Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 6, 2021
Title: Plenary I (0453–0457)
Session Type: Plenary Session
Session Time: 10:45AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Risankizumab (RZB) is a humanized immunoglobulin G1 monoclonal antibody that specifically inhibits interleukin 23 by binding to its p19 subunit. RZB is being investigated as a treatment for adults with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Methods: KEEPsAKE 1 and 2, double-blind, phase 3 trials, evaluated the efficacy and safety of RZB vs. placebo (PBO) for the treatment of active PsA. The trials enrolled adults with a diagnosis of active PsA, active plaque psoriasis or nail psoriasis, and ≥ 5 swollen joints and ≥ 5 tender joints. Both studies enrolled patients that had previously had an inadequate response or intolerance to ≥ 1 conventional synthetic disease modifying antirheumatic drug (csDMARD-IR). The KEEPsAKE 2 trial also enrolled patients that previously had an inadequate response or intolerance to 1 or 2 biologic therapies (Bio-IR).
In both trials, patients were randomized (1:1) to receive blinded subcutaneous RZB 150 mg or PBO at weeks 0, 4, and 16. The primary endpoint for this pooled analysis was the proportion of patients achieving 20% improvement in American College of Rheumatology score (ACR20) at week 24. Non-responder imputation incorporating multiple imputations to handle missing data due to COVID-19 (NRI-C) was used for categorical efficacy data and Mixed-Effect Model Repeated Measurement (MMRM) analysis was used for continuous efficacy data. Safety was assessed throughout the study. Results reported here are from the 24-week double-blind period; the open-label period with all patients receiving RZB is ongoing.
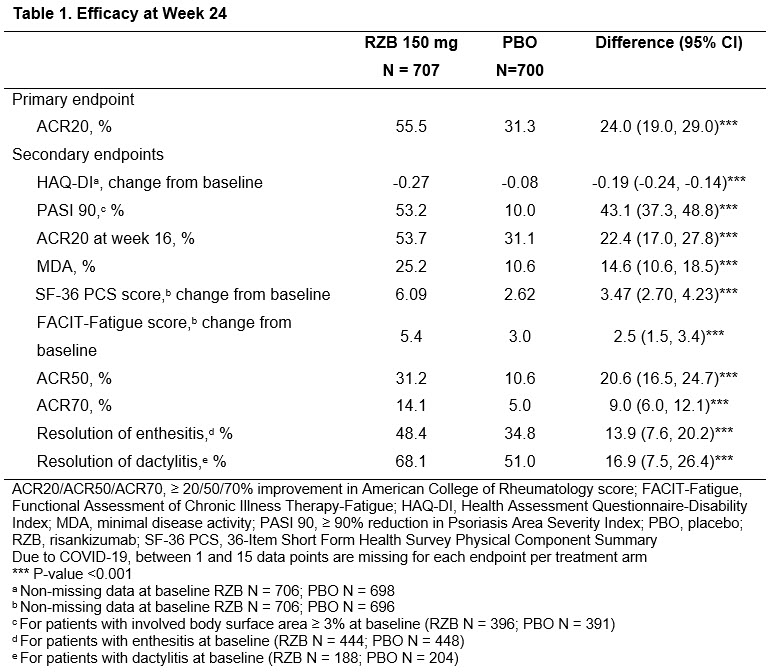
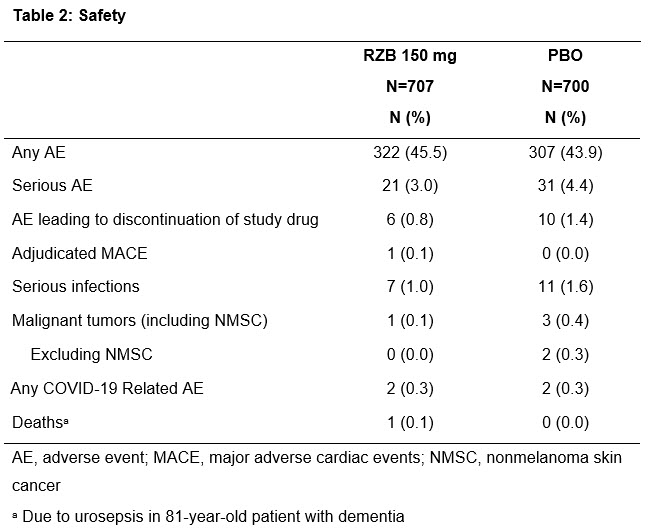
Results: A total of 1407 patients (RZB, N = 707; PBO, N = 700) were initially enrolled and 1354 (RZB, N = 688; PBO, N = 666) completed the 24-week assessments. Demographics and baseline disease characteristics were similar between the two groups. Patients receiving RZB achieved higher rates of ACR20 than patients receiving PBO at Week 24 (Table 1, 55.5% vs 31.3%, P < 0.001). Patients receiving RZB showed greater improvements than patients receiving PBO in all secondary clinical and patient-reported outcome endpoints (Table 1). RZB was well tolerated, and no new safety signals were observed (Table 2).
Conclusion: RZB resulted in statistically greater improvements in signs and symptoms of PsA compared with PBO and was well tolerated with no new safety signals.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ostor A, Papp K, Moreno M, Spargo C, Barcomb L, Soliman A, Lu W, Eldred A, Kristensen L. Efficacy and Safety of Risankizumab for Active Psoriatic Arthritis: 24-Week Integrated Results from 2 Phase 3, Randomized, Double-blind Clinical Trials for CsDMARD-IR and Bio-IR Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-risankizumab-for-active-psoriatic-arthritis-24-week-integrated-results-from-2-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-clinical-trials-for-csdmard-ir-and-bio-ir-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-risankizumab-for-active-psoriatic-arthritis-24-week-integrated-results-from-2-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-clinical-trials-for-csdmard-ir-and-bio-ir-patients/