Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Lupus nephritis (LN) is one of the most serious complication of SLE. The alteration of the structural protein in podocytes is known as a mechanism of proteinuria in LN. The signaling lymphocyte activation molecule family(the SLAM family) of typeⅠtransmembrane receptors consists of nine related members of the immunoglobulin superfamily and has been reported to mediate important regulatory signals between immune cells (Nat Rev Immunol. 2003 Oct;3(10):813-21).The 1q23 region on human chromosome 1 including the SLAMF cluster of genes, containing SLAMF6 has been identified as a lupus susceptibility locus(Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010 Jun;6(6):348-57). We sought to examine the functional role of SLAMF6 in lupus podocytes.
Methods: We evaluated the co-expression of nephrin, a podocyte marker and SLAMF6 in kidney of normal controls and LN patients, also in B6 and MRL/lpr mice by immunofluorescence analysis. We also examined nephrin positive SLAMF6 expression in isolated podocytes from B6 and MRL/lpr kidneys. Then, we analyzed the expression of SLAMF6 in CD4+T cells of isolated kidney and spleen in B6 and MRL/lpr mice. We treated human podocytes with IgG from healthy individuals and LN patients for 24 h and 48h and analyzed the expression of SLAMF6 by real-time PCR. We isolated podocyte from B6 and MRL/lpr mice by cell sorter, then extracted mRNA, and performed microarray analysis.
Results: In the histopathology, the expression of SLAMF6 was increased in LN patients and MRL/lpr mice compared to control. Although the expression of nephrin in MRL/lpr mice kidney at 16 wk old decreased compared to B6 mice at same age, the expression of SLAMF6 in podocytes increased in diseased MRL/lpr mice compared to B6 mice. Similarly, the expression of SLAMF6 in CD4+ T cells increased in diseased MRL/lpr mice kidney and spleen compared to B6 mice. The level of SLAMF6 mRNA elevated in human podocytes exposed to LN-derived IgG compared to healthy control derived IgG.
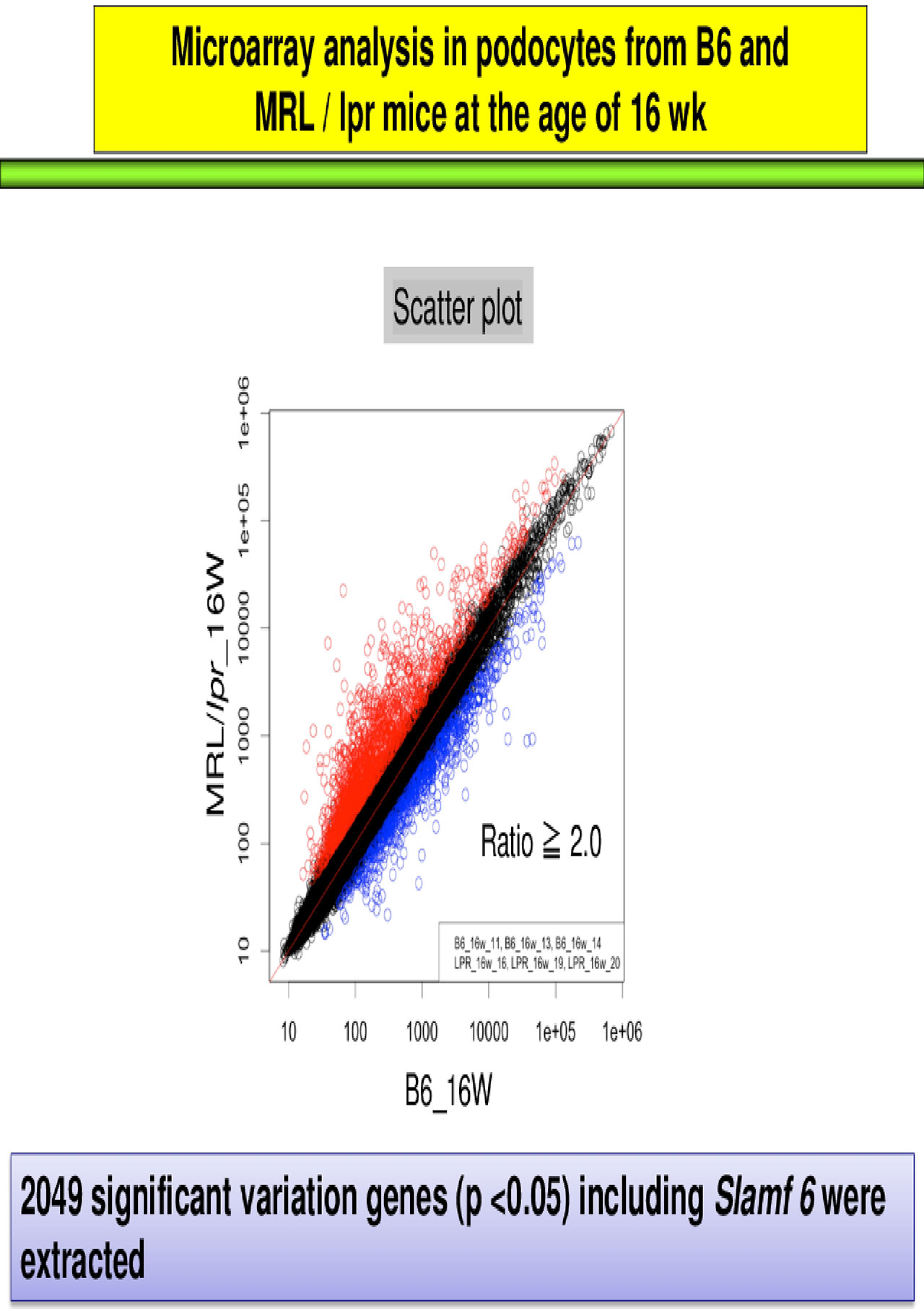
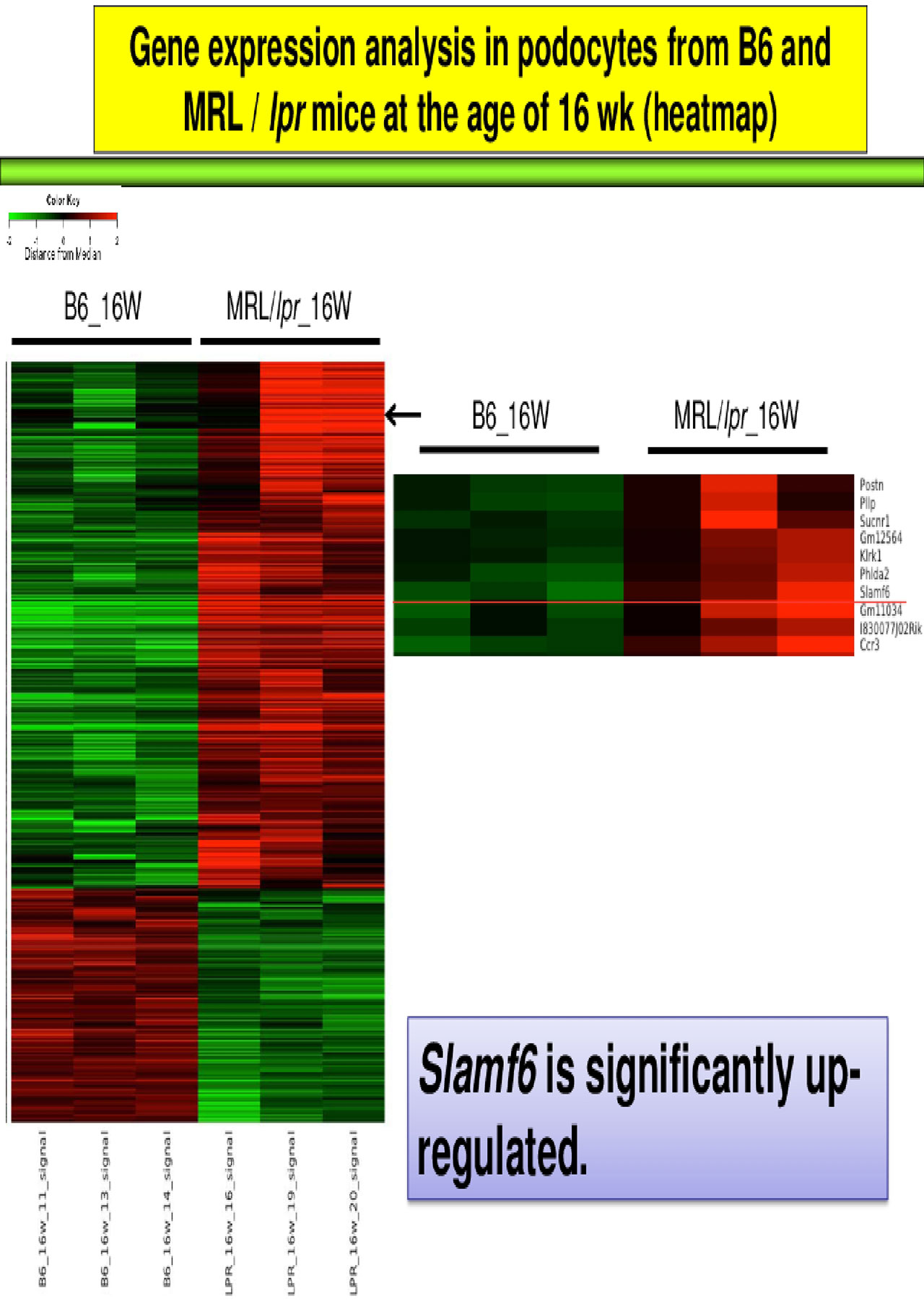
When an arbitrary difference of 2.0-fold (or greater) change was selected, 1420 genes were identified as being up-regulated and 629 as down-regulated in podocytes derived from MRL/lpr mice as compared to B6 mice (Figure 1). Above all, the expression level of SLAMF6 in podocytes was significantly increased in MRL/lpr mice (ratio 3.22, P=0.0017) (Figure 2). The expression of the gene encoding the adapter protein, which is required for SLAMF signal transduction, was also confirmed in mice, and the fluctuation of some genes was confirmed. We also confirmed a decrease in several podocyte-related genes including nphs1 (gene encoding nephrin) and an increase in apoptosis-related genes.
Conclusion: The expression of SLAMF6 is enhanced in LN podocytes, suggesting that the possibility of cooperating with CD4+T cells contributing to its dysfunction. Here, we compared the gene expression and signal transduction of podocytes in B6 mice and MRL /lpr mice by microarray. Further examination is needed to investigate in detail how SLAMF6 on downstream signals, specifically, the expression of nephrin and apoptosis markers are involved in the development of LN in the future.
MRL / lpr mice at the age of 16 wk
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Igawa T, Ichinose K, Umetsu A, Hara K, Nishihata S, Okamoto M, Endo Y, Tsuji S, Tsuji Y, Takatani A, Shimizu T, Sumiyoshi R, Koga T, Kawashiri S, Iwamoto N, Tamai M, Nakamura H, Origuchi T, Tsokos G, Kawakami A. Expression of SLAMF6 and Its Functional Significance in Podocytes of Lupus Nephritis: Report with Consideration Based on the Results of Microarray Analysis in Podocytes of MRL/lpr Mice [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/expression-of-slamf6-and-its-functional-significance-in-podocytes-of-lupus-nephritis-report-with-consideration-based-on-the-results-of-microarray-analysis-in-podocytes-of-mrl-lpr-mice/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/expression-of-slamf6-and-its-functional-significance-in-podocytes-of-lupus-nephritis-report-with-consideration-based-on-the-results-of-microarray-analysis-in-podocytes-of-mrl-lpr-mice/