Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Biologic therapy has improved prognosis of Behçet Disease (BD) uveitis. Although infliximab (IFX) is approved in Japan, most data in Caucasian patients comes from small series and no data on IFX optimization has been published. In the present study we assessed: a) long-term efficacy and safety of IFX and b) IFX optimization when ocular remission was achieved
Methods: Multicenter study of IFX-treated patients with BD uveitis refractory to conventional immunosuppressants.103 patients were treated with IFX as 1st biologic as follows: 3-5 mg/kg i.v. at 0, 2, 6 and every 4-8 weeks. The main outcomes were anterior chamber cells, vitritis, retinal vasculitis, macular thickness, best corrected visual acuity, and the glucocorticoids sparing effect that were analysed at baseline, 1st week, 1st and 6th months and 1st and 2nd years. After remission, based on a shared decision between patient and clinician, IFX optimization was performed. Efficacy, safety, and IFX cost were evaluated
Results: In whole series (n=103), main outcomes showed a rapid and maintained improvement, reaching remission in 78 patients after a mean IFX duration of 31.5 months. Severe side-effects were observed in 9 patients.
In the optimization subanalysis, comparative study between optimized and non-optimized groups showed: a) no differences in clinical baseline characteristics; b) similar maintained improvement in most ocular outcomes; c) lower severe adverse events and d) lower IFX cost in optimized group (4826.52 vs. 9854.13 euros/patient/year) (Table)
Conclusion: IFX seems effective and relatively safe in Caucasian patients with refractory BD uveitis. IFX optimization is also effective, safe, and cost-effective
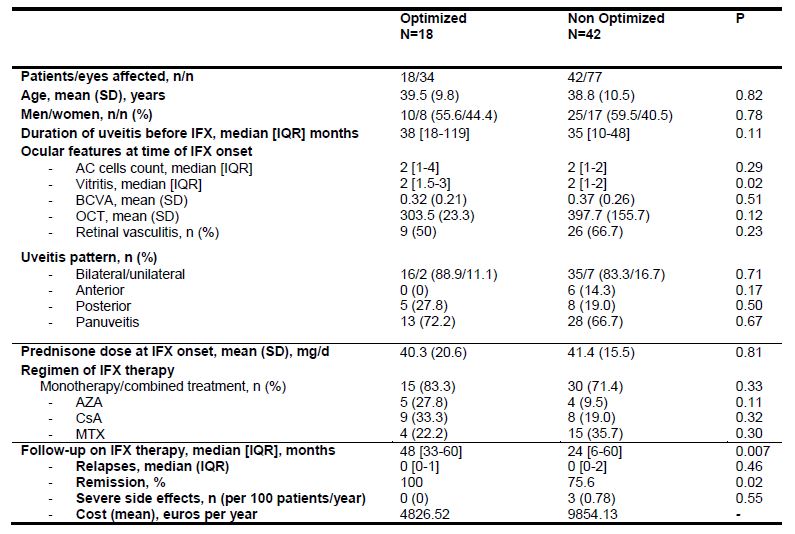 Main general features and follow-up of a subgroup of patients (n= 60) with Refractory Uveitis Due to BD who Achieved Remission after the standard dose of IFX therapy (5 mg/kg at 0, 2, 6 and then every 8 weeks). Differences between Optimized and Non-optimized patients
Main general features and follow-up of a subgroup of patients (n= 60) with Refractory Uveitis Due to BD who Achieved Remission after the standard dose of IFX therapy (5 mg/kg at 0, 2, 6 and then every 8 weeks). Differences between Optimized and Non-optimized patients
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Martín-Varillas J, Atienza-Mateo B, Calvo-Río V, Beltran-Catalan E, Adan A, Hernandez Garfella M, Valls-Pascual E, Sellas-Fernández A, Ortego N, Fonollosa A, Maiz Alonso O, Torre I, Fernández-Espartero C, Jovani V, Peiteado D, Díaz Valle D, Romero-Yuste S, Aurrecoechea E, García-Arias M, Caracuel M, Insúa S, González-Suárez S, Sánchez Andrade A, Linares L, García González A, Almodovar R, Carrasco Cubero C, Alcalde Villar M, Fernandez-Carballido C, Pages F, Peña Sainz-Pardo E, Demetrio-Pablo R, Castañeda S, González-Gay M, Hernández J, Blanco R. Infliximab in Refractory Uveitis Due to Behçet’s Disease: Long Term Follow-up and Therapy Optimization. Multicenter Study of 103 Caucasian Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/infliximab-in-refractory-uveitis-due-to-behcets-disease-long-term-follow-up-and-therapy-optimization-multicenter-study-of-103-caucasian-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/infliximab-in-refractory-uveitis-due-to-behcets-disease-long-term-follow-up-and-therapy-optimization-multicenter-study-of-103-caucasian-patients/
