Session Information
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) were the first approved biological disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) for psoriatic arthritis (PsA). IL-12/23 and IL-17-specific antibodies provide another mode of action (OMA) than TNFi and were more recently approved for PsA. In 2018, ACR recommended TNFi as a first-line treatment option for PsA. Here, we aimed to compare these two bDMARD classes for PsA in a real world setting.
We hypothesized that response to a bDMARD rather depends on the disease-related activation of a target than the pharmacological profile of different inhibitors for the same target. Consequently, we postulated better drug persistence of OMA bDMARDs than another TNFi bDMARD after having stopped a TNFi either for lack of efficacy or tolerability reasons.
Methods: We analyzed all available bDMARD treatment courses (TC) of PsA patients in the Swiss register for Clinical Quality Management in Rheumatology (SCQM), after date of launch of the first OMA bDMARD in 2014 and after use of a first TNFi. We estimated drug retention by using Kaplan-Meier plots and equality of survival using Log-Rank tests. After multiple imputation of missing covariates, we included line of bDMARD treatment with two levels, 2nd versus 3rd or later line of therapy, smoking, age, BMI and disease activity score (DAS28-CRP) baseline covariates together with the bDMARD treatment category into adjusted models
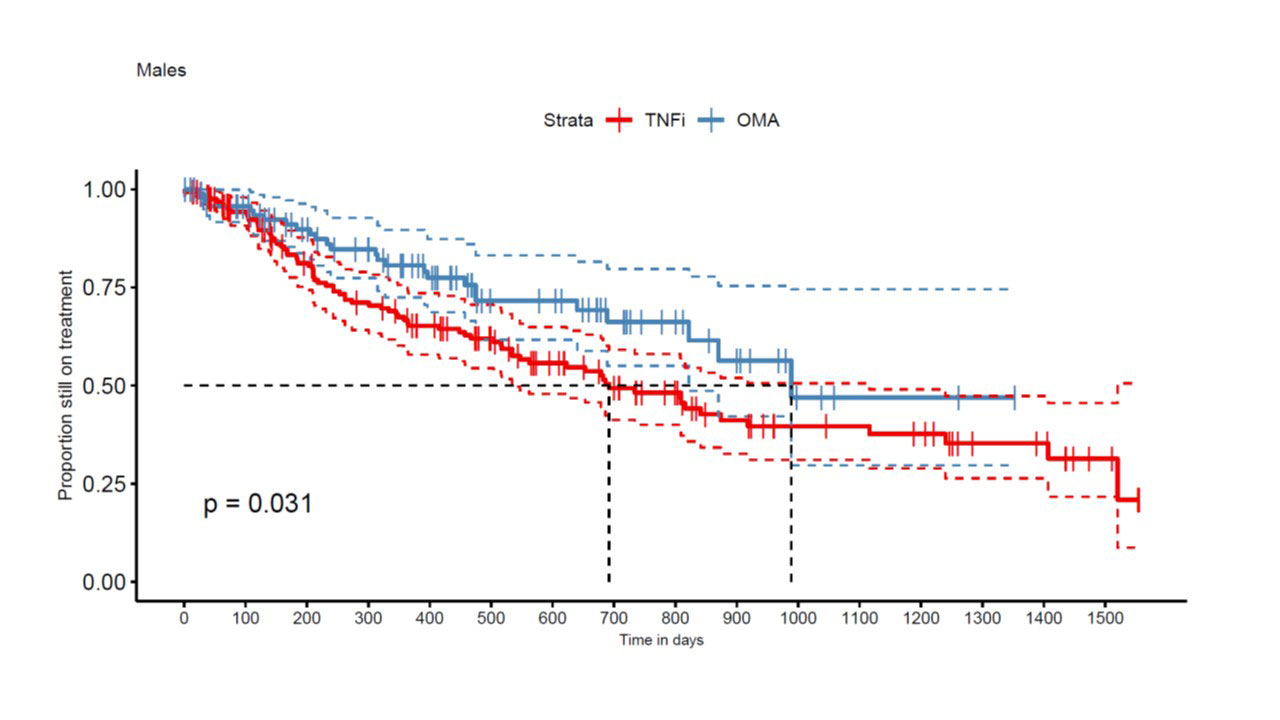
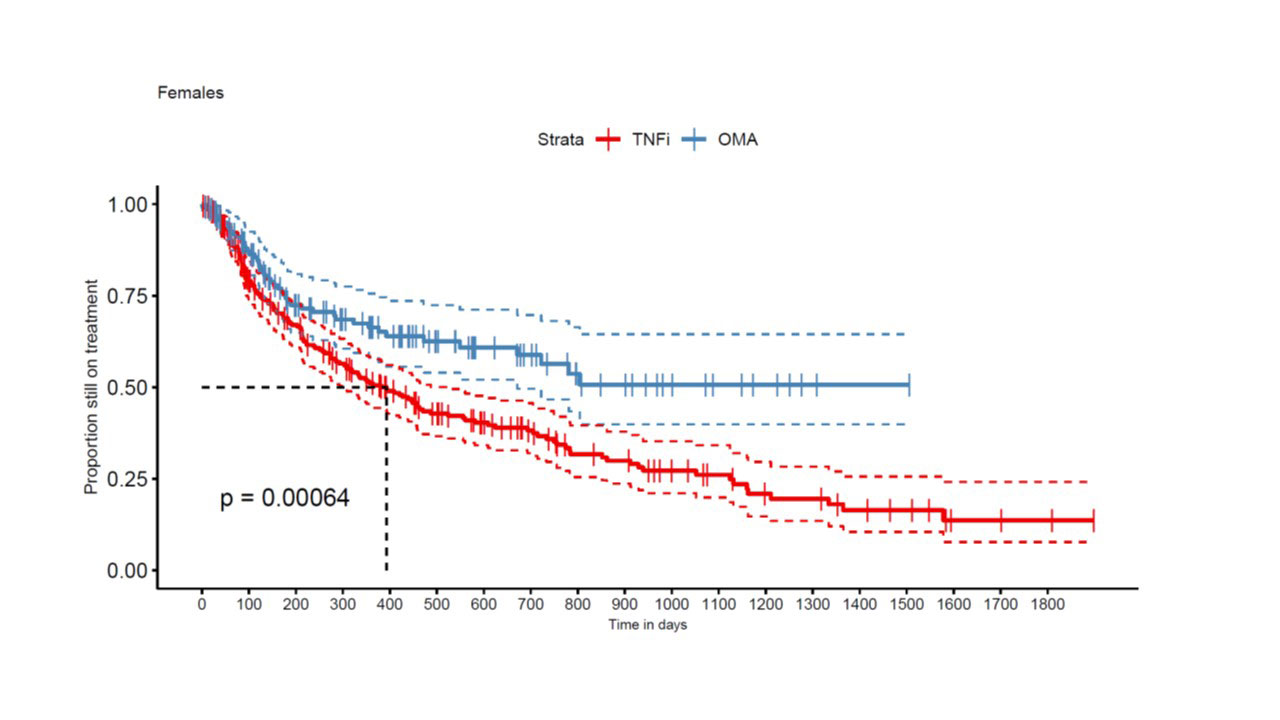
Results: A total of 663 TC from 449 patients met our inclusion criteria, with 422 TNFi TCs and 241 OMA bDMARD TCs. An IL-12/IL-23 inhibitor was used in 97 and an IL-17i specific compound in 144 OMA bDMARD TCs. At baseline, median DAS28-CRP was 2.7 [1.9; 3.9] in the TNFi group and 3.2 (2.5; 4.0) in the OMA bDMARD group (p=0.02). Furthermore, TNFi were more frequently used as a second line treatment (n=191, 45%) than OMA bDMARDs (n=53, 22%). TNFi TCs (n=397, 94%) were more frequently observed in OMA bDMARD naïve patients, but OMA bDMARD TCs were more frequent after another previous OMA bDMARD TC (n= 198, 82%, p< 0.0001). Other covariates such as sex (399 women and 264 men, p = 0.87), smoking status (n=90, p=0.30), median age (51 [42; 59] years, p = 0.25) and BMI at baseline (28 [24; 31.5] kg/m2, p = 0.57), were similarly distributed between the two treatment groups. In the crude analyses, the estimate of median drug retention time was 516 days for TNFi as compared to 989 days for the OMA bDMARD group (p < 0.0001). OMA bDMARDs had a longer drug retention both in men (p=0.031, Fig 1) and women (p< 0.001, Fig 2). In multivariable-adjusted analyses in 208 TNFi and 111 OMA bDMARD TCs, OMA bDMARDs were on average late discontinued than TNFi (HR=0.49 [0.33, 0.72], p< 0.001), but second line indication (HR=1.44 [1.02, 2.03]) and male sex (HR= 1.52 [1.07, 2.15] were associated with better drug retention rates.
Conclusion: After use of a first TNFi, OMA bDMARDs displayed better drug retention in PsA than another TNFi. As OMA bDMARD were more often used in less favorable later line indication, they appear according to this analysis as the preferential choice among the alternative bDMARD treatment options in TNFi experienced patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Moeller B, Papagiannoulis E, Christ L, Ciurea A, Hugle T, Mueller R, Nissen M, Scherer A, Scholz G, Villiger P, Yawalkar N. Drug Retention of Biological DMARDs Targeting IL-12/IL-23 or IL-17 versus TNF Inhibitors, After a First Line TNF Inhibitor, in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis – an Analysis in the Swiss SCQM Register [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/drug-retention-of-biological-dmards-targeting-il-12-il-23-or-il-17-versus-tnf-inhibitors-after-a-first-line-tnf-inhibitor-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-an-analysis-in-the-swiss-scqm/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/drug-retention-of-biological-dmards-targeting-il-12-il-23-or-il-17-versus-tnf-inhibitors-after-a-first-line-tnf-inhibitor-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-an-analysis-in-the-swiss-scqm/