Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Secukinumab (SEC), a selective inhibitor of interleukin 17A, demonstrated rapid, significant, and sustained improvement in the signs and symptoms of PsA, with a favorable safety profile, in the phase 3 FUTURE studies (FUTURE 1–5).1-5 These studies were conducted in several countries worldwide, including the United States. We evaluated SEC treatment in the US patient (pt) subpopulation in these studies and report pooled efficacy findings for SEC vs placebo (PBO).
Methods: Data from US pts enrolled in FUTURE 2 (NCT01752634), 3 (NCT01989468), 4 (NCT02294227), and 5 (NCT02404350) were pooled and included in this hypothesis-generating analysis. These studies used approved SEC doses, with pts receiving SEC 300 or 150 mg with subcutaneous loading dose (LD), 150 mg without LD, or PBO. FUTURE 1 (NCT01392326) was excluded because pts received an intravenous LD, which is not approved for treating PsA. Assessments included ACR20/50/70 and additional disease activity and quality of life (QOL) outcome measures at week 16. Responses were calculated using nonresponder imputation. No adjustment was made for multiple comparisons.
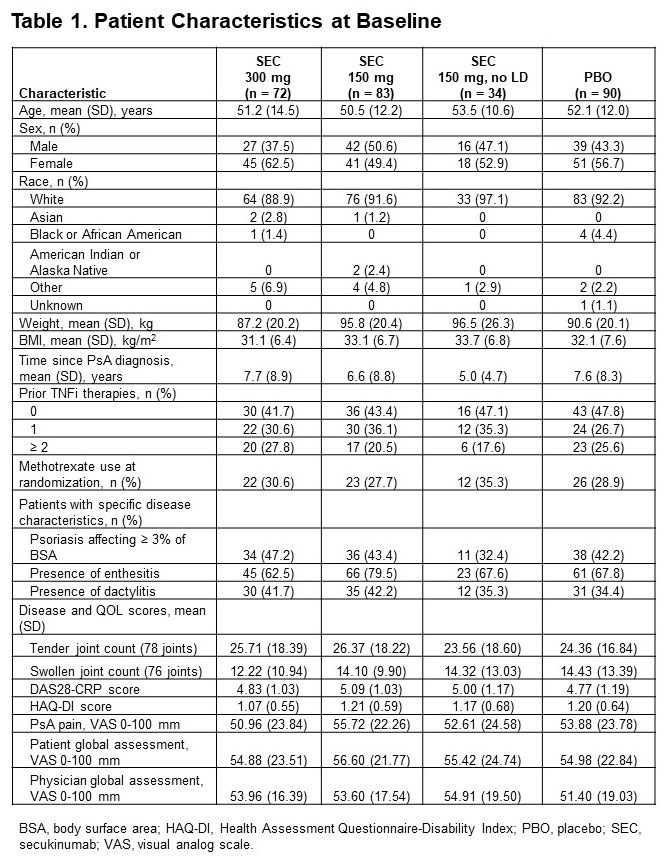
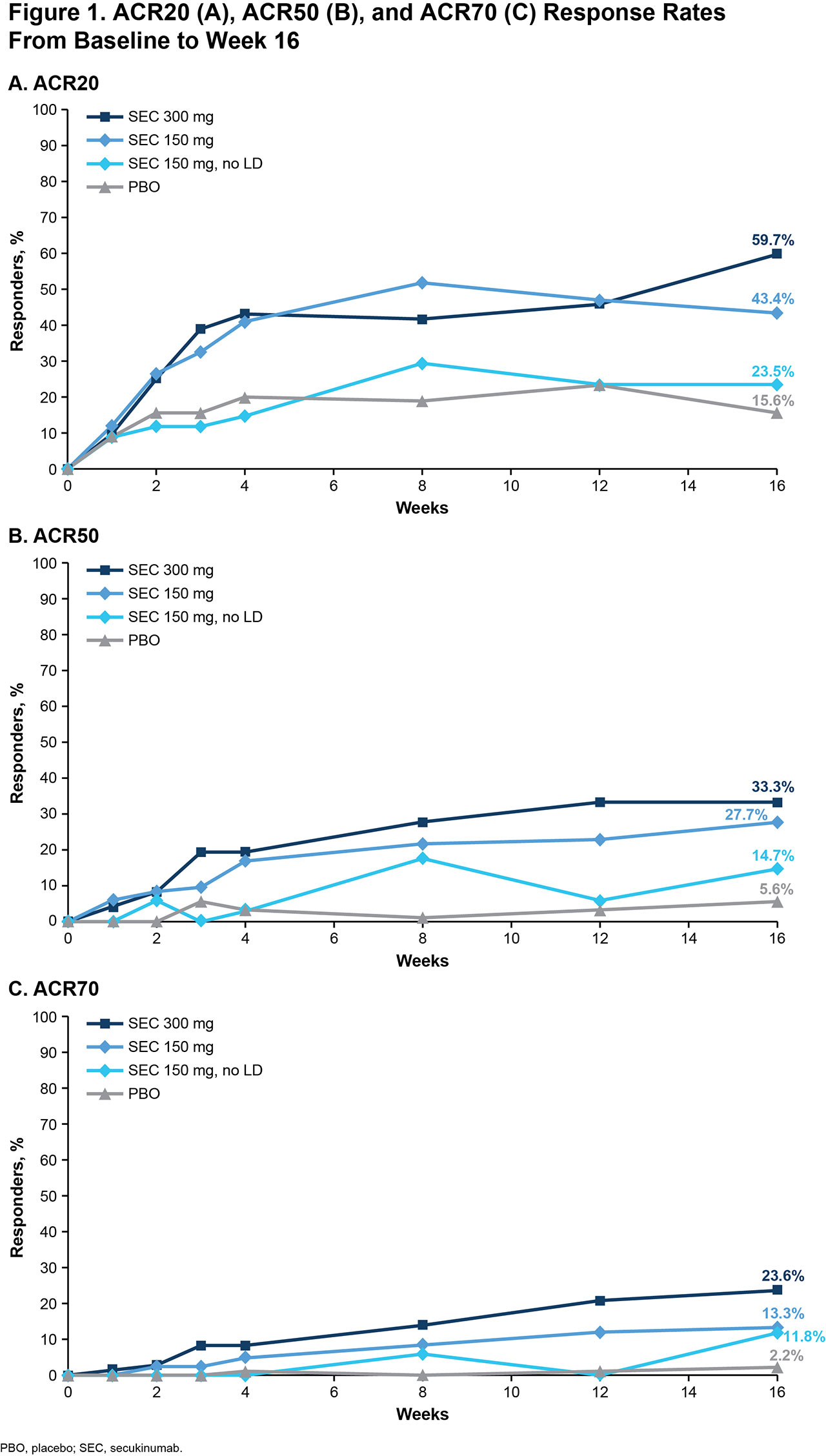
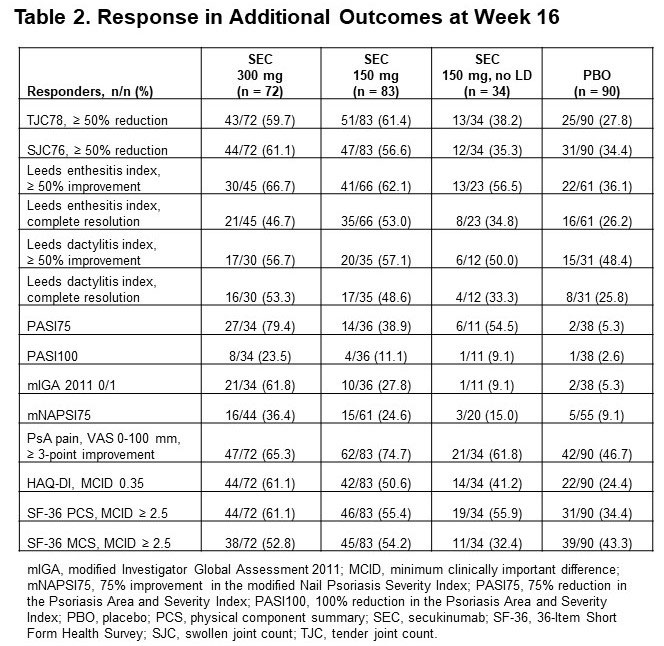
Results: Of 279 pts included in this pooled analysis, 72 were randomized to SEC 300 mg with LD, 83 to SEC 150 mg with LD, 34 to SEC 150 mg without LD, and 90 to PBO. Baseline characteristics were similar across treatment groups (Table 1). Most pts had a BMI of ≥ 30 kg/m2 and had been previously treated with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFis). At week 16, ACR20/50/70 response rates were numerically higher with all doses of SEC than with PBO; responses were seen as early as week 4 (Figure 1). SEC also improved other disease manifestations, including joint, skin, and nail disease, and various QOL measures; resolution of enthesitis and dactylitis was observed in approximately 50% of pts (Table 2). Overall, SEC 300 mg led to higher response rates than SEC 150-mg doses. SEC 150 mg with LD was associated with better response rates than that without LD.
Conclusion: SEC was efficacious in US pts with PsA, leading to rapid improvements in clinical endpoints and QOL. In general, US pts treated with SEC 300 mg achieved the highest response rates, including ACR50/70 response. SEC 150 mg also led to clinical benefits, with an LD regimen associated with higher response rates. Although US pts had high BMIs and a large proportion had been treated with ≥ 2 TNFis, response rates in these pts were similar to those seen in the overall pooled pt population.6,7 Our findings are consistent with those from previous studies and show that SEC is an effective treatment for pts with PsA.
References
- Mease PJ, et al. RMD Open. 2018;4:e000723.
- McInnes IB, et al. Lancet. 2015;386:1137-1146.
- Nash P, et al. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20:47.
- Kivitz A, et al. J Clin Rheumatol. 2018;24(suppl 3).
- Mease PJ, et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:890-897.
- Gottlieb AB, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(suppl 10) [abstract 2564].
- Orbai AM, et al. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018;70(suppl 10) [abstract 2562].
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kivitz A, Kremer J, Legerton C, Palmer J, Meng X, Pricop L, Singhal A. Efficacy of Secukinumab in a US Patient Population with Psoriatic Arthritis: A Subgroup Analysis of the Phase 3 FUTURE Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-secukinumab-in-a-us-patient-population-with-psoriatic-arthritis-a-subgroup-analysis-of-the-phase-3-future-studies/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/efficacy-of-secukinumab-in-a-us-patient-population-with-psoriatic-arthritis-a-subgroup-analysis-of-the-phase-3-future-studies/