Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster III: Giant Cell Arteritis
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In Giant Cell Arteritis (GCA) two dominant cytokine clusters have been linked to disease activity, IL-6 – IL-17 axis (Th17) and IL-12 – IFN γ axis (Th1). The first one related to systemic symptoms and the second route responsible for ischemic symptoms. Tocilizumab (TCZ) performs its effect mainly by inhibiting Th17 axis and terminally Th1 route.
Our aim was to evaluate the effect of TCZ on ischemic and systemic symptoms throughout the follow-up.
Methods: Retrospective, multicenter study of 134 patients diagnosed of GCA on treatment with TCZ. We evaluate the efficacy of TCZ by improving ischemic (visual involvement, headache, jaw claudication) and systemic symptoms (fever, constitutional syndrome, polymyalgia rheumatica (PMR)).
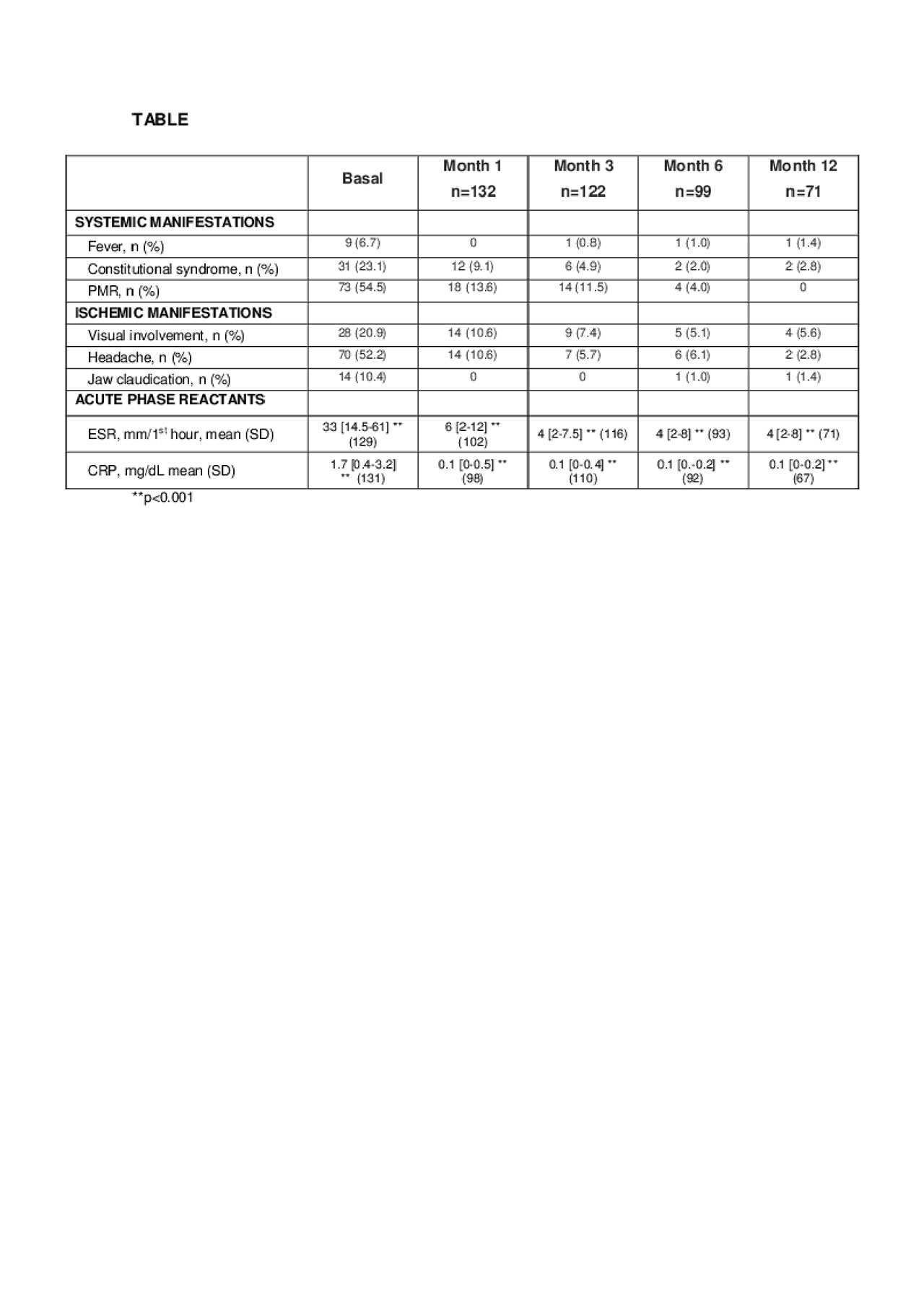
Results: We evaluated 134 patients (101 w/33 m) and its main symptoms at TCZ onset, TABLE. 73 (54.5%) patients presented PMR followed by headache in 70 (52.2%) cases, constitutional syndrome in 31 (23.1%) and visual involvement in 28 (20.9%) patients. After one month of treatment there was an important clinical improvement, persisting in 13,6% of patients PMR, 10.6% headache and 10.6% visual involvement. Throughout the follow-up, the improvement of ischemic symptoms was slower. At month 12, in 5.6% (4) of patients persisted with visual impairment, and 2.8% (2) patients presented headache and constitutional syndrome. However, the analytical improvement was statistically significant from the first month and sustained during follow-up.
Conclusion: According to the results of our study, we can conclude that in clinical practice, ischemic symptoms take longer to improve than systemic symptoms; being visual affectation the most frequent symptom after 12 months of follow-up.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Calderón-Goercke M, Loricera J, PRIETO- PENA D, Castañeda S, Aldasoro Caceres V, Villa I, Humbría A, Moriano C, Romero-Yuste S, Narváez J, Gómez-Arango C, Perez Pampín E, Melero R, Becerra-Fernández E, Revenga M, Álvarez-Rivas N, Galisteo C, Sivera F, Olivé-Marqués A, Álvarez del buergo M, Marena-Rojas L, Fernández-López C, Navarro F, Raya E, Galindez-Agirregoikoa E, Arca B, Solans-Laqué R, Conesa A, Hidalgo C, Vazquez C, Román-Ivorra J, Lluch P, Manrique S, Vela P, de Miguel E, Torres-Martín C, Nieto J, Ordas-Calvo C, salgado-Pérez E, Luna-Gómez C, Toyos-Sáenz De Miera F, Fernández-Llanio N, García A, Larena C, Varela-García M, Dos Santos R, Ortego N, Hernández J, González-Gay M, Blanco R. Response to Tocilizumab in Patients with Giant Cell Arteritis, According to Ischemic vs Systemic Symptoms [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/response-to-tocilizumab-in-patients-with-giant-cell-arteritis-according-to-ischemic-vs-systemic-symptoms/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/response-to-tocilizumab-in-patients-with-giant-cell-arteritis-according-to-ischemic-vs-systemic-symptoms/