Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster III: OA, Gout, & Other Diseases
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Big data are defined as data sets that are too large or complex for traditional data-processing application software to adequately deal with. Artificial Intelligence (AI) includes various statistical techniques which can deal with big data. The current use of these concepts in publications related to rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs) is unknown. Therefore, the aim of this literature review was to assess the current use of big data and AI in the field of RMDs.
Methods: A systematic literature review was performed in PubMed MEDLINE in November 2018, with key words referring to big data, artificial intelligence and RMDs. All original reports published in English were analyzed. A mirror literature review was also performed outside of RMDs on the same number of articles. The number of data analyzed, data sources and statistical methods used (traditional statistics, AI or both) were collected. The analysis compared findings within and beyond the field of RMDs.
Results: Of 567 articles relating to RMDs, 55 met the inclusion criteria and were analyzed, as well as 55 articles in other medical fields. The mean year of publication was 2014 for the RMDs SLR, with 72% of the articles published between 2013 and 2018; whereas the articles included in the mirror non-RMD review were all published in 2018 or 2019. Among RMDs, the most represented fields were inflammatory joint diseases (N=22, 40%) and osteoarthritis (N=16, 29%). The 3 most represented diseases were: knee osteoarthritis (N=13, 24%), rheumatoid arthritis (N=12, 22%) and post-menopausal osteoporosis (N=6, 11%). Outside of RMDs, the most represented medical fields were: oncology (N=14, 25%), neurology (N=8, 15%), infectious diseases (N=6, 11%), ophtalmology (N=5, 9%) and psychiatry (N=5, 9%).
Only two articles in the field of RMDs (4%) and seven articles out of the field of RMDs (13%) mentioned a clear definition of big data. The mean number of data points was 746 million [range 2000–5 billion] in RMDs, and 9.1 billion [range 100,000 – 200 billion] outside of RMDs.
Data sources were varied: in RMDs, 26 (47%) were clinical, 8 (15%) biological and 16 (29%) radiological; whereas outside of RMDs, the distribution was quite homogenous between clinical, biological and imaging sources (respectively 31%, 31% and 29%).
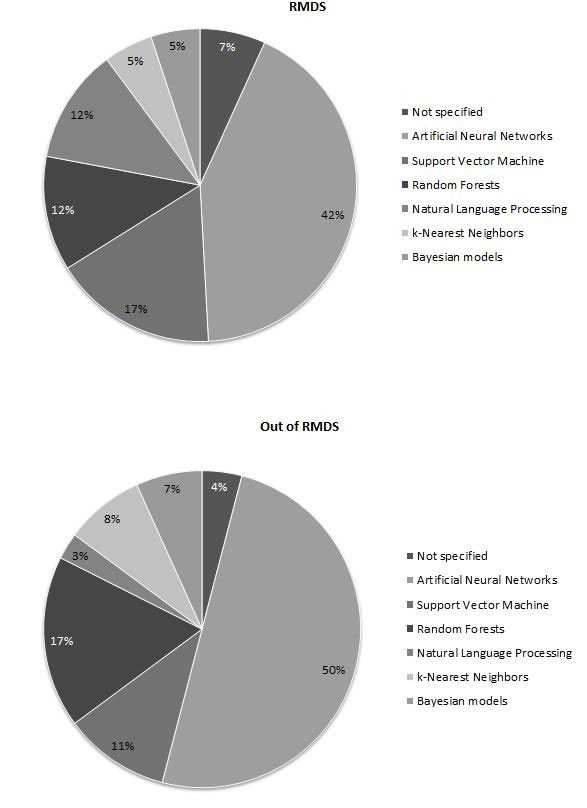
Both traditional and AI methods were used to analyze big data (respectively 10 (18%) and 45 (82%) in RMDs and 8 (15%) and 47 (85%) out of RMDs). Machine learning was used in almost all AI papers (44/45 in RMDs and 47/47 outside of RMDs), and among machine learning methods, the most represented was artificial neural network (20/44 in RMDs, and 24/47 out of RMDs). More details are provided in Figure 1.
Conclusion: Big data sources and types are varied within the field of RMDs, and methods used to analyze big data were heterogeneous. These findings informed a EULAR taskforce developing recommendations for big data in RMDs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kedra J, Radstake T, Pandit A, Baraliakos X, Berenbaum F, Finckh A, Fautrel B, Stamm T, Gomez-Cabrero D, Pristipino C, Choquet R, Servy H, Stones S, Burmester G, Gossec L. The Current State of Big Data Use and Artificial Intelligence in RMDs: A Systematic Literature Review Informing EULAR Recommendations [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-current-state-of-big-data-use-and-artificial-intelligence-in-rmds-a-systematic-literature-review-informing-eular-recommendations/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/the-current-state-of-big-data-use-and-artificial-intelligence-in-rmds-a-systematic-literature-review-informing-eular-recommendations/