Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Early RA diagnosis and initiation of DMARDs following a treat-to -target approach is recommended to optimize remission outcomes. Several RA disease activity indices are commonly used in research and practice. The choice of index however, may impact treatment decisions and quality improvement (QI) program evaluations. Study objectives were to: 1) compare remission outcomes in the first year across 4 commonly used clinical disease activity indices; 2) estimate changes in remission over time across indices coinciding with release of RA best practice recommendations, and 3) identify predictors of persistent active disease across all measures.
Methods: Data were from patients with early RA (symptoms < 1 year, 100% Met ACR/EULAR RA criteria) enrolled in a prospective national ERA cohort study between Jan- 2007 and Mar-2018. Study participants had active disease at enrollment, were treated with DMARDs, and completed clinical evaluations, laboratory assessments and patient-reported outcomes every 3-months for the first 12-months of follow up. T-tests and chi-squared tests were used to compare patient characteristics, early treatment strategies, and remission outcomes using 4 commonly used clinical indices (DAS28< 2.6 OR DAS28CRP < 2.5, CDAI ≤ 2.8, SDAI≤ 3.3, and ACR/EULAR Boolean remission – SJC28, TJC28, CRP, PGA all ≦ 1). Logistic regression was used to identify predictors of persistent active disease across all measures by 12-months among baseline sociodemographic, RA clinical characteristics and patient-reported outcomes.
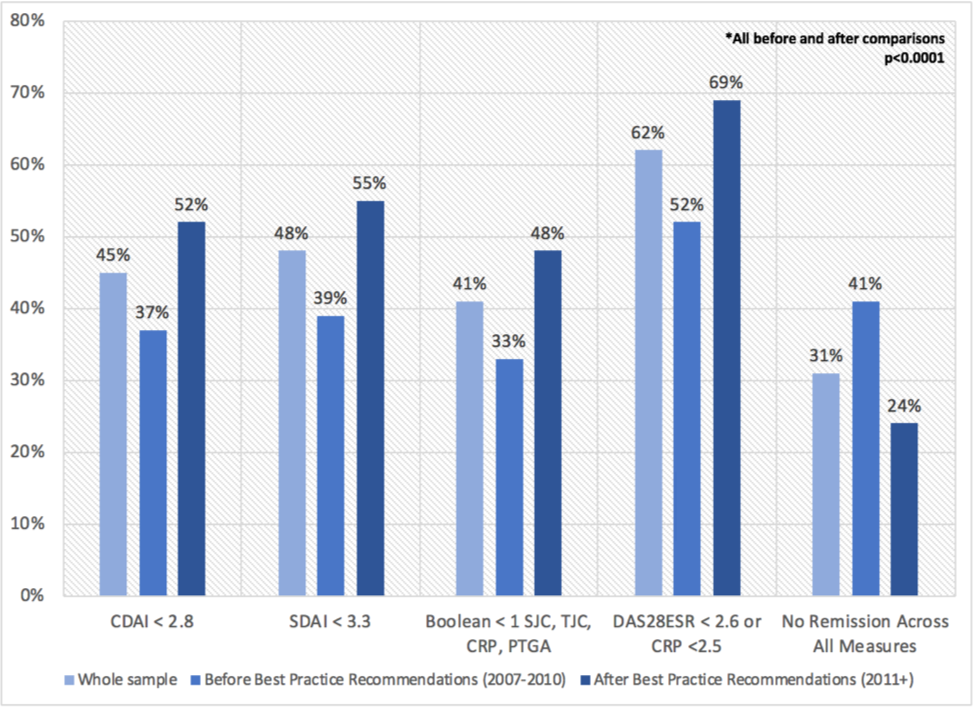
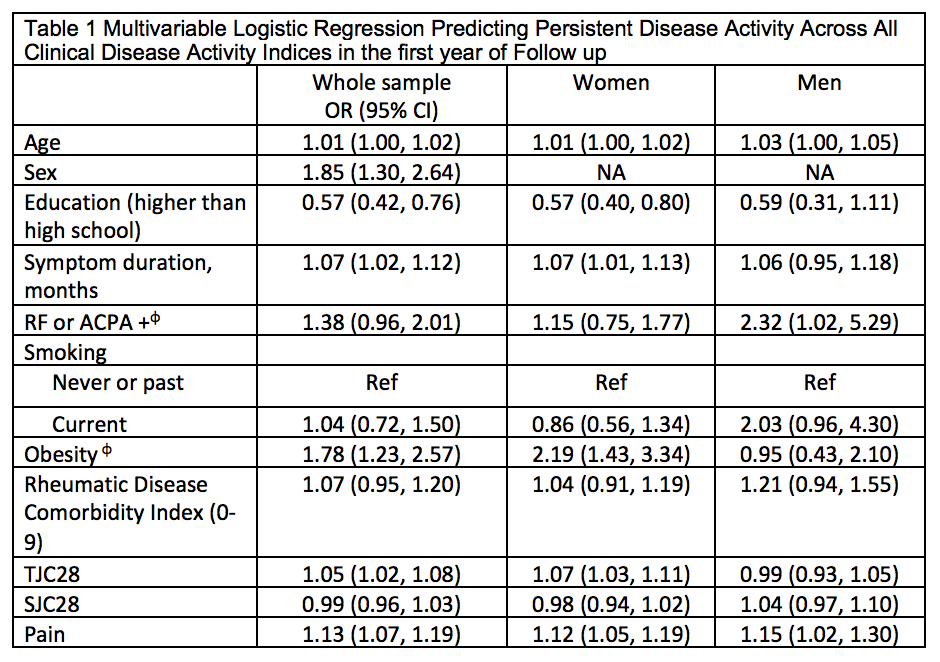
Results: Among 1202 adults eligible for this analysis, 877 (73%) were women, mean (sd) age was 55 (14), average disease activity was high across measures (DAS28 5.1 (1.4); CDAI 27 (14); SDAI 29 (15)) and majority (98%) were treated with csDMARDs +/- MTX. Remission by 12-months varied considerably across indices ranging from 33% to 62%, though improvement in remission before and after implementation of best practice recommendations was similar across all indices (~+15%) (Figure 1). 378 (31%) did not achieve remission across all indices. In adjusted logistic regression models, persistent active disease across indices was associated with baseline older age, female sex, longer symptom duration, positive serology, obesity, tender joints and higher pain (Table 1). In stratified analyses by sex, persistent active disease was more strongly associated with obesity and more tender joints in women, and positive serology and smoking in men.
Conclusion: The choice of index had a sizable impact on remission classification with important implications for decision-making surrounding treatment intensification in clinical practice. However all indices showed similar levels of improvement in remission before and after implementation of best practice recommendations suggesting that choice of index may be less important when evaluating QI programs. In the interim, in the absence of a single “best measure” that also takes in to account the patient’s perspective, study results looking across measures point to unmet needs for achieving remission in approximately 1 in 3 ERA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schieir O, Bartlett S, Valois M, Bessette L, Boire G, Hazlewood G, Hitchon C, Keystone E, Pope J, Thorne C, Tin D, Bykerk V, (CATCH) Investigators C. Real-World Remission Outcomes in the First Year Following RA Diagnosis Vary Considerably with the Disease Activity Index Used and a Sizable Proportion Have Persistent Active Disease Across All Measures: Results from the Canadian Early Arthritis Cohort (CATCH) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-remission-outcomes-in-the-first-year-following-ra-diagnosis-vary-considerably-with-the-disease-activity-index-used-and-a-sizable-proportion-have-persistent-active-disease-across-all-measure/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/real-world-remission-outcomes-in-the-first-year-following-ra-diagnosis-vary-considerably-with-the-disease-activity-index-used-and-a-sizable-proportion-have-persistent-active-disease-across-all-measure/