Session Information
The 2020 Pediatric Rheumatology Symposium, originally scheduled for April 29 – May 2, was postponed due to COVID-19; therefore, abstracts were not presented as scheduled.
Date: Thursday, April 30, 2020
Title: Poster Session 1
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 6:00PM-7:00PM
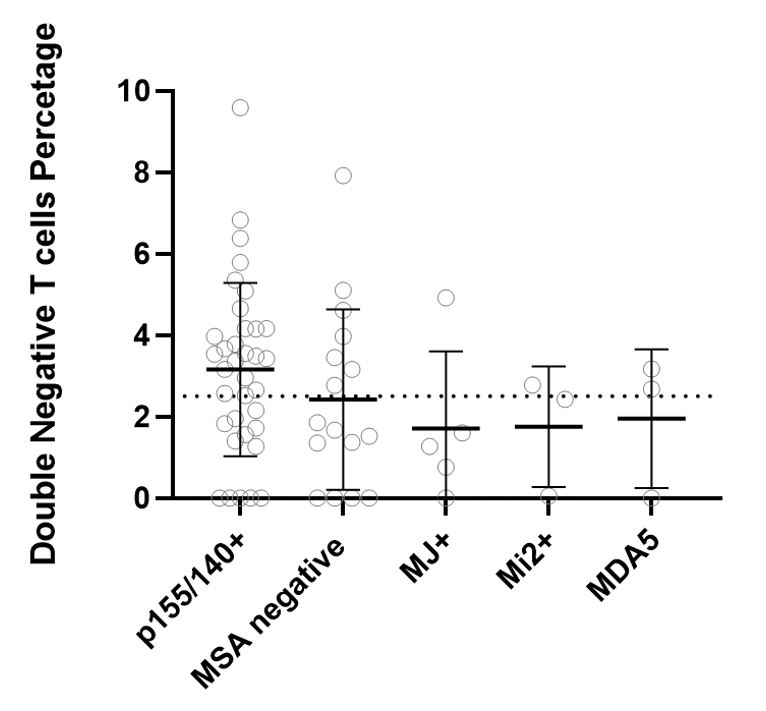
Background/Purpose: Double Negative (DN) T cells was initially described in the context of autoimmune lymphoproliferative disease, which is caused by defective T cells apoptosis due to mutation of the Fas and Fas-ligand. Subsequently, other autoimmune disorders such as Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) and Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) have been shown to have elevated DN T cells as well. Although the exact rule of these cells in autoimmunity is not completely clear, the early studies in lupus nephritis showed that DN T cells make a significant amount of IL17 and interferon-gamma promoting the inflammatory status in these patients. Elevated DN T cell have not been documented in a large Juvenile Dermatomyositis (JDM) population. The aim of this study to determine if untreated JDM patients have elevated DN T cells populations.
Methods: Informed consent was obtained and patients were enrolled in the JM Registry at Ann & Robert H. Lurie Children’s Hospital of Chicago (IRB# 2010-14117). Subjects with JDM who had T and B cell flow cytometry before the initiation of medical therapy were included in this study (IRB# 2012-14858). The years of study ranged between 1991 and 2019. Patients with overlap syndrome were excluded from the analysis. Double negative T cells were defined as CD3+ CD4- and CD8- T cells by flow cytometry. Elevated DN T cell was defined as DN T cell more than 2.5% of total T cells. We divided the study population into two groups based on their DN T cells (normal vs. elevated DN T cells). We used T-test and chi-square to measure the differences between the two groups in terms of age, gender, duration of untreated disease, disease activity scores (DAS) Childhood Myositis Assessment Score (CMAS), and myositis-specific antibodies (MSA). This study was supported by the CureJM Foundation.
Results: 69 subjects (80% female, 77% white) were included in this study. Subjects’ MSAs were as follows: 51% P155/140+, 7% MJ+, 4% Mi-2+, 4% MDA-5+, 9% multiple MSAs and 23 % MSA negative. 37 out of 69 (54%) of untreated JDM patients had elevated DN T cells (range from 2.6 – 9.6 % of T cells). There was no significant difference between subjects with normal and elevated DN T cells in term of age, gender, duration of untreated disease, MSA, CMAS, or DAS.
Conclusion: 1) More than half of JDM patients have elevated DN T cells, which is consistent with a previously published study in pediatric SLE; 2) The percentage of DN T cells did not correlate with disease activity markers such as CMAS or DAS. 3) Further study is needed to examine the role of these cells in the pathophysiology of JDM.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Khojah A, Morgan G, Marin W, Ahsan N, Pachman L. Double Negative T Cells in Juvenile Dermatomyositis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 4). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/double-negative-t-cells-in-juvenile-dermatomyositis/. Accessed .« Back to 2020 Pediatric Rheumatology Symposium
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/double-negative-t-cells-in-juvenile-dermatomyositis/