Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster II: Spondyloarthritis & Connective Tissue Disease
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) have vastly improved prognosis in patients with axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA). However, many patients treated with TNFi still fail to achieve a treatment target of remission. Hence, the aim of this study was to construct and validate a prediction model for achievement of Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) inactive disease (< 1.3) in bio-naive axSpA patients after 6 months of TNFi treatment.
Methods: Of the 14 registries in the EuroSpA Collaboration (1), 10 collected data on ASDAS and patients with a 6 months follow-up visit (time window 3-9 months) with registration of variables needed for ASDAS calculation constituted the study cohort. The study cohort was split by dividing 50% of patients from each individual registry into a derivation and validation cohort. Logistic regression analyses were used to identify conventional clinical variables (marked with bold in Table 1) associated with ASDAS < 1.3 at follow-up in the derivation cohort. Missing covariate data were imputed with Multiple Imputation with Chained Equations. Variables with a p-value < 0.25 in univariate analyses were included in the initial multivariable model. A priori it was decided to adjust for age, gender and country. Purposeful selection guided removal of variables from the multivariable model. Model fit was tested in the validation cohort by area under the Receiver Operating Curve (ROC) and misclassification error.
Results: Of the 25,988 axSpA patients in the EuroSpA database who started their 1st TNFi 7,396 had a relevant follow-up visit with registration of variables needed for ASDAS calculation. The study cohort had slightly higher disease activity at baseline than the patients without follow-up ASDAS assessment (Table 1). At 6 months, 2,203 patients (29.8%) of patients were in ASDAS inactive disease. Based on univariate analyses, all tested variables except concomitant csDMARDs were included in the initial multivariate model. During model fitting, time since diagnosis, smoking, VAS pain, VAS Global and Physician global were excluded. The final model demonstrated that HLA-B27 positivity, treatment start after 2015, moderately elevated CRP, low baseline BASDAI, low BASFI and low fatigue scores increased the probability of ASDAS inactive disease at 6 months (Table 2). The regression coefficients of the model were used to derive a prediction index for each patient in the validation cohort, determining their predicted probability of ASDAS inactive disease at 6 months. The ability of the model to correctly predict ASDAS inactive disease using different cut-offs for predicted probability are shown with the ROC (see Figure 1). The fit was deemed reasonable (median area under the curve 0.74, misclassification error 0.26).
Conclusion: A clinical prediction model for ASDAS inactive disease after 6 months of TNFi treatment was constructed correctly identifying 3 out of 4 patients as responders/non-responders. Future studies should investigate the potential of improving the model by addition of imaging and soluble biomarkers.
Acknowledgements:
Novartis Pharma AG and IQVIA for supporting the EuroSpA collaboration.
References:
- Brahe et al. Arthritis Rheumatol.2018;70 (suppl 10).
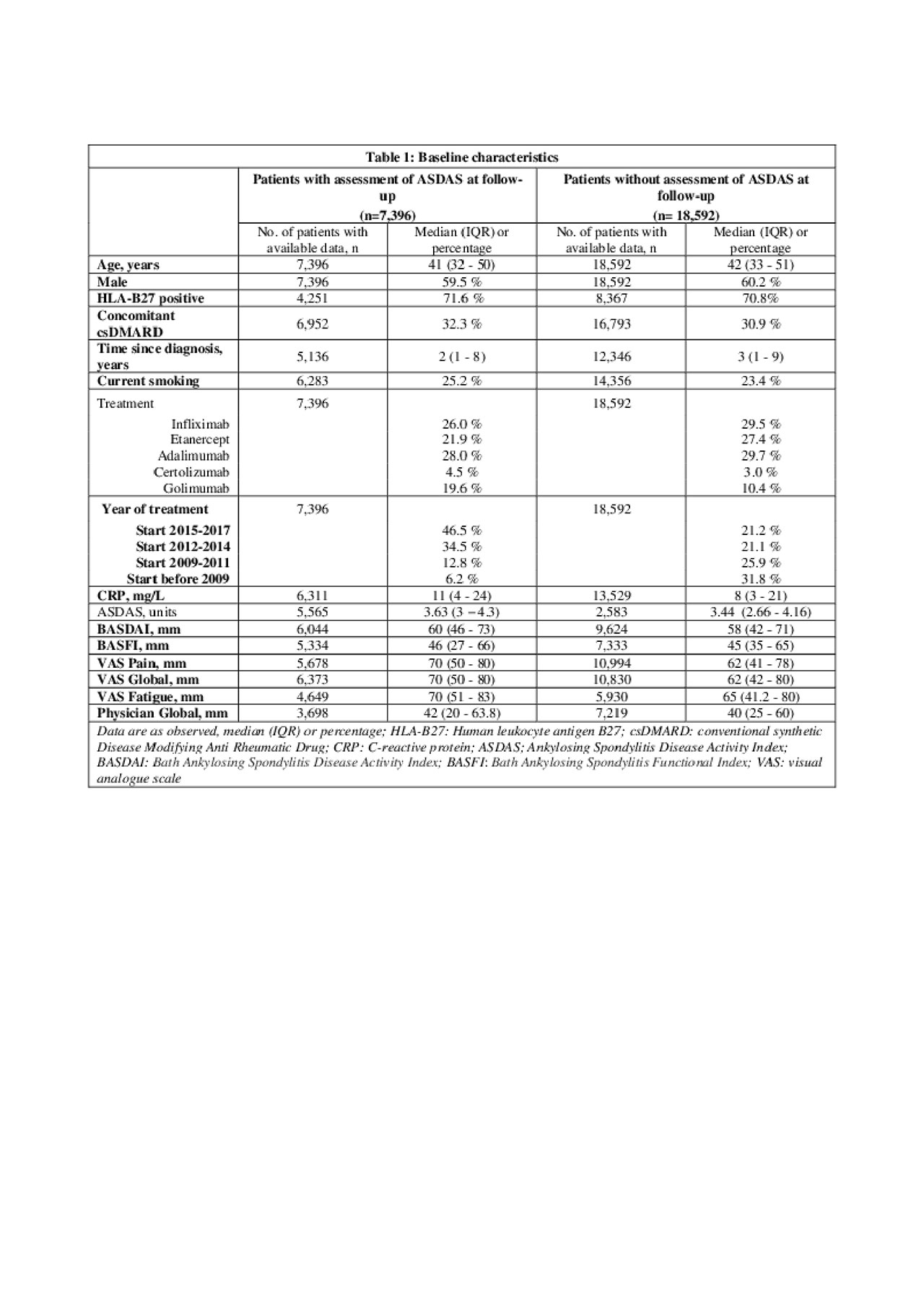
20190604_EuroSpA_study4.2_table1
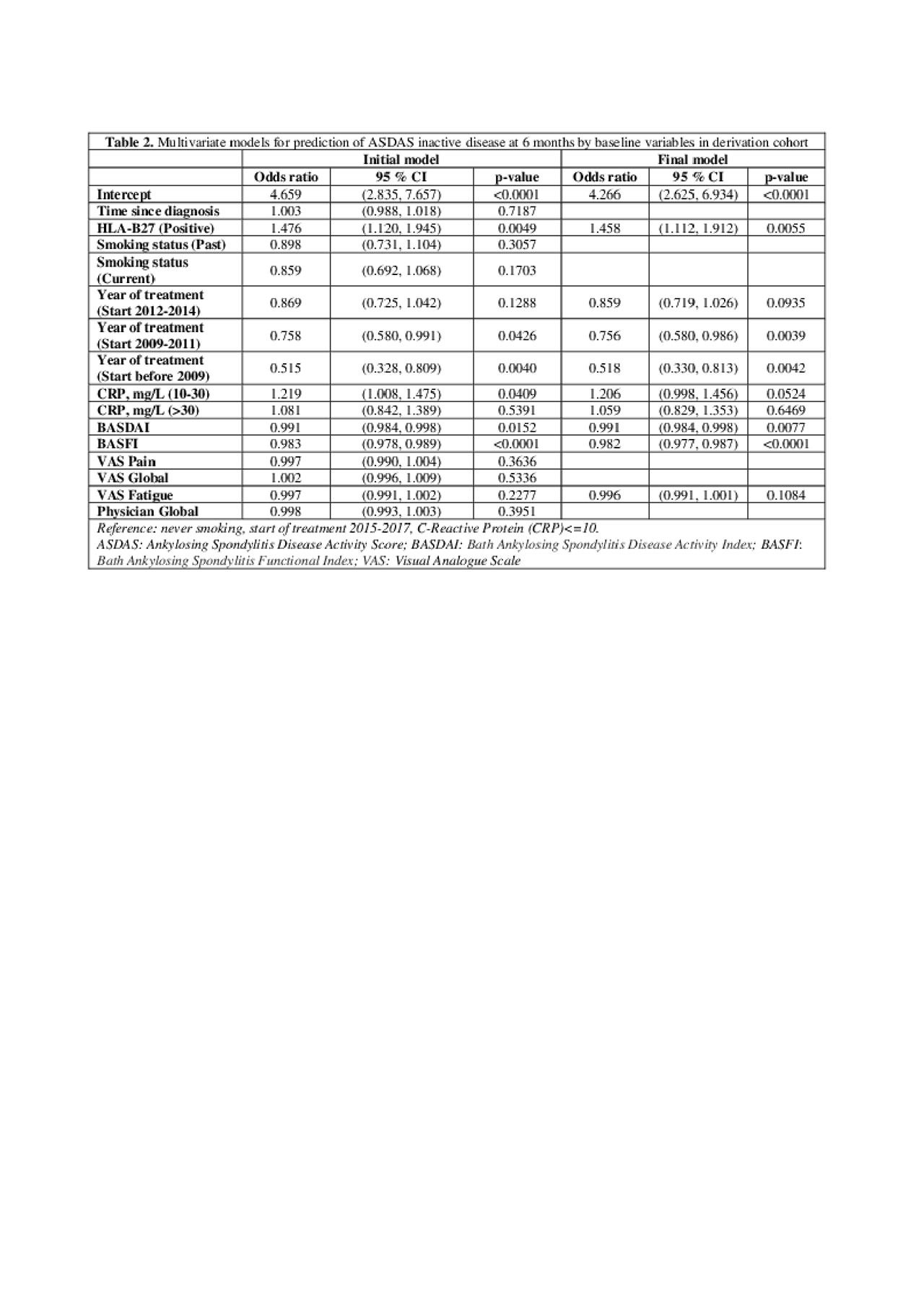
20190603_EuroSpA_study4.2_table2
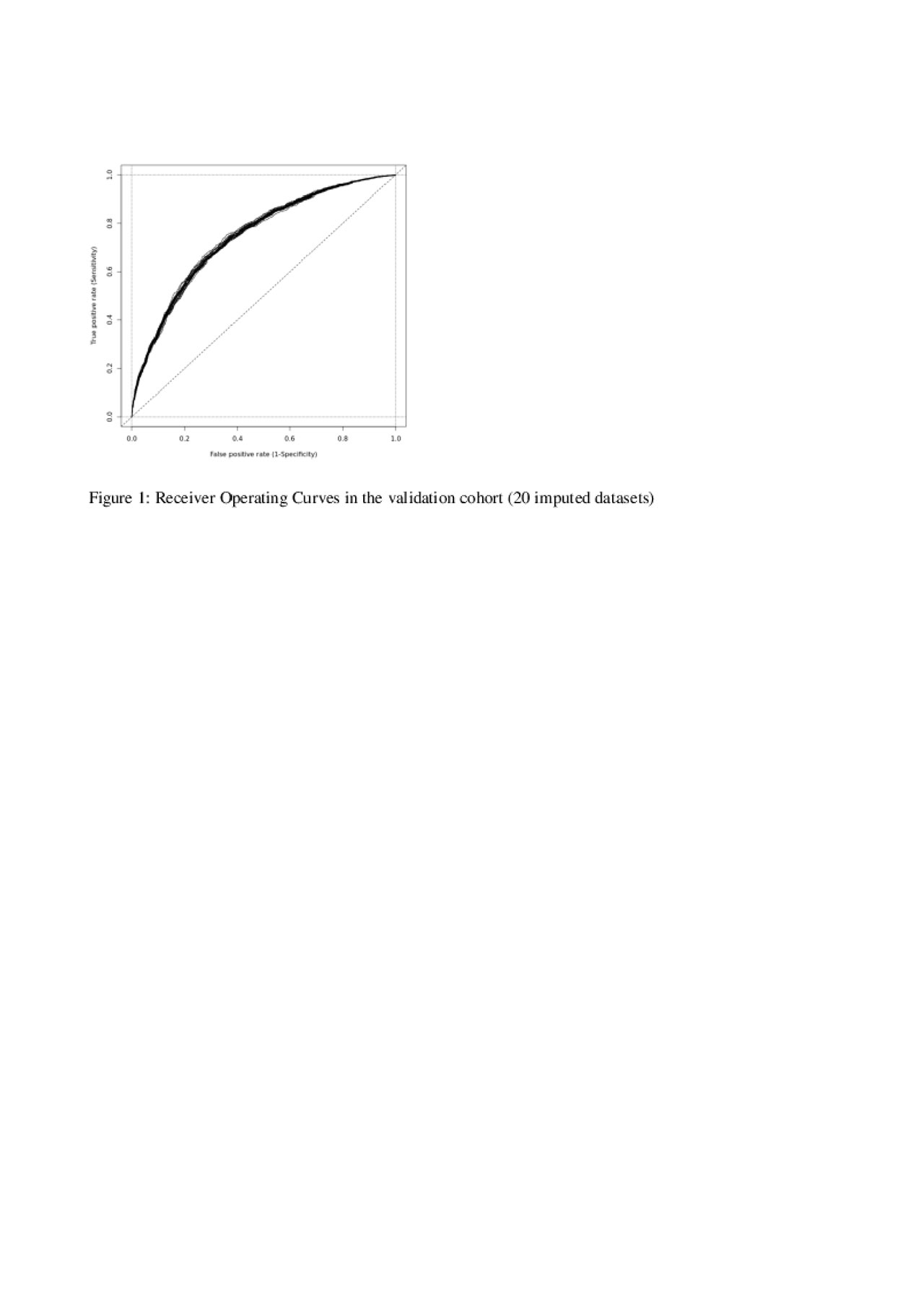
20190603_EuroSpA_abstract4.2_figure1
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ørnbjerg L, Georgiadis S, Lindström U, Loft A, Ciurea A, Mann H, Akkoç N, Iannone F, Kristianslund E, Hokkanen A, Santos M, Codreanu C, Sánchez-Piedra C, Tomsic M, Gudbjornsson B, van der Horst-Bruinsma I, Askling J, Nissen M, Pavelka K, Gunduz O, Atzeni F, Sexton J, Nordström D, Santos H, IONESCU R, Pombo-Suarez M, Rotar Z, Geirsson A, van de Sande M, Macfarlane G, Michelsen B, Lund Hetland M, Østergaard M. Predicting ASDAS Inactive Disease After 6 Months of TNFi Treatment in Bio-Naive Axial Spondyloarthritis Patients Treated in Clinical Practice – Results from the EuroSpA Collaboration [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predicting-asdas-inactive-disease-after-6-months-of-tnfi-treatment-in-bio-naive-axial-spondyloarthritis-patients-treated-in-clinical-practice-results-from-the-eurospa-collaboration/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/predicting-asdas-inactive-disease-after-6-months-of-tnfi-treatment-in-bio-naive-axial-spondyloarthritis-patients-treated-in-clinical-practice-results-from-the-eurospa-collaboration/
