Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Uveitis often occur in women who are in their reproductive years. The management of uveitis during pregnancy is a challenge, making the physician to re-evaluate the patient’s current therapy and offer alternative options with the lowest risk to the patient and fetus. Certolizumab pegol (CZP) is a PEGylated Fc-free anti-TNF therapy that differs from others anti-TNF because it does no bind the neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn). Thus, CZP does not undergo across the placenta conferring a more secure profile. However, clinical data about the use of CZP in patients with uveitis during pregnancy are absence. Our aims were: a) to assess the evolution of uveitis in pregnant patients under treatment with CZP and b) to provide information on the pregnancy outcomes of women and neonates exposed to CZP.
Methods: National Multicenter study of 8 women with uveitis who received CZP during pregnancy and their 9 neonates who were exposed to CZP. The main visual outcomes were visual acuity (VA) and anterior chamber (AC) cells. We also assessed the presence of complications during pregnancy and labor, maternal and neonatal infections and malformations. Comparisons were made between baseline and the 1st week, 1st and 6th month and 1st year. (STATISTICA, StatSoft Inc. Tulsa, Oklahoma, USA).
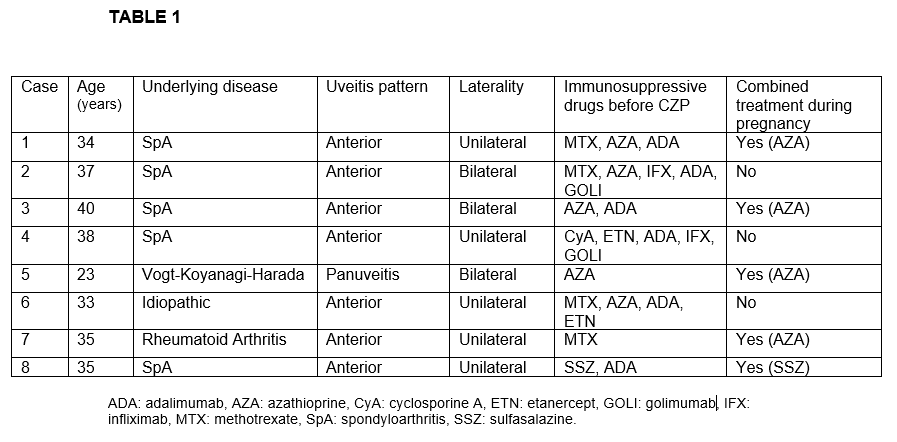
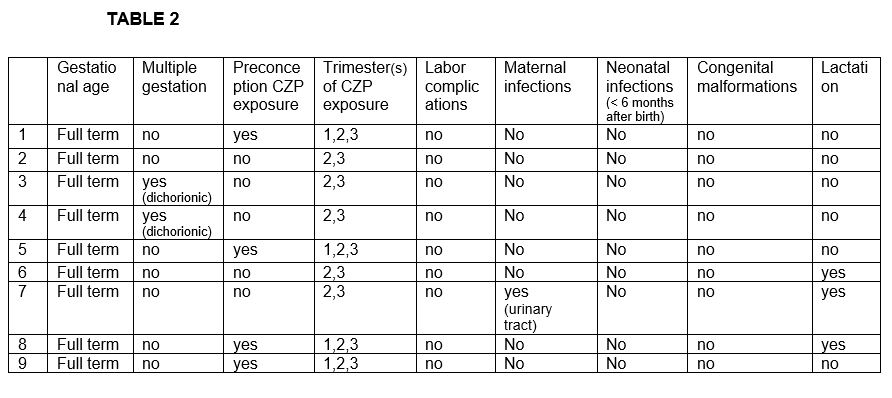
Results: We studied 8 women (11 affected eyes); mean age of 34.3 ± 5.1 years. The underlying diseases were spondyloarthritis (n=5), Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada (n=1), rheumatoid arthritis (n=1) and idiopathic (n=1). Before CZP treatment and besides oral corticosteroids, patients had received methotrexate (n=4), azathioprine (n=5), adalimumab (n=5), infliximab (n=2), golimumab (n=2), etanercept (n=2), sulfasalazine (n=1) and cyclosporine A (n=1). The characteristics of the 8 patients are shown in TABLE 1. Seven out of 8 patients had anterior uveitis while the remaining patient had panuveitis diagnosis. During CZP treatment we observed an improvement in the mean of VA [0.6±0.27 to 0.72±0.29; p= 0.14] and the mean of AC cells [2.25±1.28 to 0.33±0.08; p= 0.03] after 6 months of treatment. Pregnancy and neonatal outcomes are shown in TABLE 2. In half of the patients CZP was initiated before pregnancy. In the remaining patients CZP was initiated during the first trimester. No pregnancy nor labor complications were reported (pre-eclampsia, premature rupture of membranes, miscarriages or pre-term births). There was one case of multiple gestation (dichorionic). Cesarean delivery was reported in two patients. All neonates were healthy newborns with a mean birth weight of 3080±560 grams and a mean birth length of 50.9±2.8 cm. Fetal pH and APGAR score was normal in all of them. Three neonates received maternal lactation. In regard with infections, only one woman presented a mild urinary tract infection during pregnancy. No infections nor malformations were found in neonates after a follow-up of 6 months.
Conclusion: CZP seems to be effective and safe in patients with uveitis during pregnancy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
PRIETO- PENA D, Calvo Río V, Calderón-Goercke M, Maíz Alonso O, Jimenez-Aberasturi J, Veroz R, Blanco M, Santos J, Navarro F, Gallego A, Demetrio R, Martínez Taboada V, González-Gay M, Blanco R. Certolizumab Therapy in Patients with Uveitis During Pregnancy: Multicenter Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/certolizumab-therapy-in-patients-with-uveitis-during-pregnancy-multicenter-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/certolizumab-therapy-in-patients-with-uveitis-during-pregnancy-multicenter-study/