Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment III: Axial Spondyloarthritis (2028–2032)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:00PM-4:50PM
Background/Purpose: A lack or loss of response to TNFα inhibitors (TNFi) has been associated with low serum drug levels and formation of anti-drug antibodies (ADAb). Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM), an individualized treatment strategy based on regular assessments of serum drug levels, has been suggested to optimize efficacy of TNFi. It is still unclear if TDM improves clinical outcomes, and the value of TDM has recently been included in the research agenda across different specialties. This first randomized controlled trial on the effectiveness of TDM in a range of immune mediated inflammatory diseases including rheumatic diseases, the NORwegian DRUg Monitoring trial part A (NOR-DRUM (A)) focus on the induction period of infliximab (INX) treatment and aim to assess if TDM is superior to standard treatment in order to achieve remission.
Methods: In the investigator-initiated, randomized, open-label, multicenter NOR-DRUM (A) study, adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis (PsA), spondyloarthritis (SpA), ulcerative colitis (UC), Crohn’s disease (CD) and psoriasis (Ps) starting INX therapy were randomly assigned administration of INX according to a treatment strategy based on TDM (TDM arm) or to standard administration of INX without TDM (control arm). Study visits were conducted at each infusion. The primary endpoint was remission at week 30. In the TDM arm, the dose and interval were adjusted according to INX trough levels to reach the therapeutic range (Figure 1). If the patient developed significant levels of ADAb, INX was terminated. To guide the investigators, the TDM strategy was integrated in an interactive eCRF. The primary endpoint was analysed by mixed effect logistic regression in the full analyses set (FAS), adjusting for diagnoses. Infections and infusion reactions were specified as adverse events (AEs) of special interest.
Results: We enrolled 411 patients at 21 study centers between January 2017 and December 2018. 398 patients (RA 80, PsA 42, SpA 117, UC 80, CD 57, Ps 22) received the allocated strategy and were included in the FAS population. Demographic and baseline characteristics were comparable in both arms. TDM was not found to be superior to standard treatment with regard to the primary outcome. Remission at week 30 was reached in 100 (53%) and 106 (54%) of the patients in the TDM and control arm, respectively (adjusted difference, 1.5%; 95% confidence interval (CI), -8.2 to 11.1, p=0.78) (Figure 2). Consistent results were shown for all the secondary endpoints (Figure 3) and in the sensitivity analyses. Twenty patients (10%) in the TDM arm and 30 patients (15%) in the control arm developed significant levels of ADAb. The number of adverse events (AE) was similar in both groups, however infusion reactions were less frequent (5 patients (2.5%) vs 16 patients (8.0%)) in the TDM arm (difference 5.5% (95% CI 1.1, 9.8%))
Conclusion: NOR-DRUM (A) is the first randomized trial to address effectiveness of TDM in rheumatic diseases. In this study, TDM was not superior to standard treatment in order to achieve remission. Although improved safety is indicated by a reduction in infusion reactions, implementation of TDM as a general strategy in the induction period of INX is not supported by the NOR-DRUM (A) study.
 Figure 1. Treatment algorithm in the therapeutic drug monitoring group
Figure 1. Treatment algorithm in the therapeutic drug monitoring group
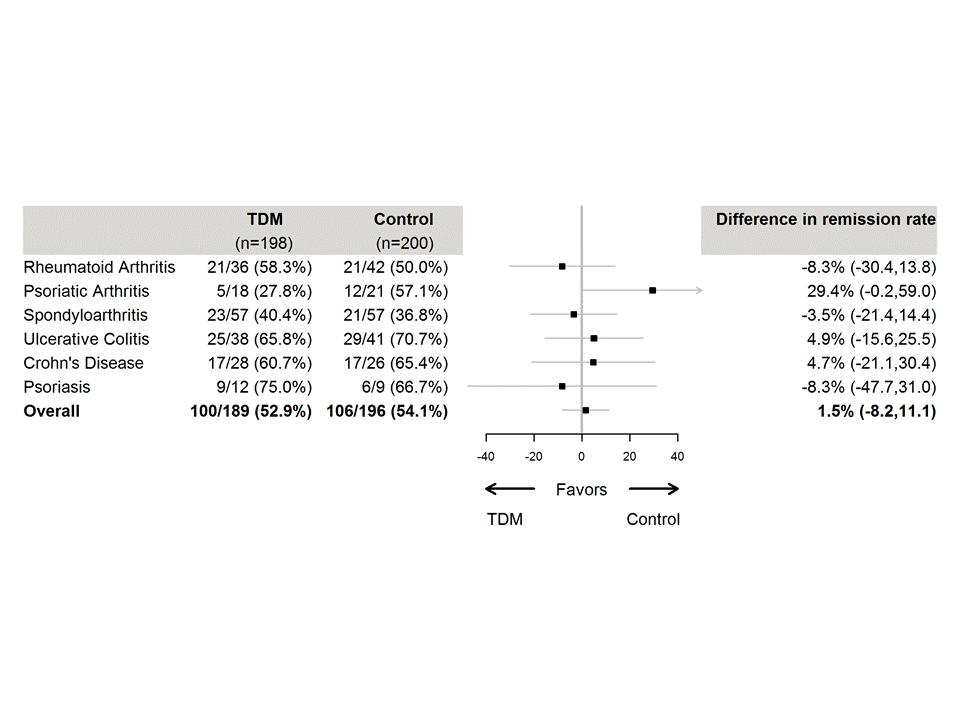 Figure 2 Forest plot of difference in clinical remission rates, overall results and according to disease Figure shows results of the main analysis (primary outcome) conducted in the full-analysis set TDM= therapeutic drug monitoring
Figure 2 Forest plot of difference in clinical remission rates, overall results and according to disease Figure shows results of the main analysis (primary outcome) conducted in the full-analysis set TDM= therapeutic drug monitoring
 Figure 3 Main secondary outcomes A-F: Generic outcomes; A Proportion of patients in clinical remission, B Patient’s Global Assessment Visual analogue scale 0-100 mm, C Physician’s Global Assessment Visual analogue scale 0-100 mm, D C-reactive protein mg/L, E Erythrocyte sedimentation rate mm/hour, F Serum infliximab level mg/L. G-L: Disease specific activity measures; G: Rheumatoid Arthritis, Disease Activity Score 28 joints, H: Psoriatic Arthritis, Disease Activity Score 28 joints, I: Spondyloarthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score, J: Ulcerative Colitis, Partial Mayo Score, K: Crohn’s Disease, Harvey Bradshaw Index, L: Psoriasis, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index. All data except for serum infliximab levels (patients still on medication) are from the full-analysis set. Values are adjusted means with 95% CI.
Figure 3 Main secondary outcomes A-F: Generic outcomes; A Proportion of patients in clinical remission, B Patient’s Global Assessment Visual analogue scale 0-100 mm, C Physician’s Global Assessment Visual analogue scale 0-100 mm, D C-reactive protein mg/L, E Erythrocyte sedimentation rate mm/hour, F Serum infliximab level mg/L. G-L: Disease specific activity measures; G: Rheumatoid Arthritis, Disease Activity Score 28 joints, H: Psoriatic Arthritis, Disease Activity Score 28 joints, I: Spondyloarthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score, J: Ulcerative Colitis, Partial Mayo Score, K: Crohn’s Disease, Harvey Bradshaw Index, L: Psoriasis, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index. All data except for serum infliximab levels (patients still on medication) are from the full-analysis set. Values are adjusted means with 95% CI.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Syversen S, Goll G, Jørgensen K, Sandanger �, Sexton J, Olsen I, Gehin J, Brun M, Mørk C, Kvien T, Jahnsen J, Bolstad N, Haavardsholm E. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Compared to Standard Treatment of Patients Starting Infliximab: Results from a Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial of 400 Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/therapeutic-drug-monitoring-compared-to-standard-treatment-of-patients-starting-infliximab-results-from-a-multicenter-randomized-controlled-trial-of-400-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/therapeutic-drug-monitoring-compared-to-standard-treatment-of-patients-starting-infliximab-results-from-a-multicenter-randomized-controlled-trial-of-400-patients/
