Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: Systemic Sclerosis & Related Disorders – Clinical Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS) is used as primary and secondary outcome measure in different trials of diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (dcSSc) 1. As part of a Phase I/II trial assessing the safety of tofacitinib 5 mg twice a day versus placebo in dcSSc (clinicaltrials.gov NCT032740762), we assessed the performance of 3 different methods of scoring the modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS)1.
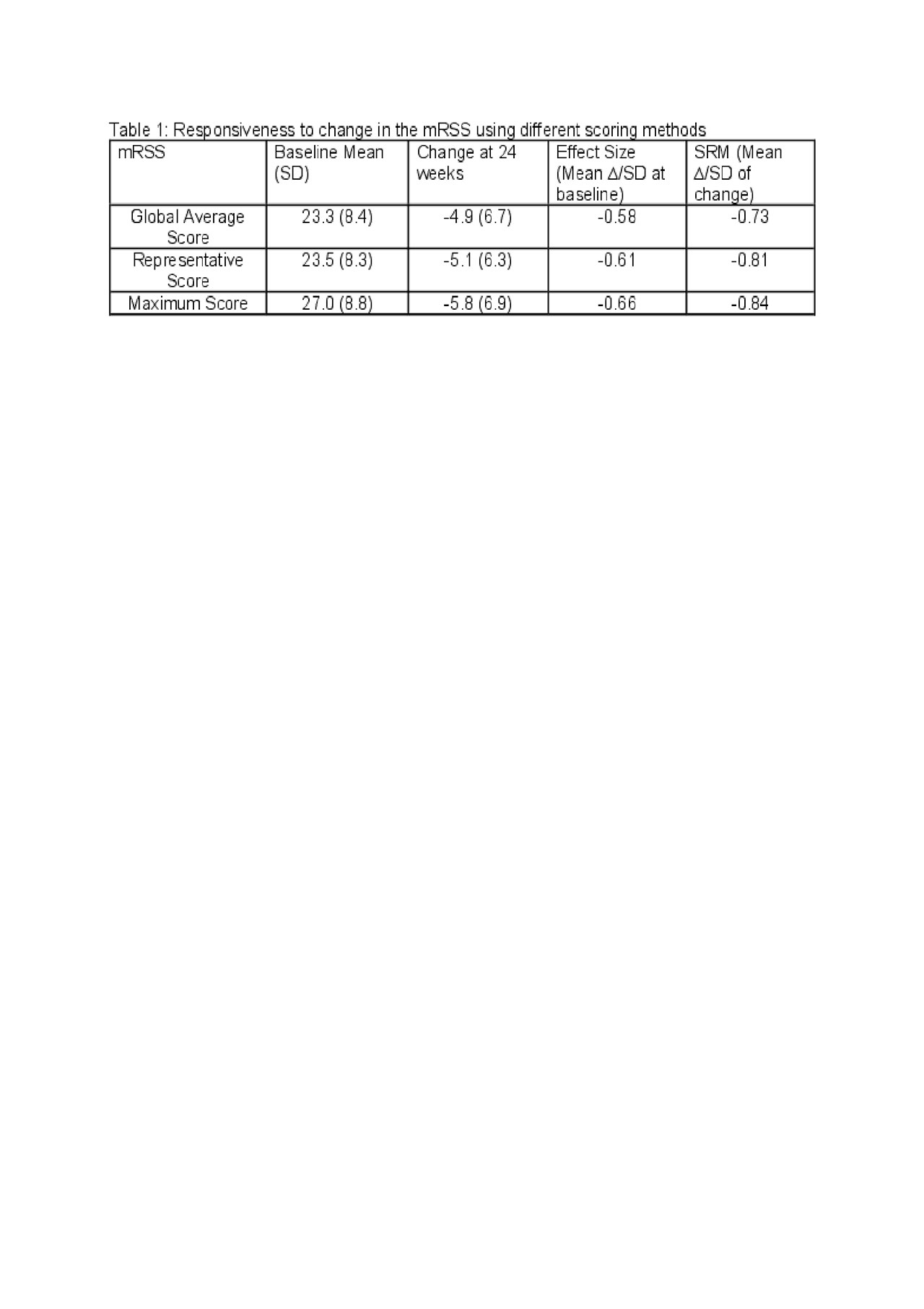
Methods: A 6-month, double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial was conducted in dcSSc with disease duration of ≤ 60 months (defined as first non−Raynaud phenomenon) and mRSS ≥ 10 and ≤ 45 units. Efficacy end point included the change in the mRSS at 6 months. Each anatomical area was scored as Global Average score where the examiner takes average of the area; Maximum score where an examiner scores the area according to the most severe local involvement; and the Representative area where the examiner assigns a score that is most representative of the area. Responsiveness to change was evaluated using the effect size (ES) and standardized response mean (SRM). Both indices are ratios of observed change to a measure of variance (also known as signal to noise). For two indices, the numerator is the mean change from the baseline to Month 6 for mRSS and the denominators are the standard deviation at baseline (ES) and the standard deviation of change (SRM). Cohen’s rule-of-thumb for interpreting responsiveness to change was applied to determine the magnitude of change where 0.20-0.49 represents a small change, 0.50-0.79 a medium change, and 0.80 or greater a large change.
Results: 15 participants were randomized (2:1; 10 to TOFA and 5 to PLA) and formed the mITT group; 10 (100%) and 4 (80%) completed the 6-month treatment period in TOFA and PLA groups, respectively. The mean baseline scores were similar in the Global Average and Representative groups and higher in the Maximum group (Table 1). Using the ES, the magnitude of responsiveness was similar in all 3 groups (Medium change). Using the SRM, the magnitude of change was numerically greater in the Representative and Maximum groups (Large change) vs. Global Average (Medium change).
Conclusion: In a small trial of 15 participants, all 3 methods to score the mRSS yielded similar magnitude of responsiveness to change. The mRSS was conducted by experienced researchers in this trial and these results should be validated in a larger trial with multiple centers.
- Khanna D, et al. JSRD 2017
- Khanna D, et al Submitted American College of Rheumatology 2019
Acknowledgment: Dr. Khanna is funded by NIAMS K24 AR063120 and R01 AR 070470.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bush E, Nagaraja V, Lafyatis R, Khanna D. Responsiveness to Change of the Modified Rodnan Skin Score in a Phase I/II Double-Blind Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/responsiveness-to-change-of-the-modified-rodnan-skin-score-in-a-phase-i-ii-double-blind-randomized-placebo-controlled-trial/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/responsiveness-to-change-of-the-modified-rodnan-skin-score-in-a-phase-i-ii-double-blind-randomized-placebo-controlled-trial/