Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: A study of patients with RA at their first visit to an academic rheumatology site indicated an unexpected observation that 75% of patients had a history of prior treatment with either glucocorticoids or disease modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) agents, while only 25% were DMARD-naïve (1). Therefore, we analyzed a hypothesis that DMARD-naïve RA patients would have greater improvement from first visit to 6-month follow-up visit than patients who had prior treatment, according to MDHAQ/RAPID3 (multidimensional health assessment questionnaire/routine assessment of patient index data3) scores.
Methods: The first visit of all RA patients (by ICD codes) to one site that occurred between 5/2011-2/2017 was identified by retrospective chart review. All patients with all diagnoses complete MDHAQ/RAPID3 at all visits. RAPID3 (0-30) is the sum of 3 0-10 scores for physical function, pain visual analog scale (VAS), and patient global assessment VAS; severity categories are ≥12=high, 6.1-12= moderate, 3.1-6= mild, ≤3= remission. Patients who had a complete MDHAQ/RAPID3 at first visit and 6-month follow-up visit were classified into 3 groups on the basis of prior DMARD therapy: 1)“DMARD-naïve” – no glucocorticoid or DMARD; 2) “active DMARD”- had DMARD therapy within previous month; 3)“DMARD-interrupted” – had prior DMARD therapy interrupted for > 1 month. Mean MDHAQ/RAPID3 and individual RAPID3 component scores within each of the 3 groups were compared at first and 6-month follow-up visits for possible change using paired t tests. Differences between the 3 groups in changes over 6 months were compared using analysis of variance (ANOVA).
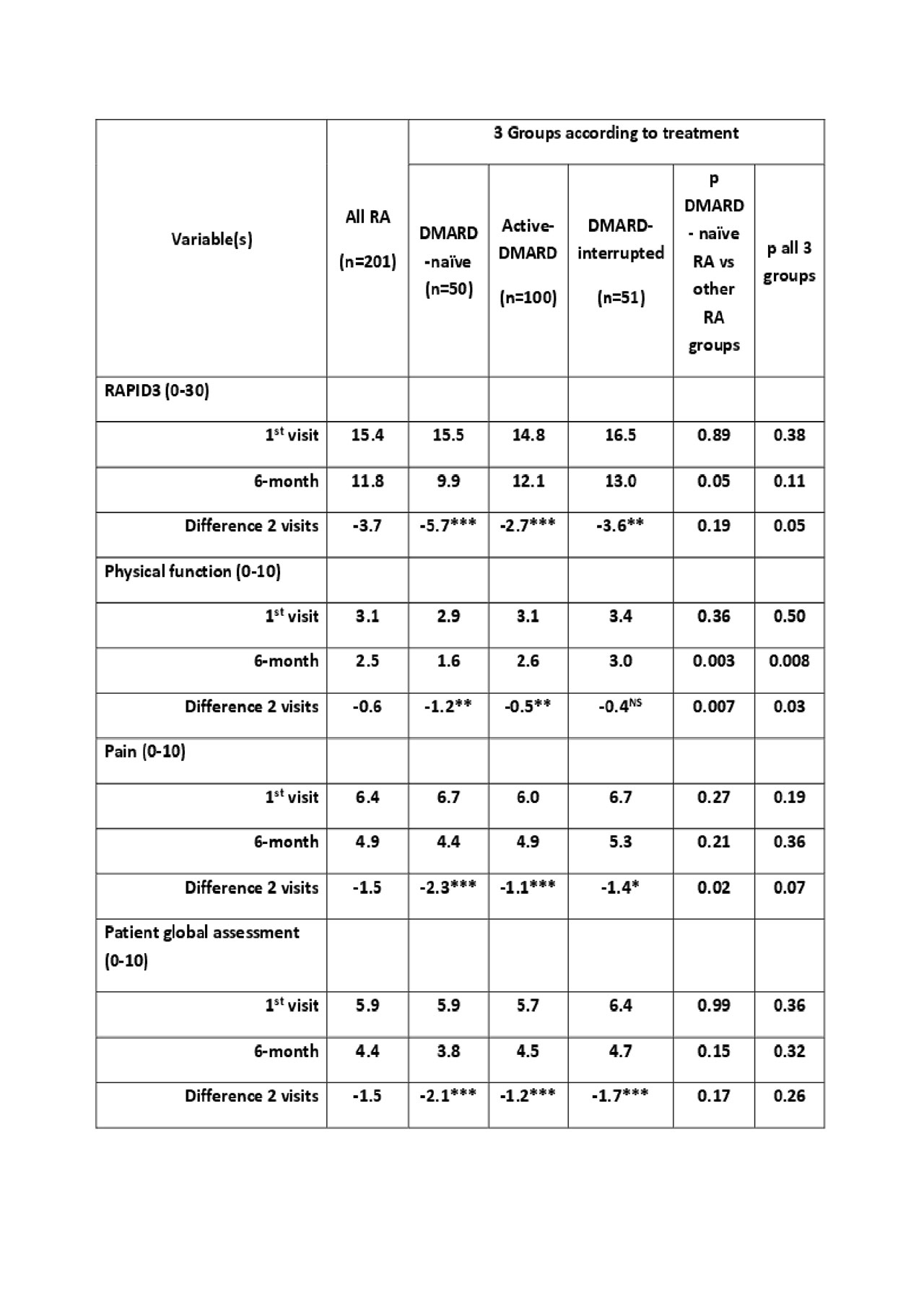
Results: Demographic data for age, sex, ethnicity, level of formal education, as well as body mass index, did not differ significantly in the 3 RA groups. Median disease duration was 1 year in DMARD-naïve patients, 2 years in active-DMARD, and 5 years in DMARD-interrupted patients (p=0.006). Mean MDHAQ/RAPID3 scores were 15.5 in DMARD-naïve, 14.8 in active-DMARD, and 16.5 in DMARD-interrupted patients, all indicating high severity (≥12) – no clinically or statistically significant differences. At 6-months follow up, MDHAQ/RAPID3 was improved in all RA groups, -5.7 in the DMARD-naïve group vs -2.7 in the active DMARD group vs -3.6 in the DMARD-interrupted group (p=0.05), also reflected in the RAPID3 component scores (Table). The difference in the DMARD-naïve group, but not the other groups, exceeded the minimum clinically important improvement (MCII) criterion of 3.8 for MDHAQ/RAPID3, which was almost met in the DMARD-interrupted group, but not in the active-DMARD group.
Conclusion: Patients with RA improved with treatment from first visit to 6 months later, greatest in DMARD-naïve, less in DMARD-interrupted, and least in the active-DMARD group. The similarity of MDHAQ/RAPID3 scores at baseline of DMARD naïve to those of previously-treated patients suggests that “treat-to-target” appears poorly implemented in routine clinical care. The data appear to reinforce the importance of early treatment for optimal control of RA.
References: 1 -Chua et al, Arth Rheum, in press
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Pincus T, Chua j, Block J, Castrejon I. DMARD-naïve Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) Patients Have Greater RAPID3 Improvement over 6 Months After 1st Visit Than Patients Who Were Treated Previously Treated with DMARDs, Although Baseline RAPID3 Was Similar: The Importance of Early Treatment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dmard-naive-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-patients-have-greater-rapid3-improvement-over-6-months-after-1st-visit-than-patients-who-were-treated-previously-treated-with-dmards-although-baseline-rapid3-was/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/dmard-naive-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra-patients-have-greater-rapid3-improvement-over-6-months-after-1st-visit-than-patients-who-were-treated-previously-treated-with-dmards-although-baseline-rapid3-was/