Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Persistence on therapy is an important consideration in rheumatic diseases. There are multiple treatment options that influence long term disease management and a better understanding of the causes for medication discontinuation are needed. Possible reasons for discontinuation may be inferred from fielded data, when present, in EMR, claims, or specialty pharmacy records; however, actual reasons may be different. We reviewed open text notes within the EMR to understand why drugs were discontinued for patients with rheumatic diseases.
Methods: The ARN-TRIO Rheumatology registry contains EMR (fielded and open text), lab, procedure, infusion, medical claims, and specialty pharmacy data generated in care of >75,000 patients by ARN, a network of independent practices with >200 rheumatologists across the US. Data present in open text notes are extracted by clinically trained scribes who review the full patient histories for each patient and collect supplemental information into customized data forms. The collected data undergo a two-level audit process. Open text notes assessed were those specific to patients who discontinued csDMARD and/or targeted immune modulating drugs (TIM) between 2015 to 2019. Only the last discontinuation event per patient drug was considered for this study. Comparisons were made using chi-square with column proportions compared by z-test.
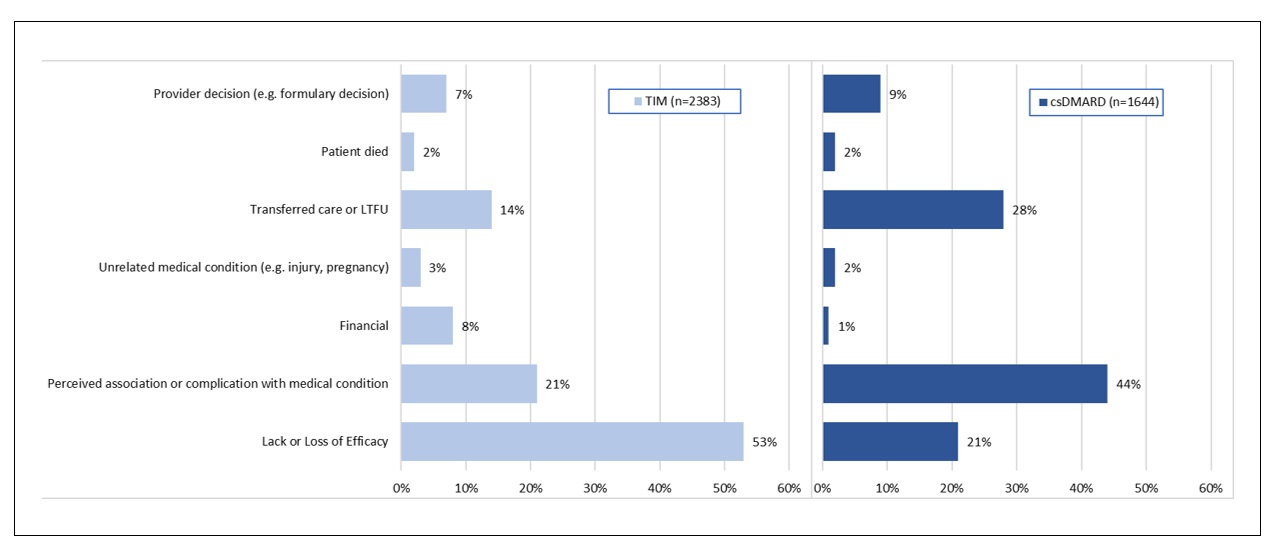
Results: Open text notes were reviewed for 2545 patients receiving 3616 regimens for which 4027 drugs were discontinued. Study population characteristics: 75% (1918) female, 77% (1325/1712) white, mean (range) age 57 (18-89), 67% (1706) with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Reasons for discontinuation differed by drug type. [FIGURE 1] Perceived association or complication with one or more medical conditions was most commonly indicated for csDMARDs (44% [725/1644]) with 49% (350/715) indicated as gastrointestinal. [FIGURE 2] Lack or loss of efficacy was listed as the predominant reason for TIM discontinuation (53% [1260/2382]). To assess alignment of fielded data with recorded discontinuation reasons within the notes, we examined disease activity scores (RAPID3 or CDAI [DAS]) closest but preceding drug discontinuation for the subset of patients with RA. Of 2780 drug discontinuations, DAS were recorded for 73% (2042); 68% (1891) within 6 months prior to discontinuation. For TIM (but not for csDMARD discontinuations), DAS scores were significantly different for those indicated as “lack or loss of efficacy” v. not. [FIGURE 3] Approximately 15% (TIM) and 16% (csDMARD) of discontinuations indicated as “lack or loss of efficacy” had near remission or low DAS.
Conclusion: Actual reasons for discontinuation may be directionally aligned with recorded data in the EMR, though the lack of fielded data for ~30% of evaluated discontinued drugs limits full understanding of what drives drug discontinuation. In addition, reported data that would appear to be at odds with the discontinuation reason suggest that other measures or inputs may contribute to how physicians or patients define successful treatment. To fully understand care, ongoing chart review along with full data extraction are necessary.
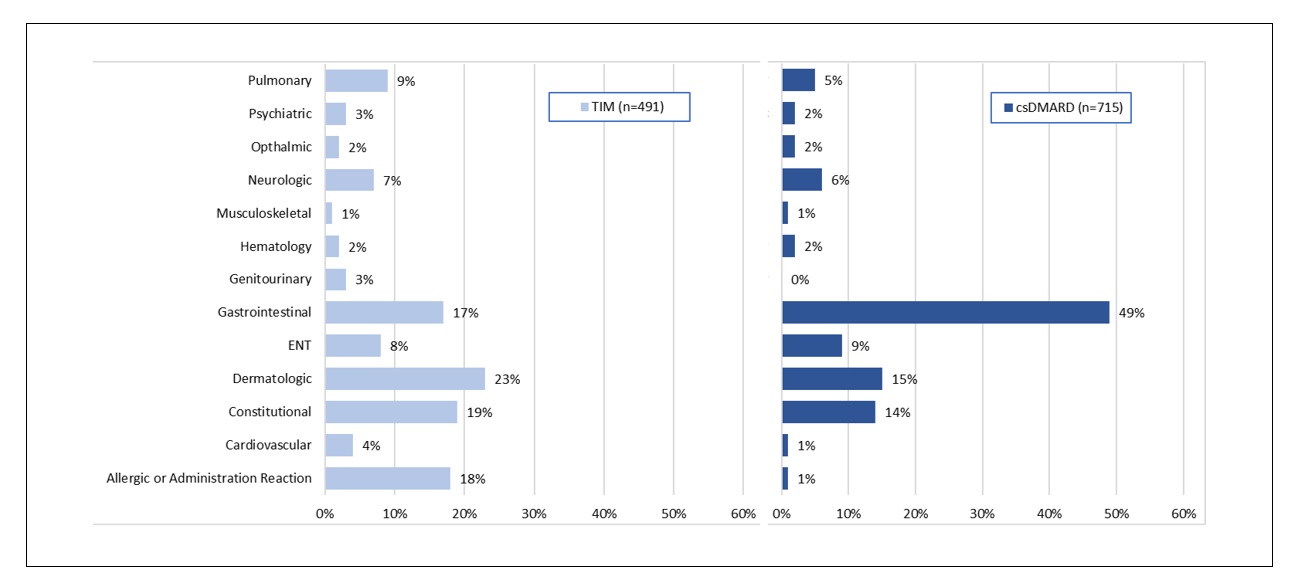 FIGURE 2: Systems indicated when discontinuation associated with 1 or more medical condition
FIGURE 2: Systems indicated when discontinuation associated with 1 or more medical condition
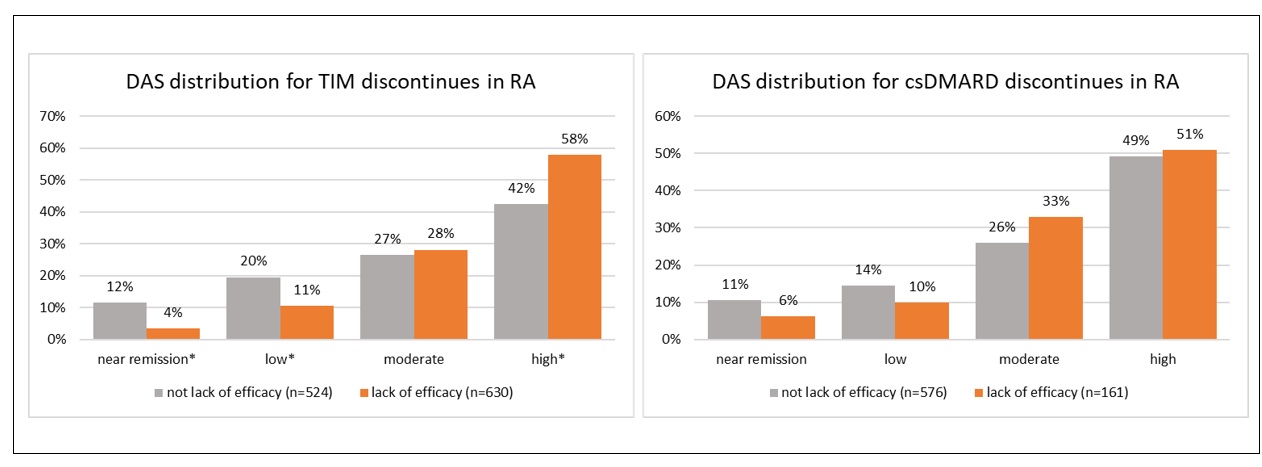 FIGURE 3: Distribution of DAS scores by discontinued drug type and reason of loss/lack of efficacy v. not in patients with RA. * indicates proportions that are significantly different (p < 0.05)
FIGURE 3: Distribution of DAS scores by discontinued drug type and reason of loss/lack of efficacy v. not in patients with RA. * indicates proportions that are significantly different (p < 0.05)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Huston K, Helfgott S, Milligan S, Singh J, Soloman N, Weil B, Edgerton C. The “Why” of Drug Discontinuation; Clinical Review of EMR Notes for 2,545 Patients with Rheumatic Diseases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-why-of-drug-discontinuation-clinical-review-of-emr-notes-for-2545-patients-with-rheumatic-diseases/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-why-of-drug-discontinuation-clinical-review-of-emr-notes-for-2545-patients-with-rheumatic-diseases/