Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In many countries, JAK-inhibitors (JAKi) have been recently accepted for the treatment of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, prescription patterns may differ notably between countries, which may influence effectiveness and safety analyses. The purpose of this study was to evaluate how and to whom JAKi are prescribed as a first investigation of an international collaboration of registers aiming at analysing the effectiveness and safety of JAKi.
Methods: Patients with diagnosis of RA, treated with either tofacitinib or baricitinib, and included in one of the registers participating in the JAK-pot collaboration registers (17 registers) were investigated. We used standard descriptive statistics to evaluate patient-, disease-, and treatment characteristics, as well as year of treatment initiation. Information on marketing and reimbursement date and national recommendations/guidelines were also retrieved using a questionnaire sent to a register representative in each country of the collaboration.
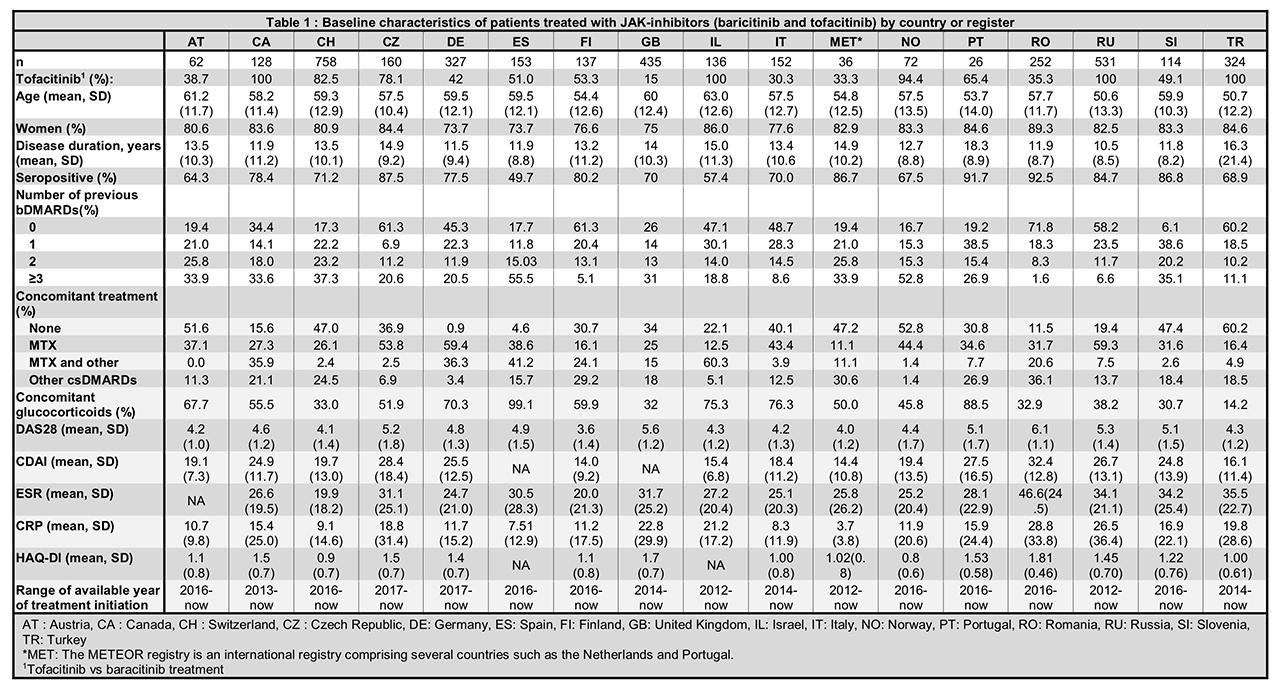
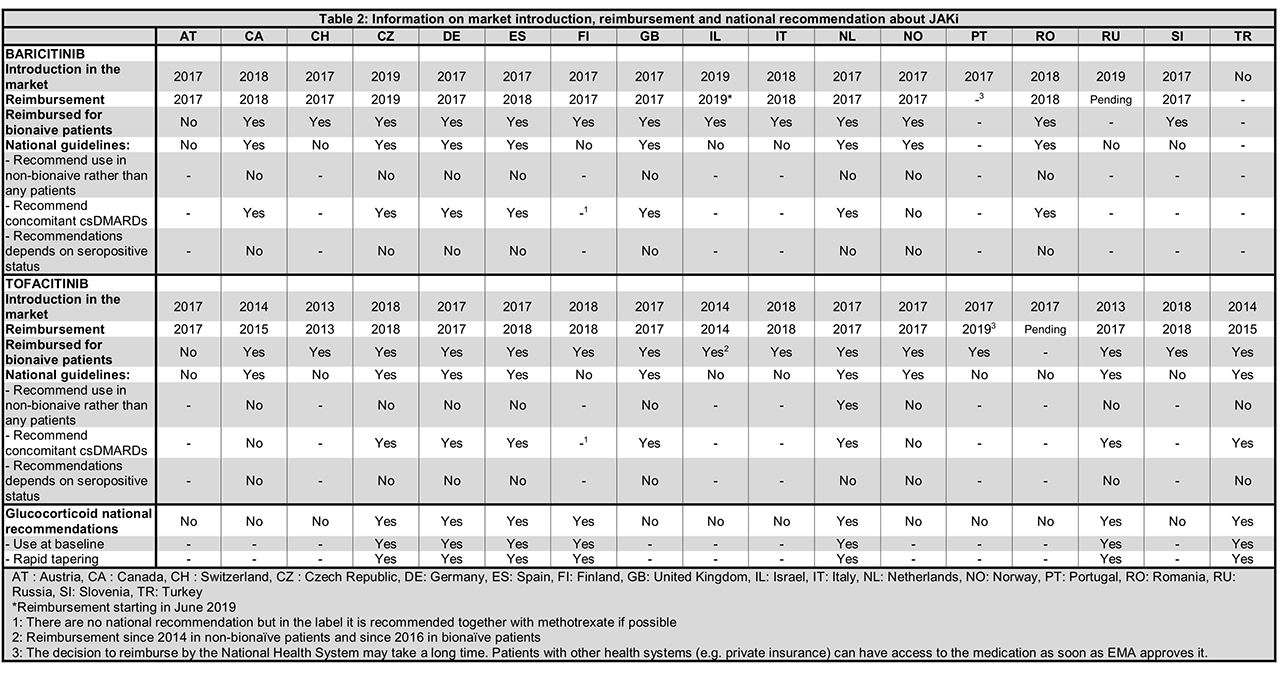
Results: A total of 3,804 patients initiating JAKi were included, with 4 countries having access only to tofacitinib (Table 1). Patients were on average >50 years old, with disease duration >10 years and mostly female. Patients generally had moderate to high disease activity (DAS28 > 3.2) at JAKi initiation, high levels of inflammatory markers and mild to moderate disability (Table 1). Seropositivity status (ACPA or RF) varied from 49.7 to 92.5% as could be expected since none of the countries had recommendations related to antibodies (Table 2). Treatment characteristics varied widely between countries: between 6.1 and 61.3% of patients had not received a previous bDMARDs (but only in one country JAKi was recommended only after failure of bDMARDs, Table 2); between 0.9 to 60.2% patients were prescribed JAKi as monotherapy; between 14.2 to 99.1% received concomitant glucocorticoids. Indeed, national recommendations on the use of concomitant csDMARD treatment varied by country (Table 2) but in every country, JAKi was prescribed after at least one csDMARDS failure. The first years of JAKi initiation in the registers ranged from 2012 to 2016 depending on the availability of this class of treatment (Tables 1 and 2). In some countries, compassionate use was possible before market availability.
Conclusion: JAKi were prescribed to a population that was similar in terms of age, gender, disease duration, disease activity and functional disability between countries, but differed greatly in terms of seropositivity, number of previous bDMARDs and use of csDMARD co-medication, which was not attributable to differences in national treatment recommendations. These differences must be taken into account when analyzing the real-life effectiveness and safety of JAKi across different countries and in collaborative studies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lauper K, Mongin D, Bergstra S, Choquette D, Codreanu C, Elkayam O, Hyrich K, Iannone F, Kristianslund E, Kvien T, Leeb B, Lukina G, Nordström D, Onen F, Pavelka K, Pombo-Suarez M, Rotar Z, Santos M, Strangfeld A, Courvoisier D, Finckh A. Heterogeneity in the Pattern of Use of JAK-inhibitors Between Countries Participating in an International Collaboration of Registers of Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients (the JAK-pot Study) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/heterogeneity-in-the-pattern-of-use-of-jak-inhibitors-between-countries-participating-in-an-international-collaboration-of-registers-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-the-jak-pot-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/heterogeneity-in-the-pattern-of-use-of-jak-inhibitors-between-countries-participating-in-an-international-collaboration-of-registers-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-the-jak-pot-study/