Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster II: Treatments, Outcomes, & Measures
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Baricitinib (BARI), a selective Janus kinase 1 and 2 inhibitor, is approved for the treatment of moderately-to-severely active RA in over 60 countries. In the RA-BEACON1 phase 3 trial, BARI 2-mg demonstrated clinical efficacy in patients (pts) with RA and an inadequate response to biologic DMARDs. The objectives of this analysis were to assess the response patterns to BARI 2-mg in the RA-BEACON trial and to describe the demographic and clinical characteristics for pts within each response pattern.
Methods: Observed data from all BARI 2-mg treated pts in the RA-BEACON trial (N=174) up to 24 weeks, protocol mandated rescue, treatment discontinuation, or loss to follow-up were included in the analysis. A Growth Mixture Model was used to classify the longitudinal disease patterns based on the time course of Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) improvement from week 0 to week 24. Baseline characteristics and disease measures were described between groups. The trajectories of HAQ-Disability Index (DI), pain, tender joint count (TJC), and swollen joint count (SJC) within each response pattern were also examined.
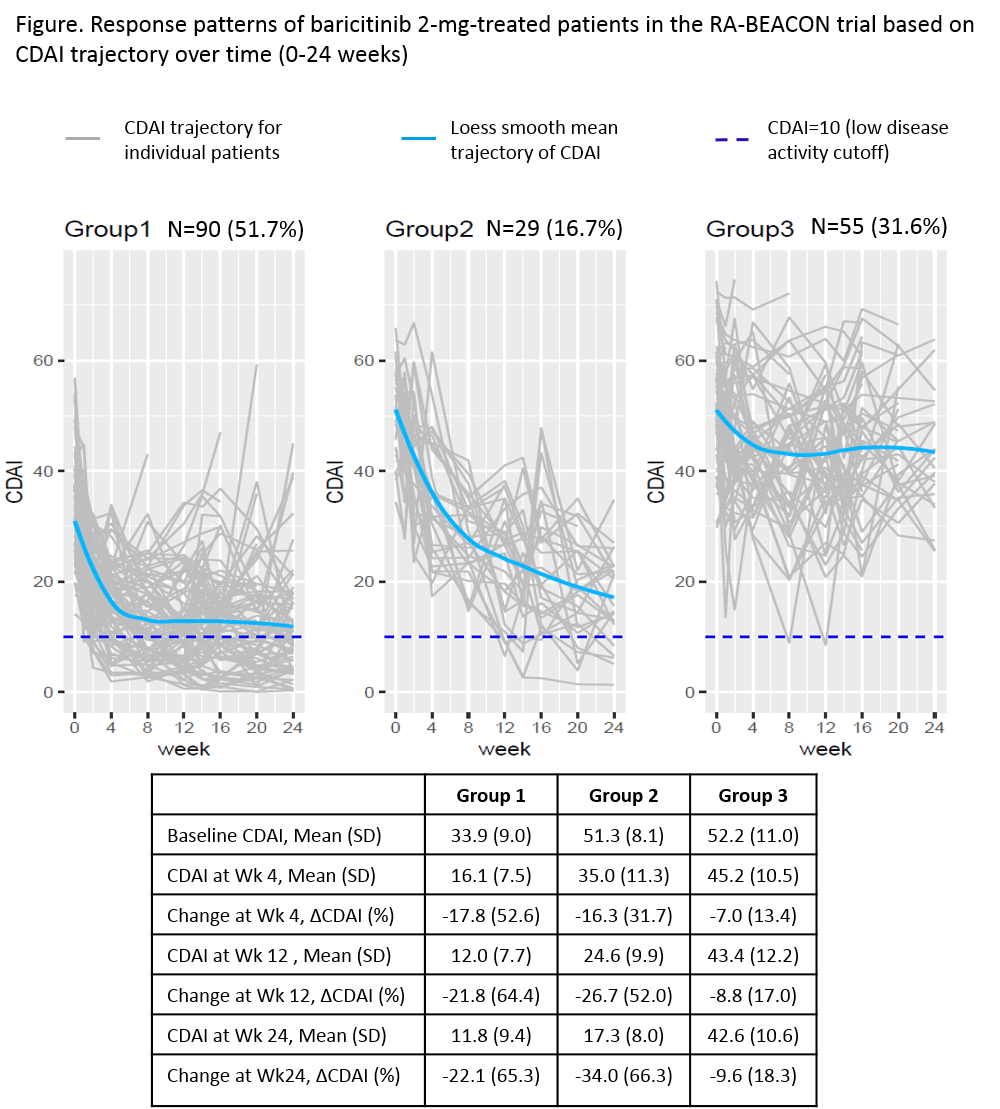
Results: BARI 2-mg treated pts were classified into 3 groups based on their CDAI trajectory patterns (Figure). Group 1 (n=90, 52%) had lower baseline CDAI (mean=34), achieved 53% improvement in group mean of CDAI at week 4 (change from baseline, ΔCDAI -18), 64% improvement at week 12 (ΔCDAI -22), and maintained similar improvement through 24 weeks. Group 2 (n=29, 17%) had higher baseline CDAI (mean=51), achieved 32% improvement in mean CDAI at week 4 (ΔCDAI -16) with greater improvement at week 12 (52%, ΔCDAI -27) and week 24 (66%, ΔCDAI -34). Group 3 (n=55, 32%) had a baseline CDAI (mean=52) similar to group 2, but had smaller improvement, achieving 18% improvement in CDAI (ΔCDAI -10) at week 24. The distributions of HAQ-DI, pain, TJC, and SJC within each response pattern showed a trajectory similar to the corresponding group CDAI trajectory. Baseline characteristics for these 3 groups are presented in Table 1. Compared to groups 1 and 2, group 3 had more pain, worse physical function (HAQ-DI), and a larger proportion of pts who used ≥3 bDMARDs at baseline.
Conclusion: There are three response patterns to BARI 2-mg treatment in the RA-BEACON trial. The majority of BARI 2-mg treated pts achieved good response (groups 1 and 2, 68%) with at least 50% improvement in CDAI by week 12. Response was observed as early as week 4 and was maintained or continued to improve in these groups through week 24. Pts with less response (group 3) tended to be more treatment experienced with more pain and worse physical function at baseline.
Reference: 1. Genovese MC et al. N Engl J Med 2016,374(13):1243-52; NCT01721044
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Genovese M, Weinblatt M, Wu J, Jia B, Quebe A, Sun L, Chen Y, Helt C, Bacani A, Reis P, Pope J. Patient Disease Trajectories in Baricitinib-2 Mg-Treated Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Inadequate Response to Biologic DMARDs [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-disease-trajectories-in-baricitinib-2-mg-treated-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-inadequate-response-to-biologic-dmards/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/patient-disease-trajectories-in-baricitinib-2-mg-treated-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-and-inadequate-response-to-biologic-dmards/