Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The additional benefit of methotrexate as a concomitant treatment in PsA has not been fully elucidated. Observational data exist for concomitant methotrexate (MTX) use with TNF inhibitors (TNFi) and suggest no additional benefit. No real-world data currently exist for ustekinumab (UST). The objective of this study was to investigate the additive effect of MTX on the ability to reach composite treatment targets beyond monotherapy with UST or TNFi, as well as the ability to improve patient-reported outcomes in a real-world clinical setting in 8 European countries.
Methods: The PsABio study (NCT02627768) evaluates effectiveness, tolerability and persistence of 1st, 2nd or 3rd-line UST or TNFi in patients with PsA. Proportions of patients reaching minimal disease activity (MDA)/very low disease activity (VLDA) and clinical Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis (cDAPSA) low disease activity (LDA) or remission, as well as reaching the 12-item Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease questionnaire (PsAID-12) patient acceptable symptom state (PASS). Baseline (BL) and 6-month data were compared in patients receiving UST or TNFi in an intention to treat (ITT) analysis, including patients who switched/stopped original treatment during the 6-month observation period, who were imputed as non-responders. Logistic regression was used to assess the effect of concomitant conventional synthetic (cs)DMARD use within UST and TNFi cohorts adjusted for baseline PSAID-12, gender, smoking, number of comorbidities, steroid use, NSAID use, dactylitis, biologic (b)DMARD treatment line, BSA, enthesitis, PsA category. Comparison of the UST and TNFi treatment effect and the interaction with csDMARD co-therapy was done using logistic regression analysis that included propensity score (PS) to adjust for BL covariates age, gender, smoking, comorbidities, psoriasis BSA, PsA type, disease duration, cDAPSA, PsAID-12, enthesitis, dactylitis, Fibromyalgia Rapid Screening Tool (FiRST) score, line of bDMARD, csDMARD use, and steroid or NSAID use.
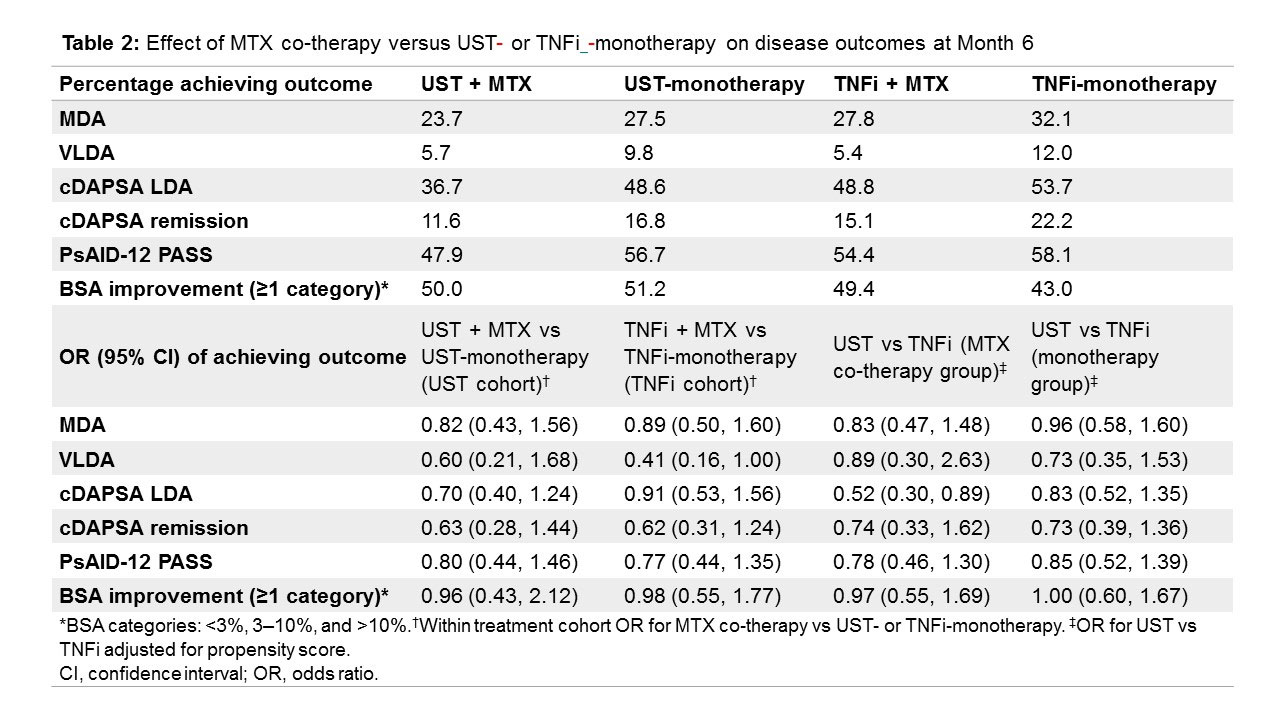
Results: Of 930 patients, data was available for 868 ITT patients (Table 1), including patients who had switched/stopped before 6 months (UST: n=28/426 [6.6%], TNFi: n=44/442 [10.0%]). For MDA assessment, 761 patients had data for both visits. Co-therapy with MTX did not increase the likelihood of achieving any of the outcomes in either the UST or TNFi cohorts (Table 2). After PS adjustment, co-treatment with MTX did not influence treatment effects differently when added to UST compared with TNFi. The concomitant use of any csDMARD or other csDMARDs apart from MTX yielded very similar results (data not shown).
Conclusion: In a real-world setting, concomitant treatment with MTX in addition to UST or TNFi was not associated with enhanced effects across a broad variety of disease outcomes, including disease activity, impact of the disease, and skin involvement within or between treatment cohorts, after PS adjustment for baseline confounders.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Siebert S, Gremese E, Bergmans P, De Vlam K, Joven-Ibáñez B, Katsifis G, Korotaeva T, Noël W, Selmi C, Sfikakis P, Smirnov P, Theander E, Nurmohamed M, Gossec L, Smolen J. Concomitant Treatment with Methotrexate Does Not Increase the Efficacy of Ustekinumab or TNF Inhibitors in Psoriatic Arthritis: Results from a Real-world, Multicenter Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/concomitant-treatment-with-methotrexate-does-not-increase-the-efficacy-of-ustekinumab-or-tnf-inhibitors-in-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-a-real-world-multicenter-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/concomitant-treatment-with-methotrexate-does-not-increase-the-efficacy-of-ustekinumab-or-tnf-inhibitors-in-psoriatic-arthritis-results-from-a-real-world-multicenter-study/