Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Fungal infections are an important cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with rheumatic diseases. Invasive aspergillosis (IA) is a fungal infection potentially fatal, which has been primarily described in patients with profound neutropenia such as those with hematologic malignancies. There is limited information in patients with rheumatic diseases. We describe herein clinical characteristics and outcomes of IA diagnosed in patients with rheumatic diseases.
Methods:
At first, we identified from microbiological records of a national referral center for rheumatic diseases, patients with Aspergillus spp. isolated and/or positive galactomannan (January 2014-December 2018); then patients with a defined rheumatic disease were selected. The charts from all the patients were reviewed and they were classified as with proven or probable IA according the EORTC/MSG criteria or putative IA with modified AspICU algorithm. In addition, relevant demographic, clinical, treatment (in previous three months) and laboratory characteristics were obtained, including the disease activity status and its severity. Descriptive statistics was used along with multivariate analysis to investigate 6-weeks mortality predictors.
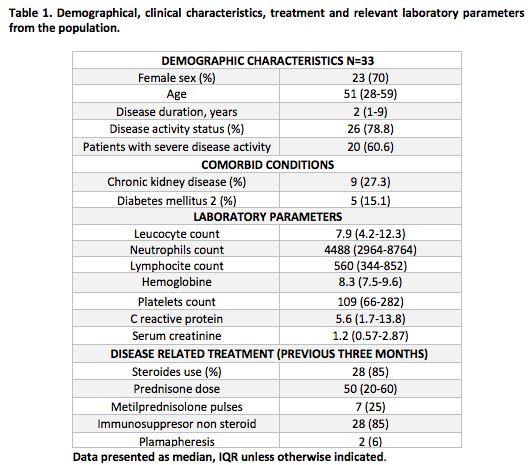
Results: Thirty-three patients with a rheumatic disease and IA were identified; of them, 14 patients (42.4%) had SLE, 9 (27.3) had polyangiitis with granulomatosis, 4 (12%) had dermatomyositis, 3 (9.1%) had RA, 2 (6%) had adult onset Still disease and 1 patient (3%) has primary antiphospholipid syndrome. The majority of the patients (29 [87.9%]) had probable IA, meanwhile, 3 (9%) had putative IA and 1 patient left (3%) had proven IA; also, 14 patients (42.4%) had a bacterial co-infection. Demographical, clinical characteristics, treatment and relevant laboratory parameters from the population are summarized in Table 1.
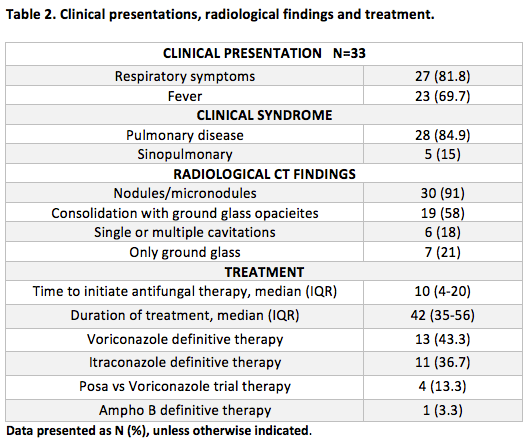
Table 2 summarizes IA clinical presentations, radiological findings and treatment. Fifteen (45.4%) patients had ≥1 culture with Aspergillus growth, the most frequent species were: A. fumigatus 10 /19 (53%), A. niger 3 (15.7%), A.flavus 1 (5%) and 5(26.3%) Aspergillus sp. Galactomannan antigen was tested on 27 (82%) of which 20/27 (74%) were positive: 14(70%) serum, 12(60%) in broncoalvoelar lavage samples and 3 cases had both.
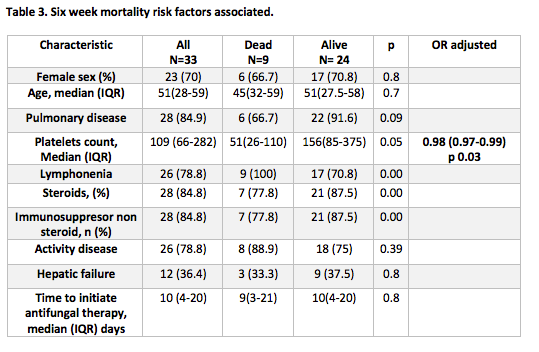
Six-week mortality was 27%. Table 3 summarizes risk factors associated to mortality. In the multivariate analysis platelets counts below 100.0 K/uL was the only risk factor identified.
Conclusion:
In this study we found specifics characteristics among the rheumatologic patients. The six week mortality of 27% was lower than has been reported in non neutropenic patients. Finally only thrombocytopenia was found as a risk factor of mortality in this group. It is necessary an increased knowledge of IA characteristics in these group of patients for early diagnosis and treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Guaracha-Basañez G, Román-Montes C, González-Lara M, Ponce-de-León A. Invasive Aspergillosis in Rheumatologic Patients in Tertiary Care Hospital in Mexico [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/invasive-aspergillosis-in-rheumatologic-patients-in-tertiary-care-hospital-in-mexico/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/invasive-aspergillosis-in-rheumatologic-patients-in-tertiary-care-hospital-in-mexico/