Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: RA improves in pregnancy and flares postpartum. Active disease causes adverse fetal outcomes. In PsA, the data is less clear as many of these studies are retrospective, lack validated disease activity scores and predate biologic use. We sought to compare disease activity plus maternal and fetal outcomes between RA and PsA.
Methods: This is a prospective study of women attending our multidisciplinary combined rheumatology obstetrics service. Patients were seen pre-pregnancy, once per trimester and at 3 months postpartum. DAS28CRP-3 was used to assess disease activity as this is validated in pregnancy. Between group differences were analyzed using Pearson Chi square, Fischer’s exact test or Mann-Whitney U test as appropriate.
Results: 34 patients were included in the study (Table 1). Overall, disease activity scores decreased during pregnancy and increased postpartum (Table 2). Maternal and fetal outcomes are shown in Table 3.
Conclusion: In this small study, disease activity generally improved in pregnancy and flared postpartum. There were adverse maternal outcomes in 33% of RA and 20% of PsA patients. Adverse fetal outcomes were seen in the offspring of 7% of RA and 20% of PsA patients. Compared to the general Irish population, birthweights were similar, maternal age was older and rates of Caesarean section were higher.
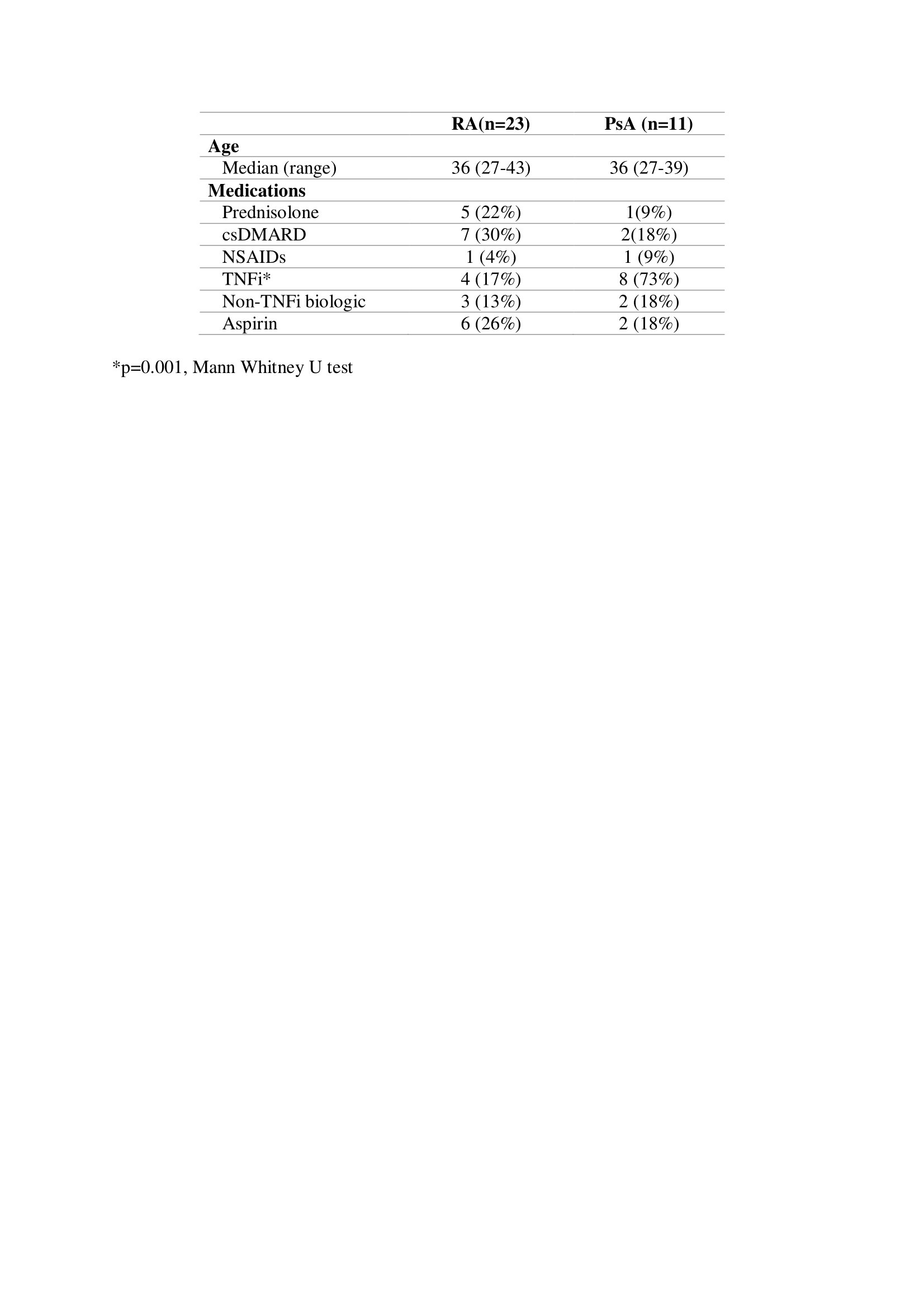 Table 1. Patient characteristics
Table 1. Patient characteristics
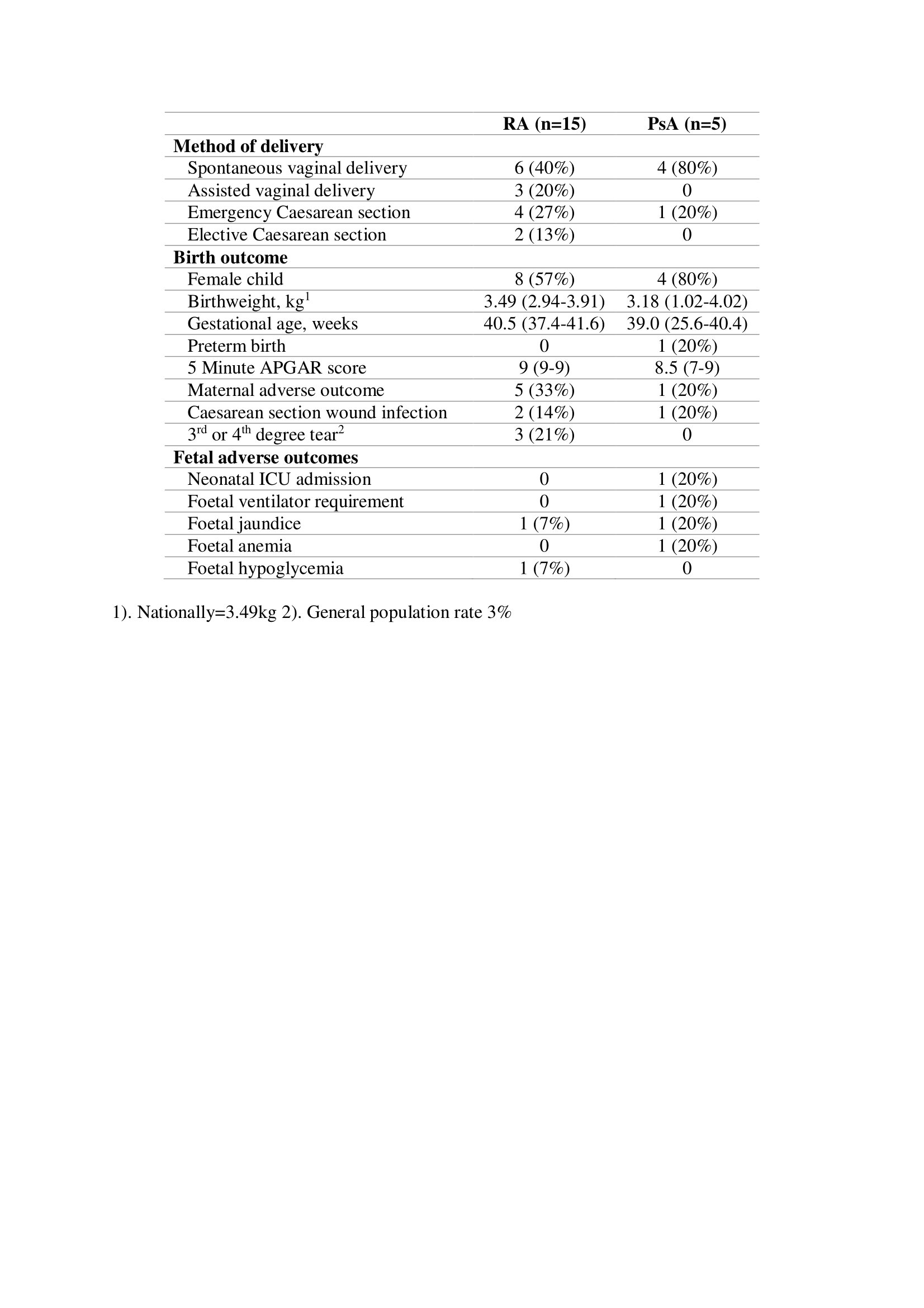 Table 3. Maternal and fetal outcomes
Table 3. Maternal and fetal outcomes
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Murray K, Moore L, Gallagher P, Alammari Y, O'Brien C, Brophy C, McAuliffe F, Veale D. Reproductive Health Outcomes in Women with RA and PsA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reproductive-health-outcomes-in-women-with-ra-and-psa/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/reproductive-health-outcomes-in-women-with-ra-and-psa/

