Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: Miscellanous Rheumatic & Inflammatory Disease Poster III: Autoimmune Conditions and Therapies
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients present high cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality. International guidelines suggest estimating CV-risk in these patients, but no indications about the strategy to use are specified. This multicentre cross-sectional study aimed to investigate the performance in real-life setting of three different 10-years CV-risk estimating algorithms in SLE and RA.
Methods: Data of 989 patients with SLE (140 patients; female 85.7%; age 40±16 years; disease duration 155±106 months) and RA (849 patients; female 79.3%; age 61±12 years; disease duration 133±110 months), according to specific classification criteria, were collected since January 2019 in 10 rheumatologic University Hospitals. Clinical and laboratory parameters were registered, and individual CV-risk was calculated using the “Progetto Cuore”, QRisk3 and Reynolds risk scores (RRS), as stated by suitable algorithms. Statistical analysis was performed with appropriate tests using the Statistical System Prism (Graphpad Instat 6.0 – San Diego CA-USA).
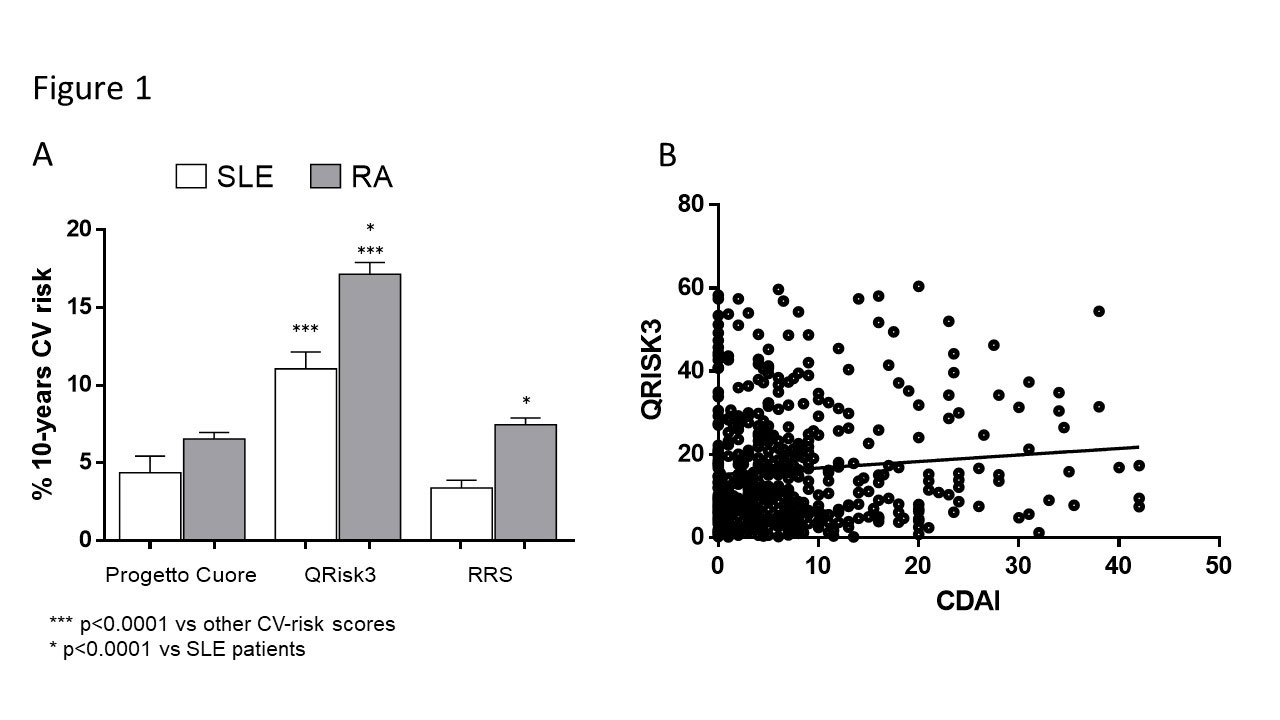
Results: Fifty-six (6.6%) RA and 14 (10%) SLE patients had experienced a previous CV event (mainly myocardial- infarction). Among traditional CV-risks RA patients were significantly older (p< 0.0001), hyperlipidaemia was more prevalent in RA then SLE (57.8% vs 37.1%; p< 0.001), and similar prevalence of hypertension and diabetes was recorded. Mean BMI was not significantly different between groups, nevertheless a BMI >25 Kg/m2 was more prevalent in RA than SLE (47.8% vs 14.2% – p< 0.0001). RA patients were more frequently smokers (23.7% vs 13.6% – p=0.007). C-reactive protein was significantly higher in RA compared to SLE patients (6.8±1.1 vs 3.8±0.4 mg/l – p=0.01). Median (IQR) CDAI and SLEDAI were 7 (3-12) and 2 (0-2) in RA and SLE, respectively, and low-disease or remission according to CDAI (< 10) and SLEDAI (< 4) was similar. Sixty-eight percent of SLE patients were on a mean prednisone-dose of 5.9±2.6 mg/day whereas 41% of RA patients took 5.0±2.8 mg/day of prednisone (p< 0.01). All SLE patients were on hydroxychloroquine, 78 (55.7%) were co-treated with an immunosuppressant agent and 9 (6.4%) with belimumab or rituximab. Seventy percent of RA patients were on csDMARDs, mainly methotrexate, and 49.5% used also a biologic agent. CV-risk with QRisk3 results 2 to 3-fold higher compared to RRS and “Progetto Cuore” score in both patient groups. Moreover, QRisk3 and RRS resulted significantly higher in RA compared to SLE (Figure1A). Interestingly, only in RA a positive correlation between CDAI and QRisk3 (r=0.1; p=0.03) was detected (Figure1B).
Conclusion: This multicentre study showed a different performance in SLE and RA patients of the commonly used algorithms to estimate CV-risk in clinical practice. With a good disease activity control, traditional CV-risk factors may differently impact on predictable CV-risk using the “Progetto Cuore” scores, QRisk3 or the RRS. These findings should be considered when CV-risk is estimated routinely in such patients.
B. Correlation between CDAI and QRisk3 score in RA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cacciapaglia F, Erre G, Sakellariou G, Viapiana O, Piga M, Bartoloni E, Manfredi A, Colella S, Castagna F, Cafaro G, Dessì M, Fornaro M, Giollo A, Grignaschi S, Vacchi C, Spinelli F, Atzeni F, Gremese E. Cardiovascular Risk Evaluation in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Preliminary Results from the “Cardiovascular Obesity and Rheumatic DISease (CORDIS)” Study Group of the Italian Society of Rheumatology [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cardiovascular-risk-evaluation-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-and-rheumatoid-arthritis-preliminary-results-from-the-cardiovascular-obesity-and-rheumatic-disease-cordis-study-grou/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/cardiovascular-risk-evaluation-in-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-and-rheumatoid-arthritis-preliminary-results-from-the-cardiovascular-obesity-and-rheumatic-disease-cordis-study-grou/