Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment I: Psoriatic Arthritis (0504–0508)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 3:00PM-3:50PM
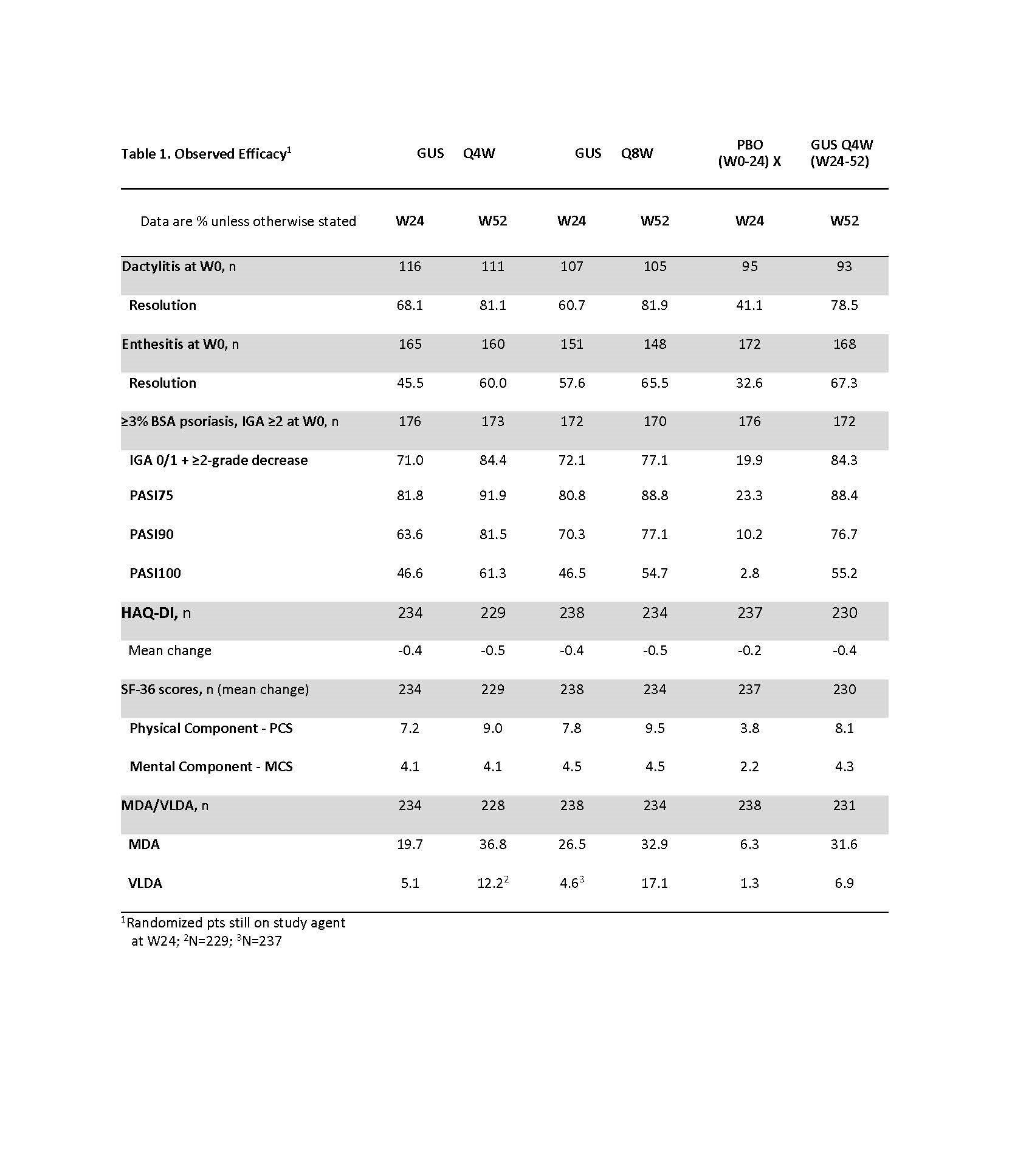
Background/Purpose: Guselkumab (GUS), a monoclonal antibody that specifically binds to the p19-subunit of IL-23, is approved to treat psoriasis. Through Week24 (W24) of the Ph3, double-blind, placebo (PBO)-controlled trial in biologic-naïve pts with active PsA (DISCOVER-2), GUS every 4 or 8 weeks (Q4W or Q8W) demonstrated efficacy for joint & skin symptoms and inhibition of structural damage progression (Q4W), and was well tolerated. This study assessed GUS efficacy and safety through W52.
Methods: Biologic-naïve adults with active PsA (≥5 swollen+≥5 tender joints; CRP ≥0.6mg/dL) were randomized (1:1:1) to GUS 100 mg Q4W; GUS 100 mg at W0, W4, Q8W; or PBO. At W24, PBO pts switched to GUS 100 mg Q4W (PBO X Q4W). ACR response rates at W52, based on nonresponder imputation (NRI) for missing data and as observed in pts who continued study agent at W24, are shown. Observed data for additional endpoints, including PsA-modified van der Heijde Sharp (vdH-S) scores derived from blinded radiographic images collected at W0, W24, W52 (or at d/c) and scored in a new Read Campaign, are shown.
Results: 712/739 (96.3%) randomized & treated pts continued study agent at W24; 689/739 (93.2%) completed Wk52. NRI ACR20 response rates continued to increase after W24, and at W52 were 70.6% for GUS Q4W and 74.6% for GUS Q8W (Fig1A). Similar response patterns were observed for the more stringent ACR50/70 criteria (Fig1C,E). Observed ACR (Fig, 1B,D,F), IGA, PASI & MDA/VLDA responses; dactylitis & enthesitis resolution; and mean improvements in HAQ-DI and SF-36 PCS/MCS scores were also sustained through W52 in pts receiving Q4W & Q8W; W52 data for PBO X Q4W pts were generally consistent with other GUS-treated pts (Fig1, Table1). Changes in vdH-S scores were similar for W24-52 (0.62) and W0-24 (0.46) for Q4W; less radiographic progression occurred from W24-52 v W0-24 for Q8W (0.23 v 0.73) & PBO X Q4W (0.25 v 1.00). In 731 GUS-treated pts, 4.2% had SAEs; 1.2% had serious infections; no pt died; and no pt had IBD, opportunistic infections or active TB, or anaphylactic or serum sickness-like reactions.
Conclusion: In biologic-naïve pts with active PsA, GUS elicited sustained improvements in joint & skin symptoms; inhibition of radiographic progression & improvements in physical function, quality of life & composite indices through W52. GUS safety in PsA was similar at W241 & W52 and consistent with GUS safety in psoriasis.
Reference:
- Mease et al. ACR 2019, abs #L13. Arth Rheumatol. 2019;71 S10:5247
 NRI and Observed ACR20 (A & B), ACR50 (C & D) and ACR70 (E & F) responses through W52 (Note: patients randomized to PBO crossed over to GUS Q4W at W24)
NRI and Observed ACR20 (A & B), ACR50 (C & D) and ACR70 (E & F) responses through W52 (Note: patients randomized to PBO crossed over to GUS Q4W at W24)
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
McInnes I, Rahman P, Gottlieb A, Hsia E, Kollmeier A, Xu X, Subramanian R, Agarwal P, Sheng S, Jiang Y, Zhou B, van der Heijde D, Mease P. Efficacy and Safety of Guselkumab, a Monoclonal Antibody Specific to the p19-Subunit of Interleukin-23, Through Week 52 of a Phase 3, Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Study Conducted in Biologic-naïve Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-guselkumab-a-monoclonal-antibody-specific-to-the-p19-subunit-of-interleukin-23-through-week-52-of-a-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-study-conducted-in-bi/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-and-safety-of-guselkumab-a-monoclonal-antibody-specific-to-the-p19-subunit-of-interleukin-23-through-week-52-of-a-phase-3-randomized-double-blind-placebo-controlled-study-conducted-in-bi/