Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 7, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Guselkumab (GUS), a novel anti-IL-23 monoclonal antibody specific to the IL-23p19-subunit, is approved to treat psoriasis. Through week (W) 24 of the Phase 3, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled DISCOVER-1 trial in patients (pts) with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA), significantly more pts receiving GUS 100 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W) or every 8 weeks (Q8W) vs PBO achieved ACR20 response. 31% of pts previously received 1-2 TNFα inhibitors (TNFi), and ACR20 response patterns through W24 were comparable in TNFi-naïve vs. experienced pts.1 Here we assess GUS efficacy and safety through 1-year by prior TNFi use.
Methods: Adults with active PsA (≥3 swollen+≥3 tender joints; CRP ≥0.3mg/dL) despite standard therapies were eligible. Pts were randomized 1:1:1, stratified by W0 DMARD use [Y/N] and prior TNFi use (Y/N), to GUS 100 mg Q4W; GUS 100 mg at W0, W4, then Q8W through W48; or PBO and then GUS 100 mg Q4W from W24-W48 (PBO→Q4W). Effects of GUS on joint (ACR20/50/70), skin (Investigator’s Global Assessment response [IGA=0/1 + ≥2-grade reduction from W0], IGA=0, and Psoriasis Area Severity Index [PASI] 75/90/100 responses, all in pts with ≥3% BSA psoriasis and IGA ≥2 at W0), physical function (HAQ-disability index [HAQ-DI] ≥0.35 improvement in pts with HAQ-DI ≥0.35 at W0), and composite disease state (minimal disease activity [MDA]) were assessed through W52 using nonresponder imputation (NRI) for missing data and summarized by prior TNFi use. Adverse events (AEs) through study completion (W60) were summarized by prior TNFi use.
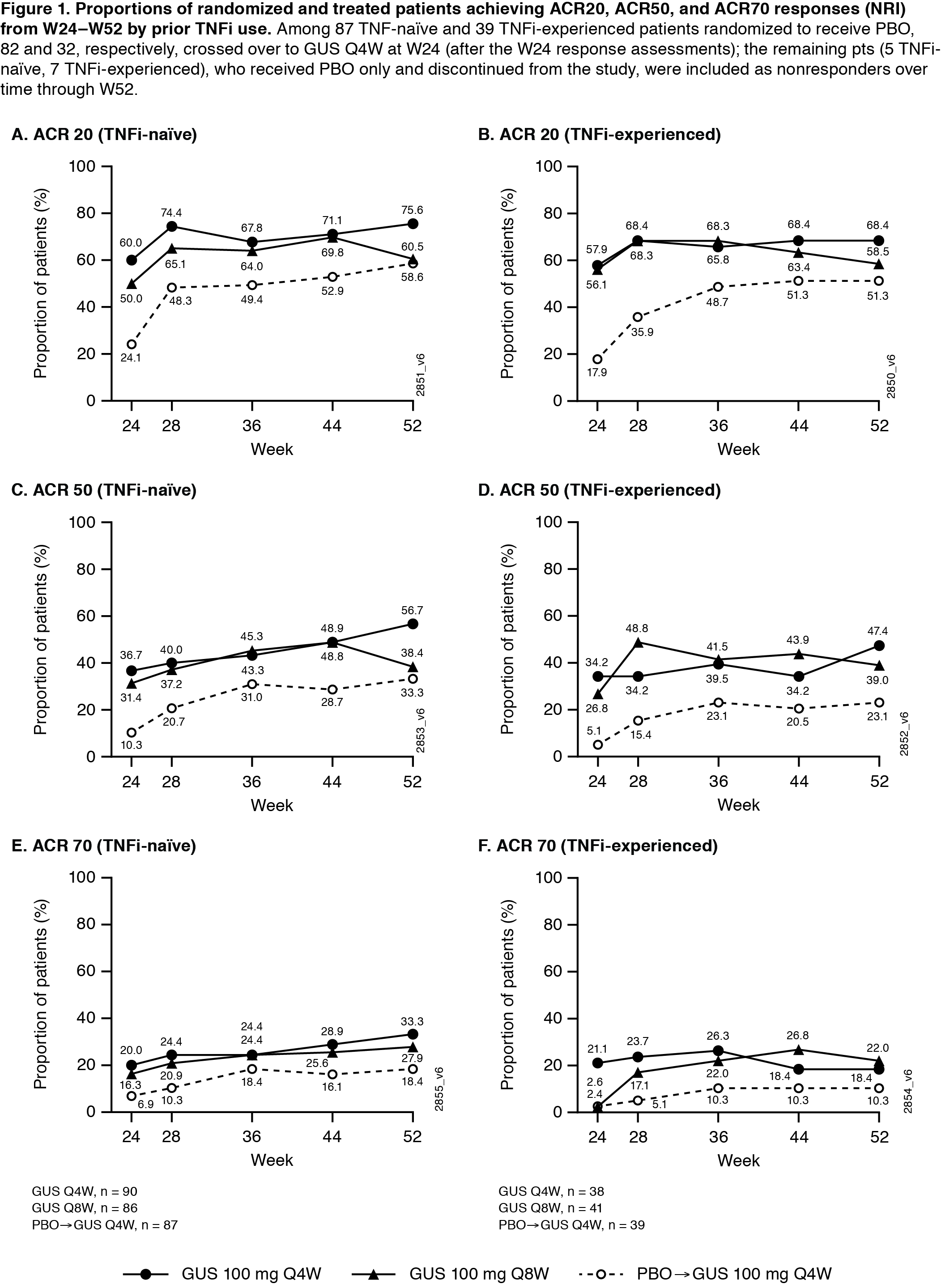
Results: Of 381 treated PsA pts, 362 continued at W24, and 347 completed treatment through W48. 65% of pts were receiving DMARDs at W0; 31% previously received TNFi (Table). In both TNFi-naïve and experienced pts, proportions of GUS-treated pts achieving ACR20/50/70 and HAQ-DI ≥0.35 improvement were maintained from W24‑W52 (Fig1). Consistent joint response patterns were seen even in the smaller number of pts who discontinued (d/c) prior TNFi use due to inadequate response, e.g., Q4W and Q8W W52 response rates were 82% (14/17) and 60% (9/15) for ACR20 and 47% (8/17) and 40% (6/15) for ACR50. Robust skin response (IGA/PASI) rates were also maintained at W52 in both TNFi exposure subgroups. Most joint and skin response rates continued to increase over time through W52 regardless of prior TNFi use (Table, Fig1,2). Through W60 in GUS-treated TNFi-naïve (n=258) and experienced (n=111) pts, 62% and 64%, respectively, reported ≥1 AE, 3% and 6% had serious AEs, 0.4% and 3% had serious infections, 3% and 2% had AEs lead to treatment d/c, and 7%/7% and 4%/3% had increased ALT/AST levels.
Conclusion: Through 1 year, GUS 100 mg Q4W and Q8W provided robust and sustained improvements in joint symptoms and physical function in both TNFi-naïve and TNFi-experienced pts with active PsA. Meaningful improvements in skin psoriasis and composite disease state were observed, and GUS appeared to be well tolerated in PsA pts, regardless of prior TNFi status.
Reference: 1Deodhar A, et al. Lancet 2020;395:1115-25.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ritchlin C, Deodhar A, Boehncke W, Soriano E, Hsia E, Kollmeier A, Xu X, Zazzetti F, Shawi M, Jiang Y, Sheng S, Agarwal P, Helliwell P. Guselkumab Efficacy and Safety in TNF-Inhibitor-Experienced and TNF-Inhibitor-Naïve Patients with Active PsA: 1-Year Results of a Phase 3, Randomized, Controlled Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/guselkumab-efficacy-and-safety-in-tnf-inhibitor-experienced-and-tnf-inhibitor-naive-patients-with-active-psa-1-year-results-of-a-phase-3-randomized-controlled-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/guselkumab-efficacy-and-safety-in-tnf-inhibitor-experienced-and-tnf-inhibitor-naive-patients-with-active-psa-1-year-results-of-a-phase-3-randomized-controlled-study/