Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the sacroiliac joints (MRI-SIJ) represents an essential tool in the evaluation of patients with spondyloarthritis (SpA). However, despite a clear definition of positive and negative MRI-SIJ formulated by the ASAS/OMERACT working group, the inter-reader agreement between readers is never perfect. Moreover, in daily practice, the radiologists in charge of the evaluation of the SIJ-MRI images are rarely experts in musculoskeletal radiology. The aim of this pilot study is to predict a positive or negative MRI-SIJ according to the ASAS definition in patients with in recent axial SpA (axSpA) applying Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning.
Methods: Patients from the DESIR cohort with MRI-SIJ available at baseline and in full agreement for positive or negative MRI-SIJ according to the three central readers were included.
We first segmented the iliac and sacrum bones in each MRI-SIJ slice. Then, we extracted the right and left joint on each slice of MRI. Finally, we reported the presence of inflammatory lesions on each joint of the MRI-SIJ. Once all the inflammatory lesions of the joints have been reported, we defined the positiveness of the MRI-SIJ based on a decision rule. All of these steps were conducted without human intervention.
We solved two tasks in this work:
Task 1: Segmentation of iliac and sacrum bones in semi-coronal axis MRIs.
Task 2: Detection of inflammation in the MRI-SIJ.
For task 1, we manually segmented 51 MRIs. We found that using two independent U-Net [1] for each bone performed better than using a single one that predicts the two bones.
For task 2, we use a ResNet-18 [2] to determine if each half-slice presents inflammation or not.
Results: Task 1: We trained two U-Net, one for each bone. We split 51 patients in 31 train, 6 validation, 14 evaluation. The results on the evaluation set are presented on table 1. We segmented successfully 104 new patients out of the 114 tested.
Task 2: We had a total of 155 segmented patients (51 manually and 104 automatically). We extract 1790 joints regions of T1 and STIR sequence. We trained a ResNet-18 classifier to determine the presence or absence of inflammatory lesions. We split the 155 patients (1790 regions) into 105 (1220 regions) train, 14 (164 regions) validation and 36 (406 regions) evaluation. We trained k = 10 identical networks. The results are shown on table 2. We compared the opinion of the three readers for each region. The positiveness for an MRI-SIJ is presented on table 3 (decision rule: #inflammation >= 3).
Conclusion: We propose a novel method to determine the presence of positive MRI-SIJ in SpA patients. We successfully segmented the iliac and sacrum bones and extracted the regions of interest. We achieved good results on the classification of inflammation for each joint region. While the results are still not on a par with the performance of a radiologist, we are optimistic that future work bill be able to reach it.
References:
[1] U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. https://arxiv.org/abs/1505.04597
[2]Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385
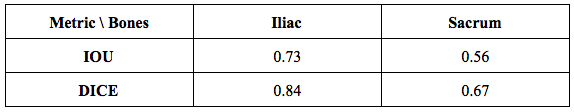 Table 1. Segmentation results on 14 patients.
Table 1. Segmentation results on 14 patients.
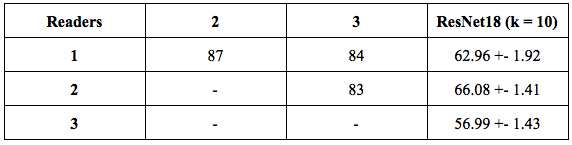 Table 2. Results of presence of inflammation in a selected region. Matthews Correlation Coefficient (multiplied by 100 for clarity).
Table 2. Results of presence of inflammation in a selected region. Matthews Correlation Coefficient (multiplied by 100 for clarity).
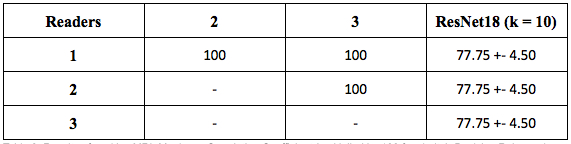 Table 3. Results of positive MRI-SIJ. Matthews Correlation Coefficient (multiplied by 100 for clarity). Decision rule: each MRI must have at least 3 regions with inflammation.
Table 3. Results of positive MRI-SIJ. Matthews Correlation Coefficient (multiplied by 100 for clarity). Decision rule: each MRI must have at least 3 regions with inflammation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Aouad T, Lopez-Medina C, Molto A, Feydy A, Martin-Peltier C, Talbot H, Dougados M. Development of a Deep Learning Algorithm to Predict Positive MRI of the Sacroiliac Joints According to the ASAS Definition in Patients with Recent Axial Spondyloarthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-a-deep-learning-algorithm-to-predict-positive-mri-of-the-sacroiliac-joints-according-to-the-asas-definition-in-patients-with-recent-axial-spondyloarthritis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/development-of-a-deep-learning-algorithm-to-predict-positive-mri-of-the-sacroiliac-joints-according-to-the-asas-definition-in-patients-with-recent-axial-spondyloarthritis/
