Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: CD4+ T cell subsets control immune system in check and prevent autoimmunity by keeping a balance among them. However, their levels of blood in ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV), especially absolute numbers, are still remains unclear. We therefore analyzed the percentages and absolute numbers of CD4+ T cell subsets as well as their diagnostic values in patients with AAV.CD4+ T cell subsets control immune system in check and prevent autoimmunity by keeping a balance among them. However, their levels of blood in ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV), especially absolute numbers, are still remains unclear. We therefore analyzed the percentages and absolute numbers of CD4+ T cell subsets as well as their diagnostic values in patients with AAV.CD4+ T cell subsets control immune system in check and prevent autoimmunity by keeping a balance among them. However, their levels of blood in ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV), especially absolute numbers, are still remains unclear. We therefore analyzed the percentages and absolute numbers of CD4+ T cell subsets as well as their diagnostic values in patients with AAV.CD4+ T cell subsets control immune system in check and prevent autoimmunity by keeping a balance among them. However, their levels of blood in ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV), especially absolute numbers, are still remains unclear. We therefore analyzed the percentages and absolute numbers of CD4+ T cell subsets as well as their diagnostic values in patients with AAV.
Methods: AAV patients (n = 54) and healthy controls (HCs) (n = 19) were enrolled. Of them, 38 patients were renal vasculitis. Proportions and absolute numbers of CD4+T cell subsets were determined by flow cytometry. The diagnostic value for Treg subsets was evaluated by the areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves (AUC). Correlations of clinical indicators with the CD4+ T subsets were systematically analyzed.
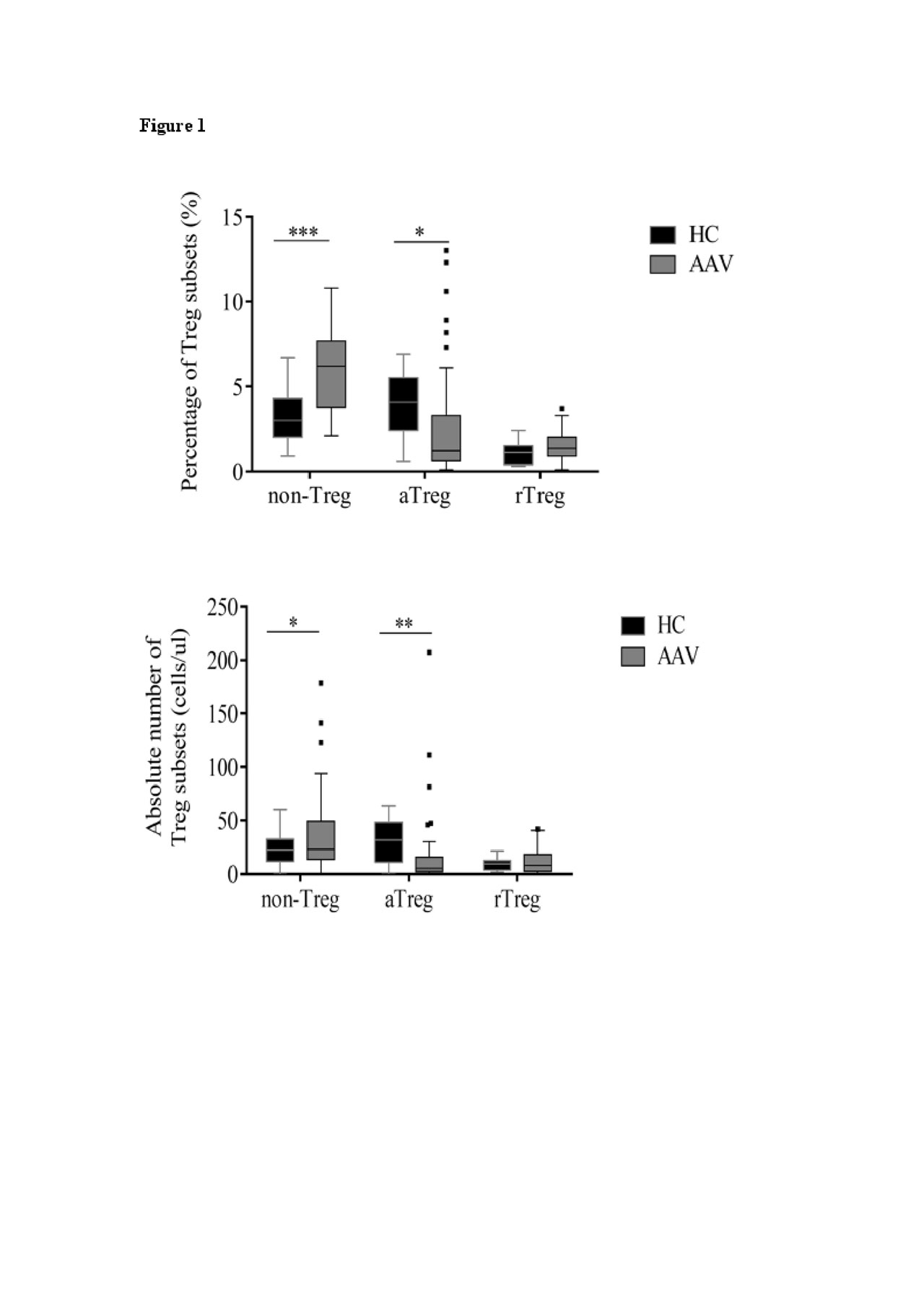
Results: Percentages of activated Treg cells (aTreg, p=0.044) in AAV patients were decreased, but those of effector memory T-cell subpopulation (TEM) (p< 0.001) and Treg cells (p=0.001) were increased. Similar results were observed when we compared absolute numbers of the above corresponding cells in AAV patients and HCs, except TEM. Furthermore, the percentage of aTreg (p=0.043) was decreased while that of Th17 cells (p=0.027) was increased in renal vasculitis patients. A significant correlation was observed between the ratio of Th17 to Treg subset and creatinine or BUN in renal vasculitis patient. Interestingly, the AUC of the aTreg improved significantly the diagnostic potential of AAV. In addition, we found that cytokine IL-2 and IL-4 exhibited a downward while IL-6, IL-10, TNF-α, IFN-γ and IL-17A trend upward in AAV patients.
Conclusion: We identified decrease in aTreg cells and increase in TEM, which associated with the ANCA-related immune response. Correcting the above-mentioned T cell abnormality will potentially be powerful therapeutic tools for AAV.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wang Y, Zhao X, Gao C, Luo J. Abnormality of Percentages and Absolute Numbers of CD4+ Memory and Regulatory T Subset Cells in ANCA-associated Vasculitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/abnormality-of-percentages-and-absolute-numbers-of-cd4-memory-and-regulatory-t-subset-cells-in-anca-associated-vasculitis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/abnormality-of-percentages-and-absolute-numbers-of-cd4-memory-and-regulatory-t-subset-cells-in-anca-associated-vasculitis/