Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
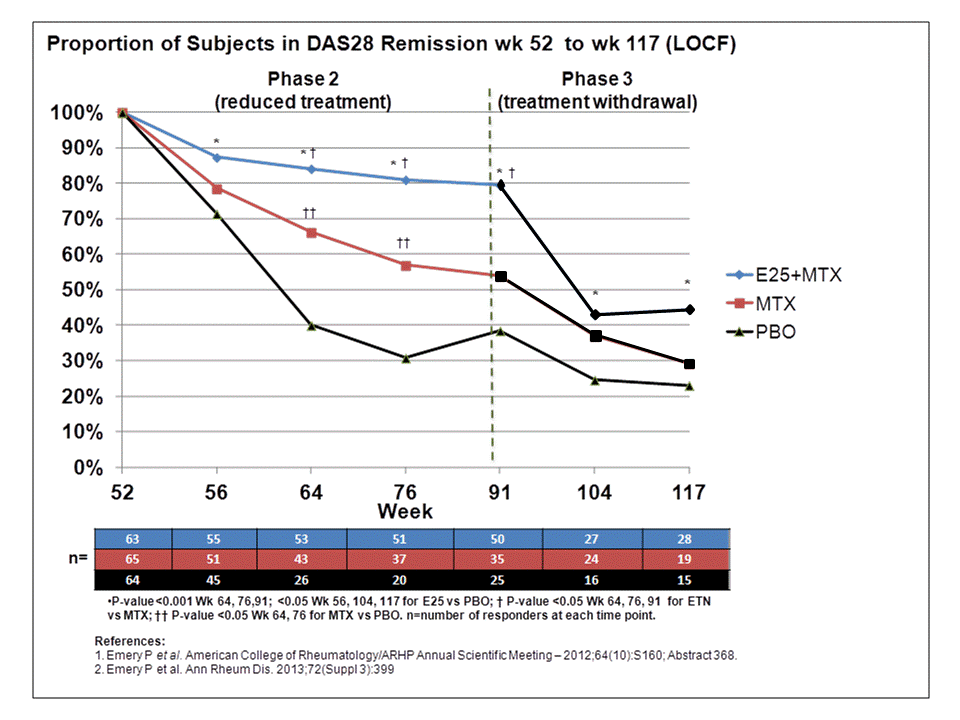
Background/Purpose: In the PRIZE study patients (pts) with early (mean 6 mos. since symptom onset) moderate-severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA), who achieved remission after open-label treatment with 50 mg etanercept (ETN) + 10-25 mg MTX (Phase 1)1 were randomized to a double-blind 39-wk period of (25mg) ETN25+MTX, MTX alone, or placebo (PBO, Phase 2)2; the study drugs were then withdrawn (randomized treatment remained blinded) and pts were monitored for an additional 26 weeks (Phase 3). Using patients who achieved remission in Phase 1, the objective of this analysis was to assess sustained remission and other clinical and safety outcomes in randomized pts (Phase 2) and subsequent withdrawal of drug treatments (Phase 3).
Methods: Pts with DAS28 remission (<2.6, n=193) began Phase 2 at wk 52; those maintaining DAS28 LDA by wk 91 (≤3.2, n=131) continued and had study drugs withdrawn (MTX tapered to week 95) through wk 117 (end of study). Remission and other standard clinical outcomes were assessed during Phase 2 and 3. LOCF was used for missing data. Fisher's exact test was used for significance.
Results: Between wks 52 and 91, the proportion of pts in the ETN25+MTX group who maintained DAS28 remission declined slower than those treated with MTX or PBO; at wk 117, significantly more pts in the ETN25+MTX group maintained remission relative to PBO following withdrawal of randomized treatment (Figure). Other outcomes had similar results. At the beginning of Phase 2, the proportions of pts in the ETN25+MTX group with DAS28 LDA, Boolean remission, ACR50/70 and normal HAQ (≤0.5) were 100%, 71%, 92%/83%, and 84%, respectively; MTX group: 100%, 72% 95%/87% and 86%, respectively; PBO group: 100%, 63%, 95%/82%, and 75%, respectively. At wk 91, the proportions declined to 89%, 68%, 78%/71%, and 78% (ETN25+MTX); 69%, 46%, 71%/62%, and 72% (MTX); 46%, 23%, 45%/37%, and 45% (PBO), respectively. After treatment withdrawal at wk 117, the proportions of pts who maintained these outcomes were 56%, 47%, 46%/41%, and 67% (ETN25+MTX), 43%, 25%, 38%/29%, and 59% (MTX), 37%, 16%, 35%/23%, and 40% (PBO), respectively. There were no unexpected safety findings.
Conclusion: Of the early RA pts with DAS28 remission at the beginning of Phase 2, those randomized to a reduced dose of ETN had a modest loss of efficacy in Phase 2, but randomization to PBO and withdrawal of ETN in Phase 3 both led to steep declines in all outcomes.
Disclosure:
P. Emery,
Abbott Laboratories, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer Inc, Roche-Chugai, UCB Pharma Ltd,
5;
W. Spieler,
None;
M. Stopinska-Polaszewska,
None;
N. I. Korshunov,
Pfizer Inc, Merck, Roche, Novarits,
5;
J. Bukowski,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
R. Pedersen,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
T. Williams,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
S. Gaylord,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3;
B. Vlahos,
Pfizer Inc,
1,
Pfizer Inc,
3.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessing-maintenance-of-remission-after-withdrawal-of-etanercept-plus-methotrexate-methotrexate-alone-or-placebo-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-who-achieved-remission-with-etanercept-and-me/