Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Based on recent publications suggesting an association between COVID-19 and vascular inflammation, our aim was to explore new associations between coronavirus infections and vasculitis utilizing semantic mining of PubMed results.
Methods: The following literature search string: “(vasculitis OR vascular inflammation OR vascular damage) AND (coronavirus OR SARS virus OR MERS-CoV OR Covid-19)” was used to retrieve abstracts from the whole PubMed database, using Semantic MEDLINE 2 on 6/7/2020. This application represents a network of semantic predications (triples of the form subject-predicate-object, e.g. COVID-19 causes Disease) on a knowledge graph. The system allows for choosing the maximum number of nodes represented, the central topic, and the length of the network. For our network we chose to display all relations, COVID-19 (31 edges) as the central term, 3 lengths, and selecting the most informative nodes. Automatic summarization eliminated the less informative predications.
Results: The search string retrieved 152 citations from PubMed and identified 1,028 predications. The network (Figure 1), displayed using COVID-19 as the central term, consisted of 72 nodes and 140 edges. The 5 most connected nodes were ’Patients: 19 nodes’, COVID-19: 13’, ‘Inflammation: 13’, ’Lung: 11’, and ‘Disease: 11’.
Multiple links have been found between coronavirus and vasculitis. Animal coronaviruses, including the one causing feline infectious peritonitis (FIP), the murine coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus (MHV), the SARS-CoV in transgenic mice and coronavirus in ferrets, are known to cause vasculitis in animals. It is known that coronaviruses that infect animals can evolve and become new human coronaviruses. SARS produces inflammation in blood vessels. In 2005, a link between the coronavirus HCoV-NL63 or New Haven Coronavirus (HCoV-NH) and Kawasaki Disease (KD) was reported, although later studies concluded that HCoV-NH did not play a dominant role in the etiology or pathogenesis of KD. In 2014, serological testing suggested the possible involvement of HCoV-229E in the development of KD. There has also been a report of KD patients being infected by coronavirus OC43/HKU1. SARS-CoV2 may infect the vessels and trigger inflammatory reactions like those of vasculitis, including vasculitis-like cutaneous lesions. Some COVID-19 patients develop thrombosis, and increased risk of thrombosis is also present in primary vasculitic syndromes. Children, many of whom tested positive for COVID-19 antibodies, developed Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome (MIS-C), an inflammatory condition similar to KD.
Conclusion: Knowledge integration and discovery methods are an efficient and powerful way of retrieving and analyzing relevant information from multiple papers. Their main advantages are finding relations among biomedical concepts, generating new hypotheses, and opening them to literature-based discovery.
SARS-CoV-2 may cause vasculitis or vasculitis-like syndromes. The KD-like syndrome reported mainly in children with COVID-19 revives the previous suspicion of coronavirus as a possible triggering agent of KD and the decades-old hypothesis of infection involvement in the pathogenesis of vasculitis.
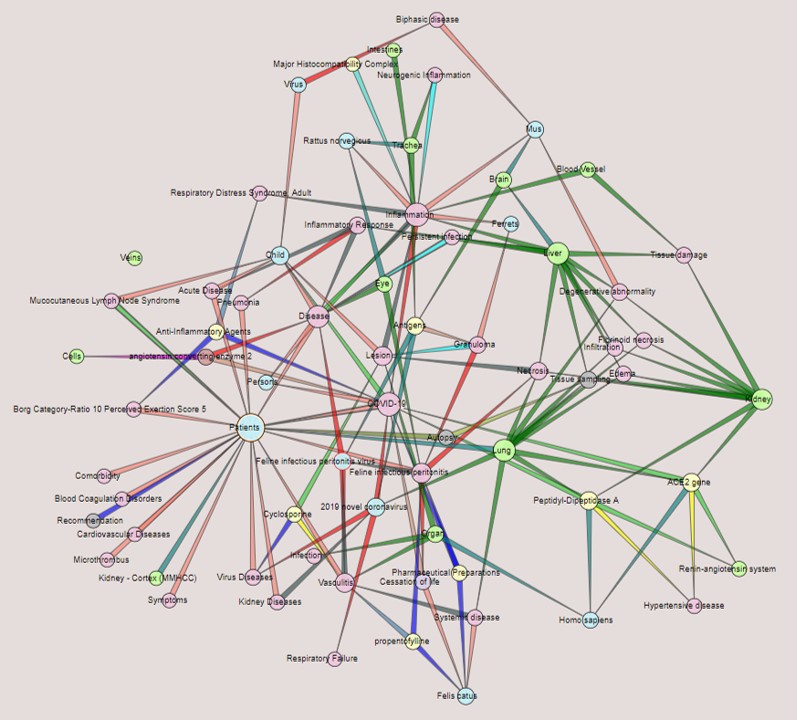 Figure 1. Semantic Network Resulting from PubMed Results
Figure 1. Semantic Network Resulting from PubMed Results
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rodriguez Pla A, Cartin-Ceba R. Coronavirus Infection and Vasculitis: Identifying Associations Mining the Biomedical Literature [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/coronavirus-infection-and-vasculitis-identifying-associations-mining-the-biomedical-literature/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/coronavirus-infection-and-vasculitis-identifying-associations-mining-the-biomedical-literature/
