Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In 2016, the American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) published recommendations designed to reduce hydroxychloroquine induced retinopathy via early detection and reduction of hydroxychloroquine dosing from 6.5 mg/kg to less than 5 mg/kg. We prospectively determined the frequency and the predictive role of blood levels of hydroxychloroquine to identify those at greater future risk of retinopathy. Blood hydroxychloroquine levels are preferred over plasma levels, as they more accurately reflect exposure over the last month.
Methods: 382 SLE patients were examined by ophthalmologists with retina specialization, with a fundus examination and one or more of the newer retinal screening tests: Spectral-Domain Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT); Multifocal Electroretinogram (mfERG); Microperimetry (MP1); and Fundus Autofluorescence (FAF). Hydroxychloroquine blood levels were tested at every visit and quantified by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry.
Results: Twenty-three patients had confirmed hydroxychloroquine toxicity for an overall retinopathy frequency of 4.3%. The frequency of retinopathy was: 1% in the first 5 years, 1.8% from 6 to 10 years, 3.3% from 11 to 15 years, 11.5% from 16 to 20 years, and 8.0% after 21 years of use (Table 1). Higher hydroxychloroquine blood levels (both mean and maximum) predicted later hydroxychloroquine retinopathy (Table 2).
Conclusion: The frequency of retinopathy in our prospective study was much less than in the retrospective Kaiser Permanente study. Hydroxychloroquine blood levels in the upper tertile predicted retinopathy. Mean hydroxychloroquine levels likely better predict risk than the maximum level. Hydroxychloroquine blood levels would allow clinicians to either decrease the dose or increase monitoring in those with blood levels in the highest tertile. Currently, however, availability of hydroxychloroquine blood levels has been limited.
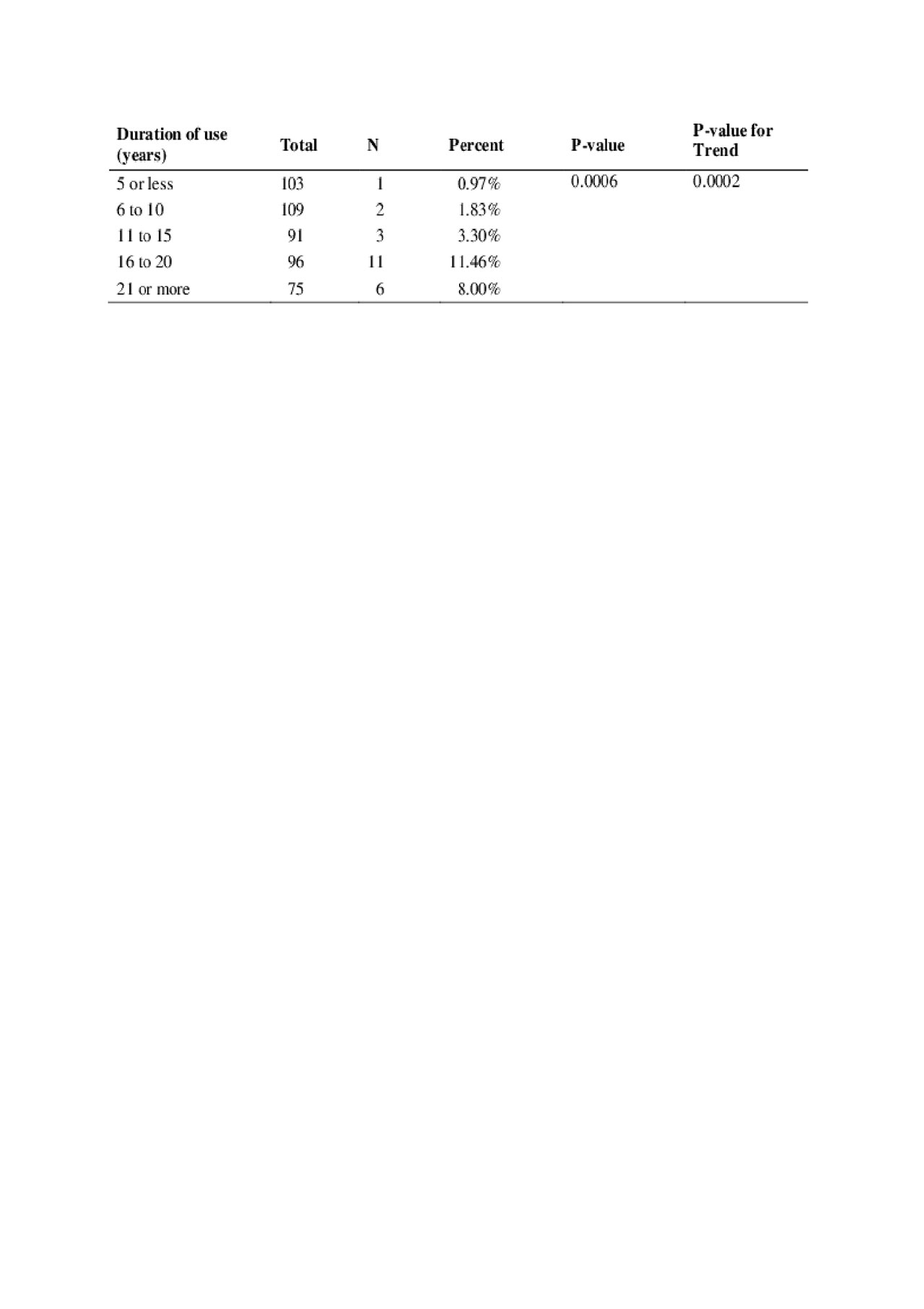
ACR 2019-Early Prediction of Hydroxychloroquine Induced Retinopathy in SLE-Table1
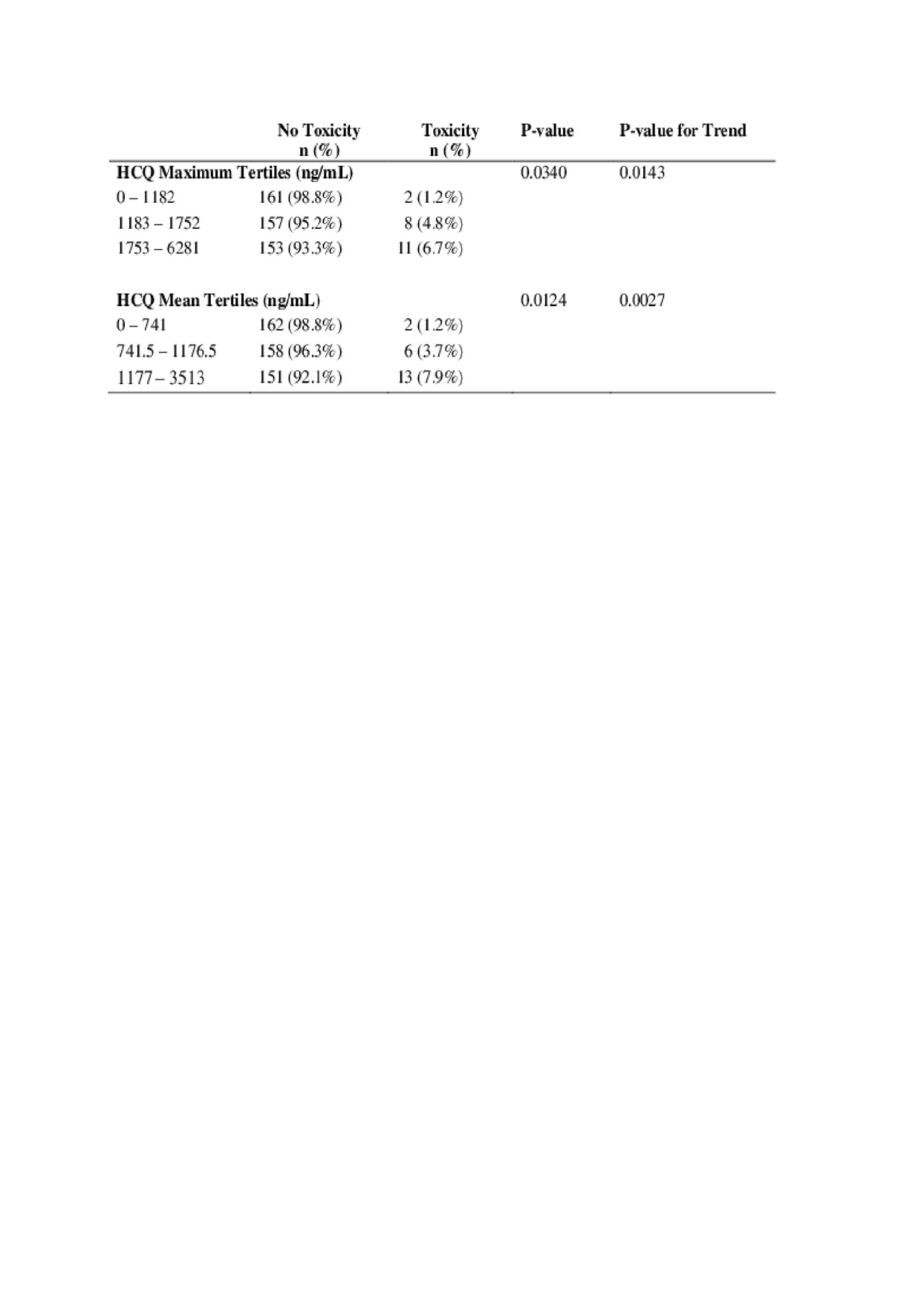
ACR 2019-Early Prediction of Hydroxychloroquine Induced Retinopathy in SLE-Table2
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Li J, Goldman D, Petri M. Frequency and Early Prediction of Hydroxychloroquine Induced Retinopathy in SLE [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/frequency-and-early-prediction-of-hydroxychloroquine-induced-retinopathy-in-sle/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/frequency-and-early-prediction-of-hydroxychloroquine-induced-retinopathy-in-sle/
