Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Belimumab is approved in adults with active SLE and for childhood-onset SLE (cSLE). PLUTO, a Phase 2, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial (114055; NCT01649765), was the first study of belimumab in cSLE. Efficacy, safety, and pharmacokinetics (PK) of intravenous (IV) belimumab 10 mg/kg, plus standard therapy were evaluated. Pediatric and adult belimumab exposures were compared.
Methods: Patients with cSLE, 5–17 years of age, who were randomized to belimumab 10 mg/kg IV every 4 weeks, and for whom ≥1 PK sample was obtained, were included. Patients were required to have active SLE according to ACR classification criteria. A linear 2-compartment population PK model with first-order elimination described the pharmacokinetics of the population. An exploratory post hoc exposure-response analysis assessed the impact of between-patient exposure variability on clinical response (SLE Responder Index 4 [SRI4]) at Week 52, and the occurrence of a serious adverse event (SAE) at any time during the study.
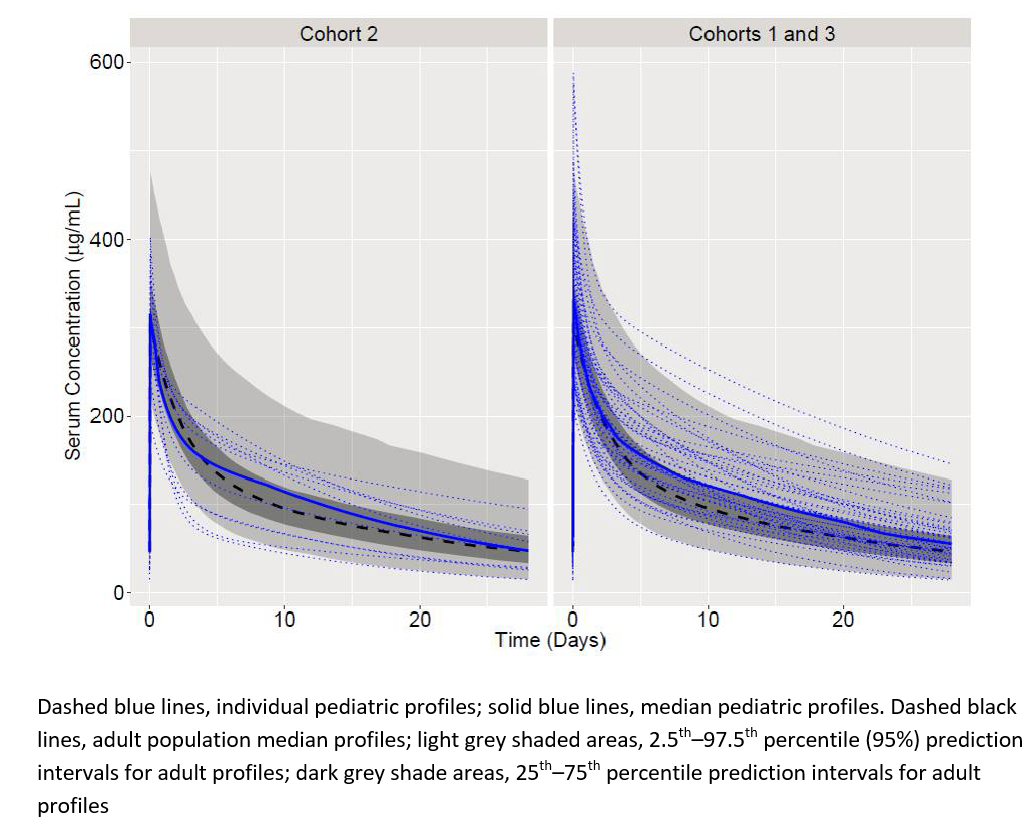
Results: Data for 53 belimumab-treated patients were analyzed. Following three biweekly loading doses on Days 0, 14, and 28, belimumab pre-infusion (Cmin) and post-infusion (Cmax) concentrations reached steady-state levels over 8 weeks of treatment and were maintained over the 52-week treatment period for all cohorts. Week 24 Cmax and Week 52 Cmin values were consistent across cohorts, with a trend towards slightly higher exposure in the older versus younger age group (Table). The population PK model estimated a clearance of 158 mL/day, a steady-state volume of distribution of 3.5 L, a terminal half-life of 16.3 days, and a distribution half-life of 0.8 days in the overall population. Body size dependence was defined by the fat-free mass, a pharmacokinetically relevant covariate of clearance, and volume of distribution. Baseline white blood cell count on the central volume of distribution, and baseline IgG, proteinuria, and estimated glomerular filtration rate on central clearance, were also relevant covariates, although their relative influence on PK was smaller. After accounting for body size, age had no statistically significant effect on clearance. Individual and median steady-state pediatric PK profiles were similar to adult profiles1 (Figure). At Week 52, SRI responders (n=28) had similar exposures to non-responders (n=25); median (interquartile range [IQR]) concentrations were 116 [96–140] µg/mL and 109 [88–134] µg/mL, respectively) and variability in exposures of both groups overlapped. Patients who experienced a SAE (n=9) had similar exposures to those who did not (n=44) (median [IQR] 128 [108–161] µg/mL and 110 [86–136] µg/mL, respectively).
Conclusion: Exposure estimates for belimumab 10 mg/kg IV in the pediatric population were consistent with adult exposures. No clinically meaningful correlations between exposure parameters and efficacy or safety were identified, confirming that the belimumab 10 mg/kg IV dose used in adults is appropriate for pediatric patients with cSLE.
Study funding: GSK. Medical writing support: Liam Campbell, PhD, Fishawack Indicia Ltd, UK (funded by GSK).
Reference: 1Struemper H, et al. J Clin Pharmacol 2013; 53(7): 711–20
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Dimelow R, Ji B, Struemper H. Pharmacokinetics and Exposure-response of Intravenous Belimumab in Children with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacokinetics-and-exposure-response-of-intravenous-belimumab-in-children-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/pharmacokinetics-and-exposure-response-of-intravenous-belimumab-in-children-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus/