Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Interferon (IFN)-α contributes to susceptibility and severe manifestations in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The PRKG1 rs7897633 variant has been previously identified as the top hit in European ancestry patients with SLE and high IFN-α compared to those with low circulating IFN activity. However, the mechanisms by which PRKG1 polymorphisms impact the immune system remain unknown. PRKG1 codes for the cGMP-dependent protein kinase I (PKGI). Activation of PKGI leads to VASP phosphorylation, and the inhibition of RhoA and Rho-associated kinases (ROCK). A subgroup of patients with SLE exhibit higher ROCK activity in circulating immune cells compared to healthy controls. ROCK inhibition decreases IFN-α production and ameliorates disease in murine models of lupus. Accordingly, we aimed to assess whether the PRKG1 gene variant was associated with decreased gene expression and activity of PRKG1, hyperactivation of the ROCK pathway, and altered response to type I IFN.
Methods: We used B lymphoblastoid cell lines (LCL) derived from healthy subjects of European ancestry (Coriell repositories) homozygous (AA or CC) and heterozygous (AC) at the rs7897633 SNP for all experiments. Gene expression of PRKG1, RHOA, and ROCK was assessed by RT-qPCR using gene-specific primers, normalized by GAPDH, and measured by the 2-ΔΔCT method. IFN score at baseline and after treatment of LCL with increasing doses of IFN-α was measured by quantifying 3 canonical IFN-stimulated genes (IFIT1, MX1 and PKR) and summing to generate a score reflecting the degree of IFN-induced gene expression in the cells. Abundance of PKGI and VASP phosphorylation (as a surrogate of PKGI activity) were determined by Western blotting at baseline and after treatment with a PKGI agonist. ROCK2 enzymatic activity was performed by a colorimetric assay (Cell Biolabs). Unstimulated and stimulated cells were compared among PRKG1 genotype categories. Statistically significant differences were determined by Mann Whitney U test or sum-of-squares F test, as appropriate.
Results: PRKG1 expression was lower in the homozygous AA genotype as compared with the homozygous CC genotype in LCL (p< 0.05). In contrast, ROCK expression was higher in LCL with the AA rs7897633 genotype (p< 0.05). Compared to LCL with the homozygous AA variant of rs7897633, homozygous CC LCL have greater abundance of PKGI, phosphorylated VASP/total VASP ratio in response to a PKGI agonist (indicating increased PKGI activity), and lower baseline ROCK activity (sum-of-squares F test, p< 0.05). The IFN score was significantly higher in the homozygous CC allele LCL, both at baseline and with increasing doses of IFN-α, suggesting increased sensitivity to type I IFN (p< 0.05).
Conclusion: PRKG1 AA genotype associates with lower PRKG1 and higher ROCK mRNA expression, decreased PKGI abundance and activity, and greater ROCK baseline activity. In contrast, the rs7897633 CC genotype is associated with increased response to IFNα. Overall, these findings suggest an important role of genetic variation at PRKG1 in modulating the RhoA-ROCK pathway and regulating response to type I IFNs in LCL, which may have therapeutic implications in patients with SLE.
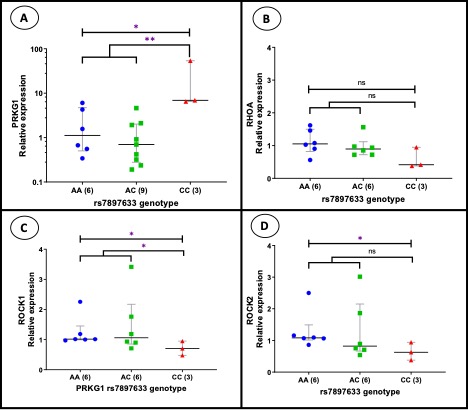 FIGURE 1. mRNA expression of PRKG1, RHOA, ROCK1 and ROCK2 in B lymphoblastoid cell lines according to the PRKG1 rs7897633 genotype category. (A) PRKG1, (B) RHOA, (C) ROCK1 and (D) ROCK2 mRNA levels are shown for B lymphoblastoid cell lines of different rs7897633 genotypes. Each symbol represents a cell line assessed in duplicate, n = 3 to 9. The median and interquartile ranges are shown. Mann-Whitney U was used to test significant differences for mRNA levels between genotype groups. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ns=not significant.
FIGURE 1. mRNA expression of PRKG1, RHOA, ROCK1 and ROCK2 in B lymphoblastoid cell lines according to the PRKG1 rs7897633 genotype category. (A) PRKG1, (B) RHOA, (C) ROCK1 and (D) ROCK2 mRNA levels are shown for B lymphoblastoid cell lines of different rs7897633 genotypes. Each symbol represents a cell line assessed in duplicate, n = 3 to 9. The median and interquartile ranges are shown. Mann-Whitney U was used to test significant differences for mRNA levels between genotype groups. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ns=not significant.
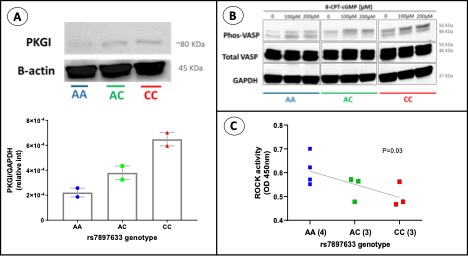 FIGURE 2. The rs7897633 AA variant is associated with lower PKGI abundance, decreased VASP phosphorylation, and greater baseline ROCK2 activity in B lymphoblastoid cell lines. (A) Representative Western blot analysis comparing PKGI (80 KDa) abundance, normalized for beta-actin (45 KDa), in different rs7897633 genotype categories. (B) Representative Western blot analysis comparing phosphorylated VASP and total VASP (46, 50 KDa) with increasing doses of 8-CPT-cGMP, a PKGI agonist, compared by rs7897633 genotype categories, n=2 (as a surrogate marker of PKGI activity). (C) Baseline ROCK2 activity in cells of different rs7897633 genotypes, with each symbol representing an individual cell line assessed in triplicate, and the P value reflecting the probability of the null hypothesis as compared to a regression line across genotype categories calculated using the sum-of-squares F test, n=3 to 4.
FIGURE 2. The rs7897633 AA variant is associated with lower PKGI abundance, decreased VASP phosphorylation, and greater baseline ROCK2 activity in B lymphoblastoid cell lines. (A) Representative Western blot analysis comparing PKGI (80 KDa) abundance, normalized for beta-actin (45 KDa), in different rs7897633 genotype categories. (B) Representative Western blot analysis comparing phosphorylated VASP and total VASP (46, 50 KDa) with increasing doses of 8-CPT-cGMP, a PKGI agonist, compared by rs7897633 genotype categories, n=2 (as a surrogate marker of PKGI activity). (C) Baseline ROCK2 activity in cells of different rs7897633 genotypes, with each symbol representing an individual cell line assessed in triplicate, and the P value reflecting the probability of the null hypothesis as compared to a regression line across genotype categories calculated using the sum-of-squares F test, n=3 to 4.
 FIGURE 3. The rs7897633 CC genotype is associated with higher baseline and IFN-induced mRNA expression (as calculated by the interferon score) in B-lymphoblastoid cells. (A) Interferon (IFN) score (calculated from mRNA expression levels of the IFN-stimulated genes MX1, IFIT1, and PKR) at baseline in B-lymphoblastoid cells. Each symbol represents a cell line assessed in duplicate, n=3 to 7. The median and interquartile ranges are shown. Mann-Whitney U was used to test significant differences in IFN scores at baseline between genotype groups. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. (B) Association between rs7897633 genotypes and IFN score in B lymphoblastoid cells treated with increasing doses of IFNα (0, 25 U/mL, 100 U/mL). P value reflects the difference in slope between the regression lines of each genotype category, calculated using the sum-of-squares F test, n=2.
FIGURE 3. The rs7897633 CC genotype is associated with higher baseline and IFN-induced mRNA expression (as calculated by the interferon score) in B-lymphoblastoid cells. (A) Interferon (IFN) score (calculated from mRNA expression levels of the IFN-stimulated genes MX1, IFIT1, and PKR) at baseline in B-lymphoblastoid cells. Each symbol represents a cell line assessed in duplicate, n=3 to 7. The median and interquartile ranges are shown. Mann-Whitney U was used to test significant differences in IFN scores at baseline between genotype groups. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01. (B) Association between rs7897633 genotypes and IFN score in B lymphoblastoid cells treated with increasing doses of IFNα (0, 25 U/mL, 100 U/mL). P value reflects the difference in slope between the regression lines of each genotype category, calculated using the sum-of-squares F test, n=2.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fernandez Ruiz R, Shum J, Van Buren K, Niewold T. Functional Effects of a Lupus-associated PRKG1 Variant on the RhoA-ROCK Pathway and Response to Type I Interferon [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/functional-effects-of-a-lupus-associated-prkg1-variant-on-the-rhoa-rock-pathway-and-response-to-type-i-interferon/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/functional-effects-of-a-lupus-associated-prkg1-variant-on-the-rhoa-rock-pathway-and-response-to-type-i-interferon/
