Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Studies show a long diagnostic delay in Hypophosphatasia (HPP) and the accessibility for the genetic testing is not always possible. Our previous cross-sectional study (Tornero et al. OJRD (2020) 15:51) revealed alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels < 25 IU/L seemed to be useful to identify individuals with ALPL variants among subjects with persistent hypophosphatasaemia. These data highlight the importance of establishing a specific biochemical profile and the value of including TNSALP substrates is a matter of interest. First, to confirm our previous results in a one-year follow-up of a longitudinal study. Second, to determine the value of including TNSALP substrates (serum pyridoxal phosphate-PLP-and urinary phosphoetanolamine-PEA) in a specific biochemical profile to detect variants in ALPL in individuals with persistent low ALP levels.
Methods: Biochemical parameters of subjects included in a prospective longitudinal study conducted at La Paz Hospital were employed. Subjects were divided into two groups according to their genetics (+ GT or -GTgroup). Substrates were determined at baseline and at one-year visit and ALP levels also at six-months. To confirm the threshold, diagnostic utility measures were calculated at the 3 visits. ROC curves were employed to determine PLP and PEA best cut-off levels. Hierarchical binary logistic regression analysis was used to determine how well the different models fit (Nagelkerke R2). Finally, diagnostic utility measures for each model were calculated.
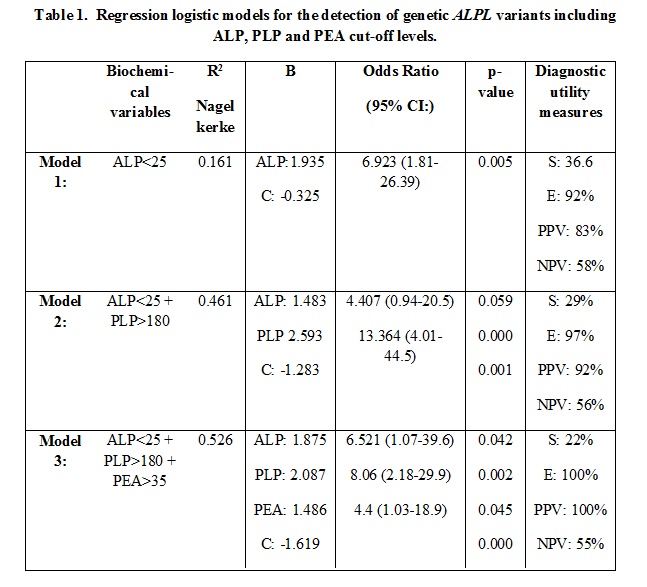
Results: Using ALP data from the three visits, Specificity (E) ranged between 84-91%; positive predictive value (PPV), 76-87% and +LR 3-6.1%. The ROC curves revealed cut-off PLP levels with the best combination of S and E for PLP were 180 nmol/L (S: 72%, E:86%) and for PEA, 35 (S:58%, E89%) umol/g creat. The regression model showed an OR (95% IC) for ALP< 25 IU/L, PLP >180 and PEA >35 of 6.52 (1.07-39.6), 8.06 (2.2-29.9) and 4.4 (1.03-18.9). Compared to the model just including ALP, R2 improved (0.161 to 0.526) when substrates were added (E and PPV:100% and S:22%), especially when PLP was included (Table 1).
Conclusion: This study confirms that ALP levels < 25 IU/L could be useful to identify individuals displaying ALPL variants. Additionally, the combination of this threshold with the proposed cut-off levels of its substrates, especially PLP, have shown a very high specificity to detect the disease and could help vigorously in the diagnostic work-up of HPP.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tornero C, Navarro-Compán V, Tenorio J, Garcia-Carazo S, Buño A, Monjo I, Plasencia C, Iturzaeta J, Lapunzina P, Heath K, Balsa A, Aguado P. Biochemical Algorithm to Identify Individuals with ALPL Variants Between Subjects with Persistent Hypophosphatasaemia [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biochemical-algorithm-to-identify-individuals-with-alpl-variants-between-subjects-with-persistent-hypophosphatasaemia/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biochemical-algorithm-to-identify-individuals-with-alpl-variants-between-subjects-with-persistent-hypophosphatasaemia/