Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Amyloidosis is characterized by accumulation of insoluble fibrils composed of different monomers in extracellular spaces of different organs, and demonstration of deposits by non-invasive methods is important especially for organs difficult to sample. Transient elastography (fibroscan) is a diagnostic method being used to measure liver stiffness (LS) in different chronic liver diseases. We herein aimed to test the place of fibroscan method for detecting increased LS associated with amyloid deposition in patients with amyloidosis.
Methods: Six categories of patients enrolled into this cross-sectional study; AA amyloidosis (AA-a), AL amyloidosis (AL-a), Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF) patients without amyloidosis, cirrhotic chronic liver disease, non-cirrhotic chronic hepatitis B infection (CHB) and healthy controls (HC). LS assessment by fibroscan were categorized as normal for kPa< 7, significant stiffness for kPa≥7, advanced stiffness for kPa≥9.5 and kPa≥F4 stiffness. FIB-4 and APRI scores were calculated for each patient when they indicated chronic liver disease. Patients with known chronic liver disease and viral hepatitis excluded from amyloidosis and FMF groups.
Results: A total of 165 patients (AA-a, n=65; AL-a, n=15; FMF, n=20; cirrhotic patients, n=16; CHB, n=22; HC, n=27) constituted the study group. Clinical and laboratory features of patients are given in Table 1. Average age was higher in the AL-a group compared to others. Median LS was highest in cirrhotic patients, and it was also higher in AA-a and AL-a patients compared to FMF and HC. Median LS was numerically higher in AL-a compared to AA-a, but it did not reach statistical significance. Median LS was also higher in FMF patients compared to HC. FIB-4 and APRI scores were lower compared to cirrhotic patients in AA-a and AL-a. ALP levels were higher in AA-a and AL-a groups compared to FMF, CHB and HC. FIB-4 and APRI scores, ALP and GGT levels were correlated with LS both in AA-a, AL-a and FMF-AA groups (Table 2). The scores of amyloid depositions were higher in non-FMF-AA-a patients compared to FMF-AA-a. In FMF-AA-a group, median LS, FIB-4 score, GGT, creatinine, cardiac septal wall thickness (CSWT) and frequency of advanced stiffness were higher in patients who had one exon 10 MEFV variant compared to those with two variants. Frequency of advanced and F4 stiffness, GIS involvement and CSWT were lower in M694V homozygous compared to other MEFV variants.
Higher patient age, age at diagnosis of amylodosis, FIB-4 and LS scores, ALP levels, non-FMF causes of AA were associated with hepatic AA amyloid involvement in biopsy-proven patients. A cut-off value 12.05 kPa of LS provided 100% sensitivity and 85.5% specificity (LR=6.9, AUC=0.901, 95% CI 0.81-0.99) for patients with AA-a.
Conclusion: In our single center cohort, we showed a higher median LS by fibroscan in both AL-a and AA-a patients compared to CHB, FMF and HC. Additionally, hepatic amyloid involvement and median LS was higher in non-FMF-AA-a compared to FMF-AA-a, and in FMF-AA-a patients with one exon 10 MEFV variant compared to those with two variants suggesting presence of amyloidogenic genetic factors additional to pathogenic MEFV variants.
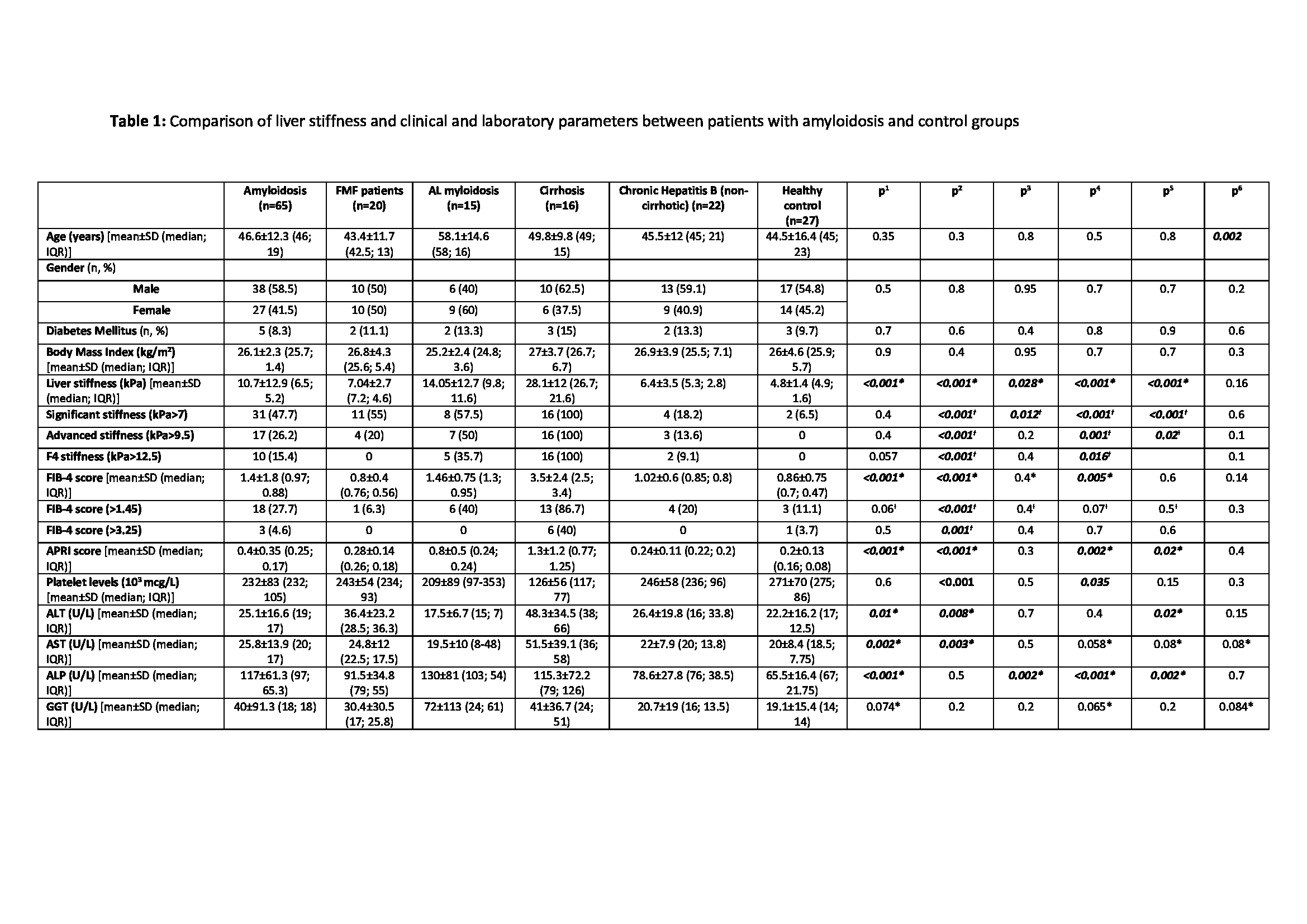 Yeni-Microsoft-Word-Belgesi.jpeg”p1: comparison of amyloidosis and FMF patients p2: comparison of amyloidosis and cirrhosis p3: comparison of amyloidosis and chronic liver disease p4: comparison of amyloidosis and healthy control p5: comparison of FMF and healthy control p6: comparison of AA and AL amyloidosis * Mann Whitney U test Ɨ Fischer’s exact test SD: Standard deviation, IQR: Interquartile range, FMF: Familial Mediterranean Fever, kPa: Kilopascal, FIB_4: Fibrosis_4 index, APRI: AST to platelet ratio index, ALT: Alanine aminotransferase, AST: aspartate aminotransferase, ALP: Alkaline phosphatase, GGT: Gama glutamyl transferase
Yeni-Microsoft-Word-Belgesi.jpeg”p1: comparison of amyloidosis and FMF patients p2: comparison of amyloidosis and cirrhosis p3: comparison of amyloidosis and chronic liver disease p4: comparison of amyloidosis and healthy control p5: comparison of FMF and healthy control p6: comparison of AA and AL amyloidosis * Mann Whitney U test Ɨ Fischer’s exact test SD: Standard deviation, IQR: Interquartile range, FMF: Familial Mediterranean Fever, kPa: Kilopascal, FIB_4: Fibrosis_4 index, APRI: AST to platelet ratio index, ALT: Alanine aminotransferase, AST: aspartate aminotransferase, ALP: Alkaline phosphatase, GGT: Gama glutamyl transferase
 *After exclusion of patients had chronic renal failure SD: Standard deviation, IQR: Interquartile range, FMF: Familial Mediterranean Fever, CRP: C-reactive protein, FIB_4: Fibrosis_4 index, APRI: AST to platelet ratio index, ALT: Alanine aminotransferase, AST: Aspartate aminotransferase, ALP: Alkaline phosphatase, GGT: Gama glutamyl transferase
*After exclusion of patients had chronic renal failure SD: Standard deviation, IQR: Interquartile range, FMF: Familial Mediterranean Fever, CRP: C-reactive protein, FIB_4: Fibrosis_4 index, APRI: AST to platelet ratio index, ALT: Alanine aminotransferase, AST: Aspartate aminotransferase, ALP: Alkaline phosphatase, GGT: Gama glutamyl transferase
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bektaş M, Çavuş B, Agargun B, Şenkal V, Koca N, Ince B, Özer Karaca P, Mestanzade M, Büyük M, Buğra M, Güllüoğlu M, Beşışık S, Yalcinkaya Y, Esen B, İnanç M, Beşışık F, Gül A. Transient Elastography (fibroscan); As a New Non-invasive Diagnostic Method for Detecting Hepatic Involvement of Amyloidosis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/transient-elastography-fibroscan-as-a-new-non-invasive-diagnostic-method-for-detecting-hepatic-involvement-of-amyloidosis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/transient-elastography-fibroscan-as-a-new-non-invasive-diagnostic-method-for-detecting-hepatic-involvement-of-amyloidosis/
