Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Enteropathic spondylitis (eSpA) is younger brother of spondyloarthritis, and the retention rate of biological DMARD in eSpA was not yet clear. The objective of this study was to assess anti-TNF response and retention rate in enteropathic spondylitis patients.
Methods: HUR-BIO (Hacettepe University Rheumatology Biologic Registry) is a prospective, single center database of biological treatments since 2005. Sacroiliitis was defined as modified New York criteria or based on magnetic resonance imaging. Enteropathic spondylitis was defined as inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and radiological sacroilitis with inflammatory back pain/spine symptoms. Demographic, clinical, laboratory, therapeutic data and imaging features were collected from this database: age, gender, age at disease onset, disease duration, type of IBD. Baseline disease activity before the first biologic DMARD initiation was assessed with BASDAI, BASFI, VAS-patient global assessment, ESR and CRP. Retention rates for first biologic DMARDs were assessed by Kaplan-Meier survival analysis. Anti-TNF response was defined as BASDAI50% improvement, ASAS partial remission, and ASAS 20% improvement.
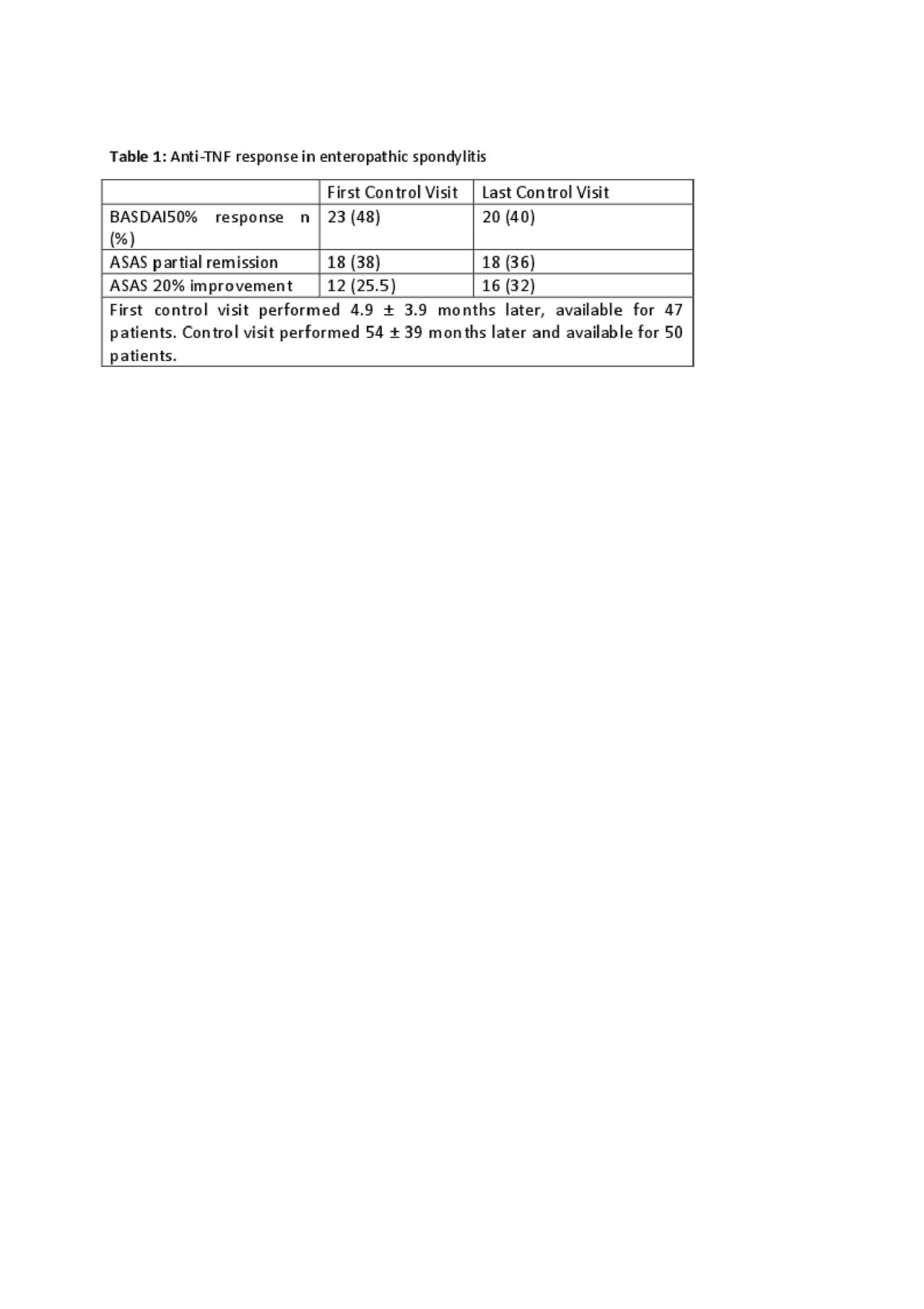
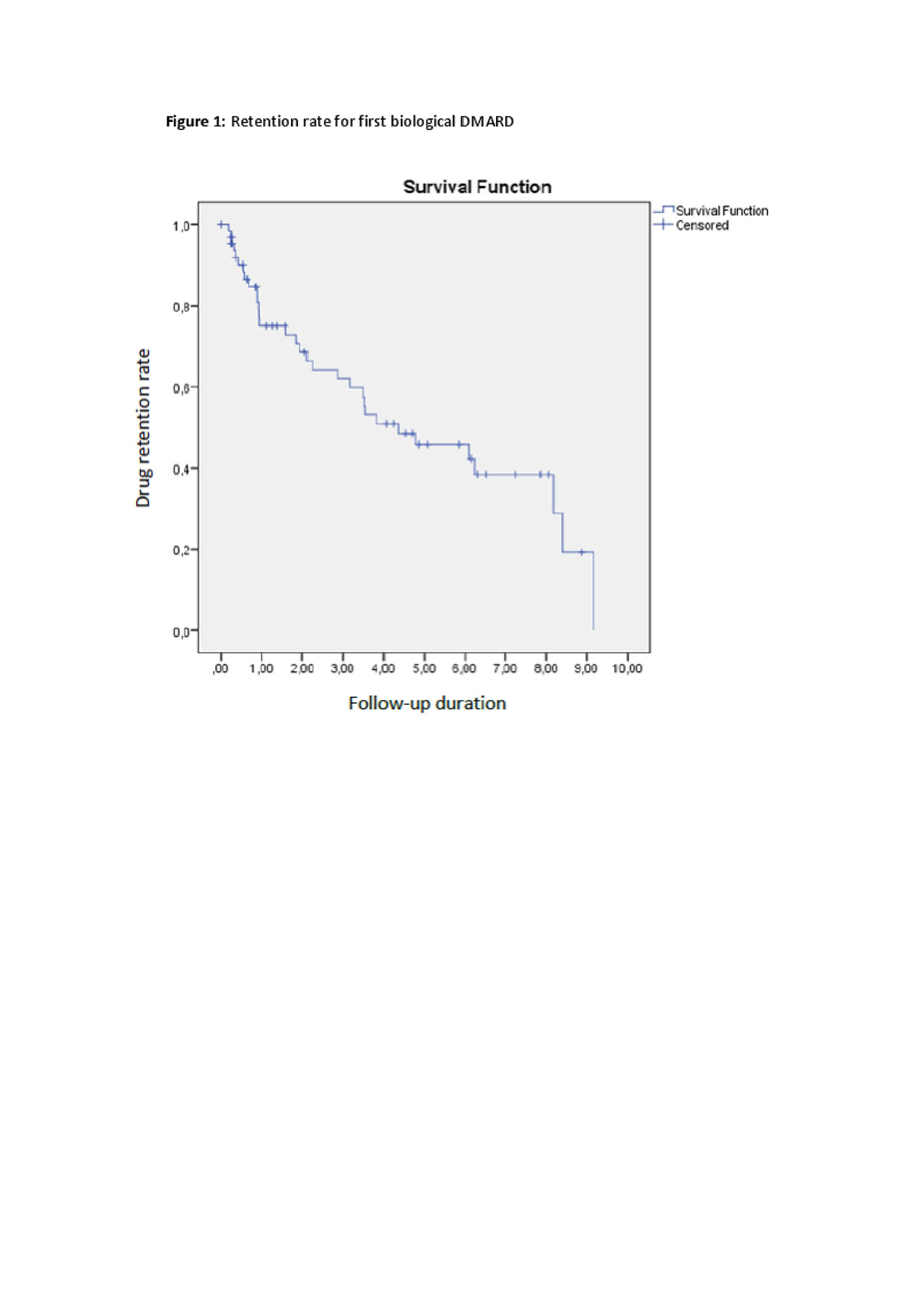
Results: HUR-BIO SpA registry included 2576 SpA patients, and 90 (3.5%) patients had enteropathic arthritis (EA). Sixty four (71.1%, 47% female) of 90 patients had sacroiliitis and those patients enrolled into analysis. Mean age was 45.0 ± 12.0 years, mean disease duration was 9.2 ± 6.9 years. Of the 64 eSpA, IBD type was ulcerative colitis (UC) in 34 (53%) patients, Crohn’s disease (CD) in 30 (47%) patients. Initial bDMARDs were infliximab 26 (40.6%), adalimumab 24 (37.5%), etanercept 9 (14.1%), golimumab 4 (6.3%) and certolizumab 1 (1.6%). Forty one (64.0%) out of 64 eSpA patients used concomitant cDMARDs. Baseline disease activity parameters were as follows; BASDAI 5.7 ± 2.1, BASFI 4.3 ± 2.7, patient global assessment-VAS 6 .0 ± 1.9, ESR 38 ± 27 mm/hour, and CRP 3.2 ± 3.6 mg/dl. Patients were followed mean 54 ± 39 months. First control visits were performed 4.9 ± 3.9 months later. Anti-TNF response rate were shown in table 1. The cumulative retention rate of the TNF inhibitors at 12-, 24-, 36-, 48-, and 60-months of follow-up visits were 75.1, 68.6, 62.0, 50.9, and 45.8%, respectively (Figure 1). No differences were identified according to the use of concomitant DMARDs (p = 0.393) or IBD type (p=0.144).
Conclusion: Retention rate for first TNF inhibitor was not different from other SpA subtypes in HUR-BIO registry (1). IBD subtype or concomitant synthetic DMARDs did not have effect on the retention rate of anti-TNF treatments. ASAS partial remission was achieved only one third of eSpA patients during follow-up.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yardımcı G, Farisoğulları B, Sarı A, Kilic L, Armagan B, Bilgin E, Bolek E, Karadag O, Akdoğan A, Apras Bilgen �, Ertenli A, Kiraz S, Kalyoncu U. Retention Rates and Response of Anti-TNF Treatments in the Enteropathic Spondylitis: HUR-BIO Real Life Results [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/retention-rates-and-response-of-anti-tnf-treatments-in-the-enteropathic-spondylitis-hur-bio-real-life-results/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/retention-rates-and-response-of-anti-tnf-treatments-in-the-enteropathic-spondylitis-hur-bio-real-life-results/