19: A Follow-up of the CORIMUNO-TOCI-1 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA internal medicine 2021 doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.2209 [published Online First: 2021/05/25]
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
He L, Strohbehn G, Reid P. Low-dose Tocilizumab in the Treatment of COVID-19 Pneumonitis: 90-day Mortality Follow-up [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/low-dose-tocilizumab-in-the-treatment-of-covid-19-pneumonitis-90-day-mortality-follow-up/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/low-dose-tocilizumab-in-the-treatment-of-covid-19-pneumonitis-90-day-mortality-follow-up/