Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Guselkumab (GUS), a novel monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to the p19-subunit of IL-23, demonstrated efficacy in the Ph 3 DISCOVER-1 (D1) & DISCOVER‑2 (D2) trials of patients (pts) with active PsA.1,2 Dactylitis & enthesitis, key PsA clinical manifestations, can be difficult to treat and may portend more significant disease burden.3,4 This study assessed 1) changes in symptoms over time and 2) relationships between improvements in dactylitis or enthesitis and other PsA domains in pts with dactylitis or enthesitis at baseline.
Methods: Adults with active PsA despite standard therapies were eligible for D1 & D2. Approx. 30% of D1 pts previously received 1-2 TNF inhibitors; D2 pts were biologic-naïve. Pts were randomized 1:1:1 to GUS 100mg Q4W; GUS 100mg at W0, W4, Q8W; or PBO. Independent assessors evaluated dactylitis (total score: 0-60) & enthesitis (Leeds Enthesitis Index [LEI]; total score 0-6). Dactylitis and enthesitis findings through W24 were prespecified to be pooled across D1 & D2. P-values are unadjusted. We assessed changes in dactylitis and LEI scores over time (ANCOVA); associations between dactylitis or enthesitis resolution and ACR/PASI responses at W24 (Chi-square); and correlations between dactylitis or LEI and HAQ-DI/SF-36 change scores at W24 (Spearman’s correlation). AEs through W24 were reported.1,2
Results: At W0, 42% of pooled D1+D2 pts had dactylitis; 65% had enthesitis. GUS improved dactylitis and LEI scores vs PBO at W8, W16, W24. GUS vs PBO differences were significant for dactylitis changes at W16 & W24 and LEI changes at W8 (Q4W only), W16 & W24; no dose response was observed (Fig). Rates of dactylitis or enthesitis resolution by W24 were consistently significantly (p< 0.001) associated with ACR20/50/70 and PASI75/90 response (Table). In GUS-treated pts at W24, significant correlations were observed between dactylitis change scores and PASI (p< 0.001 Q4W; p=0.006 Q8W) and SF-36 MCS (p=0.038 Q4W; p=0.003 Q8W) changes, and between LEI and HAQ-DI change scores (p< 0.001 Q4W; p=0.005 Q8W). No consistent correlations/associations were observed between dactylitis or LEI scores and other clinical outcomes.
Conclusion: In PsA pts with dactylitis or enthesitis at W0, GUS improved dactylitis or LEI scores vs PBO by W8; treatment differences were significant at W16 & W24. Resolution of dactylitis or enthesitis was significantly associated with clinically meaningful improvements in PsA joint & skin symptoms. Improved dactylitis scores correlated with improved skin symptoms and mental health; improved LEI scores correlated with improved physical function.
References:
- Deodhar et al. ACR 2019, abs #807. Arth Rheumatol. 2019;71 S10: 1386
- Mease et al. ACR 2019, abs #L13. Arth Rheumatol. 2019;71 S10:5247
- Polachek et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):189
- Kaeley et al. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2018;48(2):263‐273
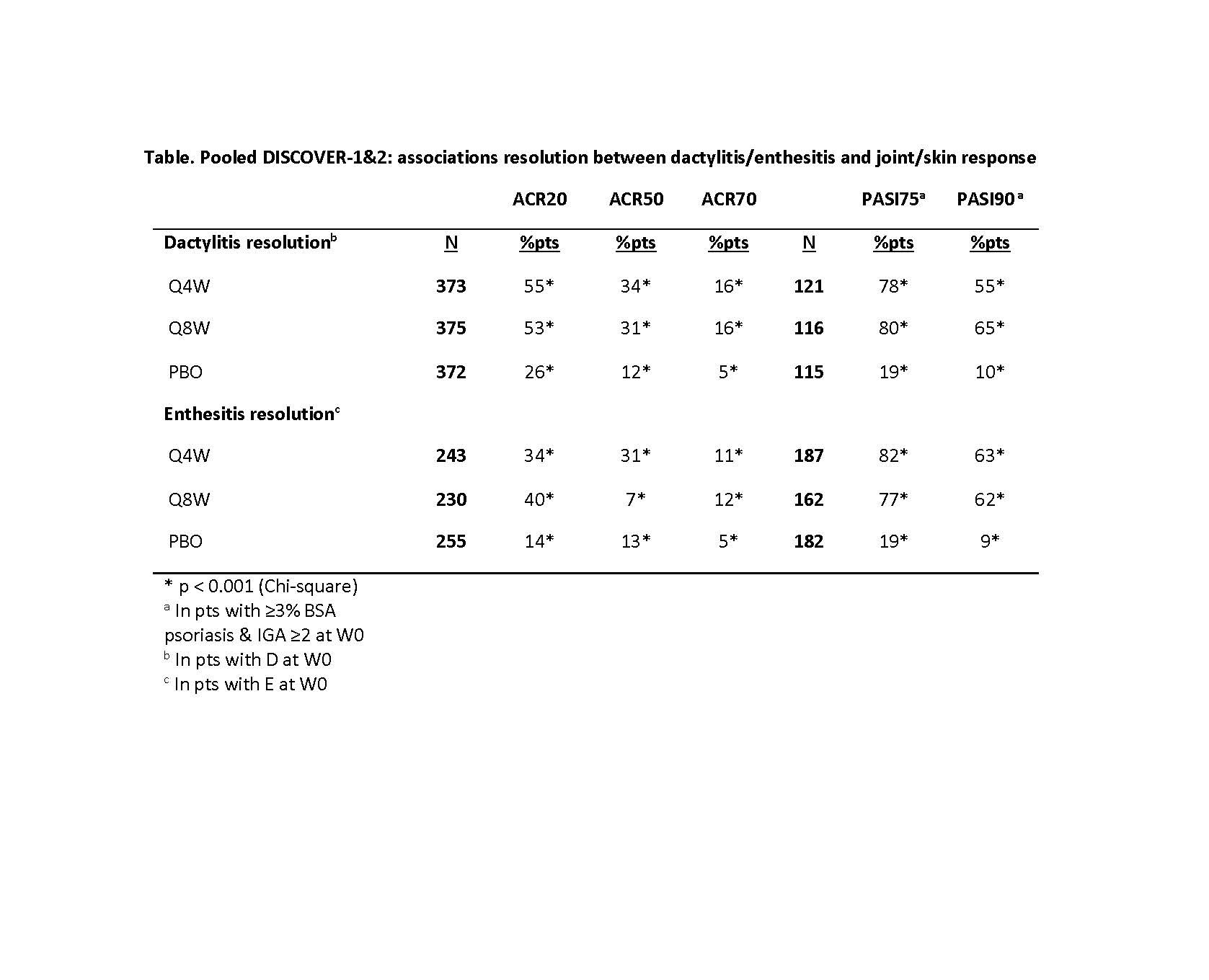 Table. Pooled DISCOVER-1&2: associations between dactylitis/enthesitis resolution and joint/skin response
Table. Pooled DISCOVER-1&2: associations between dactylitis/enthesitis resolution and joint/skin response
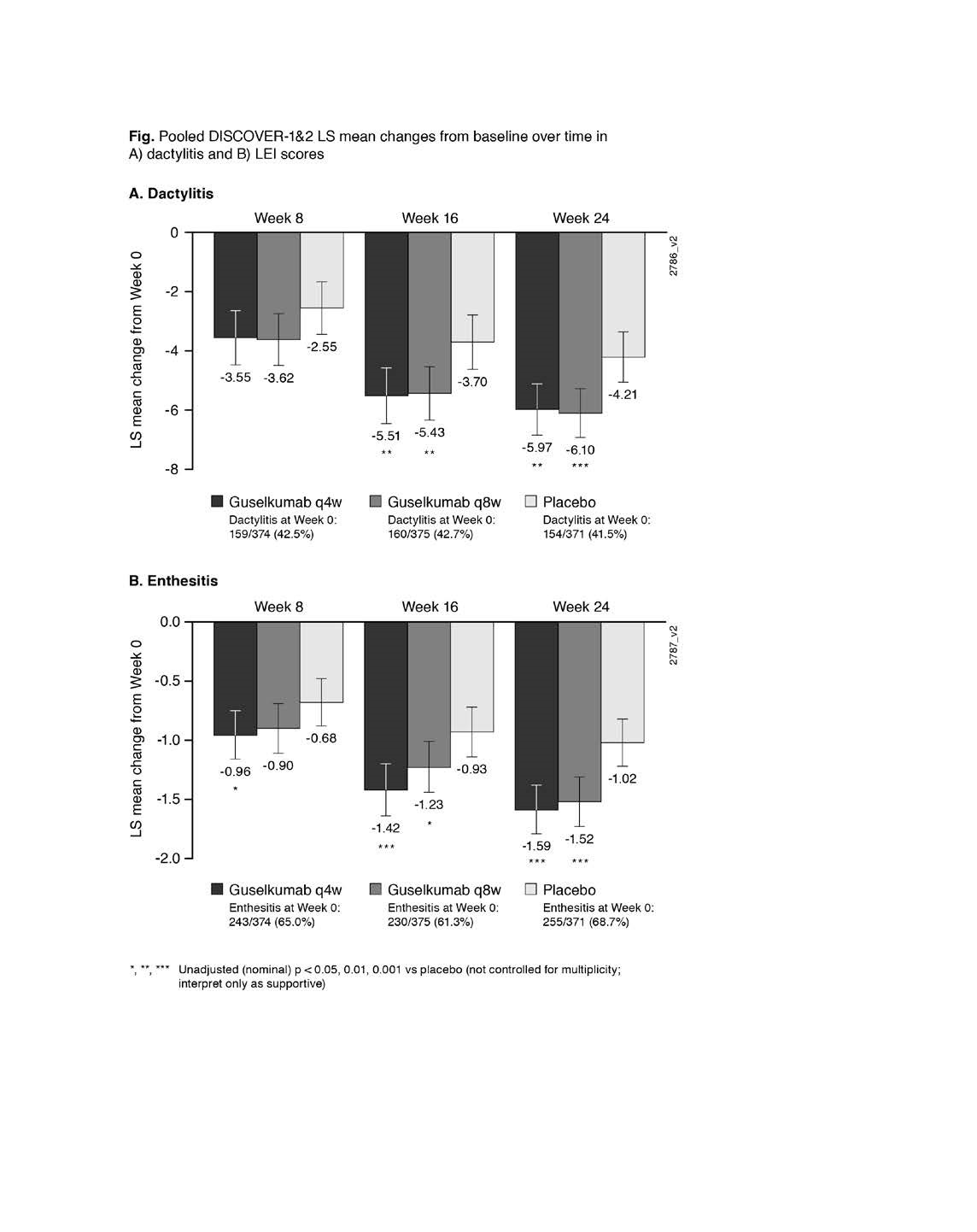 Figure: Pooled DISCOVER 1&2 LS Mean changes from baseline over time
Figure: Pooled DISCOVER 1&2 LS Mean changes from baseline over time
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
McGonagle D, McInnes I, Deodhar A, Schett G, Mease P, Shawi M, Kafka S, Karyekar C, Kollmeier A, Hsia E, Xu X, Sheng S, Agarwal P, Zhou B, Ritchlin C, Rahman P. Effects of Guselkumab, a Monoclonal Antibody That Specifically Binds to the p19-Subunit of Interleukin-23, on Dactylitis and Enthesitis in Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis: Pooled Results Through Week 24 from Two Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-guselkumab-a-monoclonal-antibody-that-specifically-binds-to-the-p19-subunit-of-interleukin-23-on-dactylitis-and-enthesitis-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-pooled-results-thro/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-guselkumab-a-monoclonal-antibody-that-specifically-binds-to-the-p19-subunit-of-interleukin-23-on-dactylitis-and-enthesitis-in-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-pooled-results-thro/
