Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: Epidemiology & Public Health Poster II: Spondyloarthritis & Connective Tissue Disease
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Biosimilars hold the potential to improve access to needed therapies at a reduced cost. In Canada, biosimilar etanercept (bsETA-Brenzys® and Erelzi®) were recently approved for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and other rheumatologic conditions; however, comparisons of patterns of use of biosimilar with its originator product (boETA-Enbrel®) are scarce. Our objective was to describe the recent use of bsETA and boETA in patients with RA, ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Methods: Data from patients initiating bsETA (either biologic-naïve users, patient transitioning from boETA, swappers and switchers from other biologic agents) were extracted from RHUMADATA®, a practice-based registry (14 Quebec rheumatologists) for the period of January 2015 to November 2018. For comparison purposes, we identified patients initiating/switching/swapping to the boETA product in the same period. We obtained baseline demographics and clinical data for all patients. Therapy persistence in bsETA versus boETA initiators was compared using Kaplan-Meier methods and adjusted hazard ratios (HR). Our hazard models adjusted for age, sex, disease duration, methotrexate (MTX) dose at baseline, and comorbidities (Charlson comorbidity index)
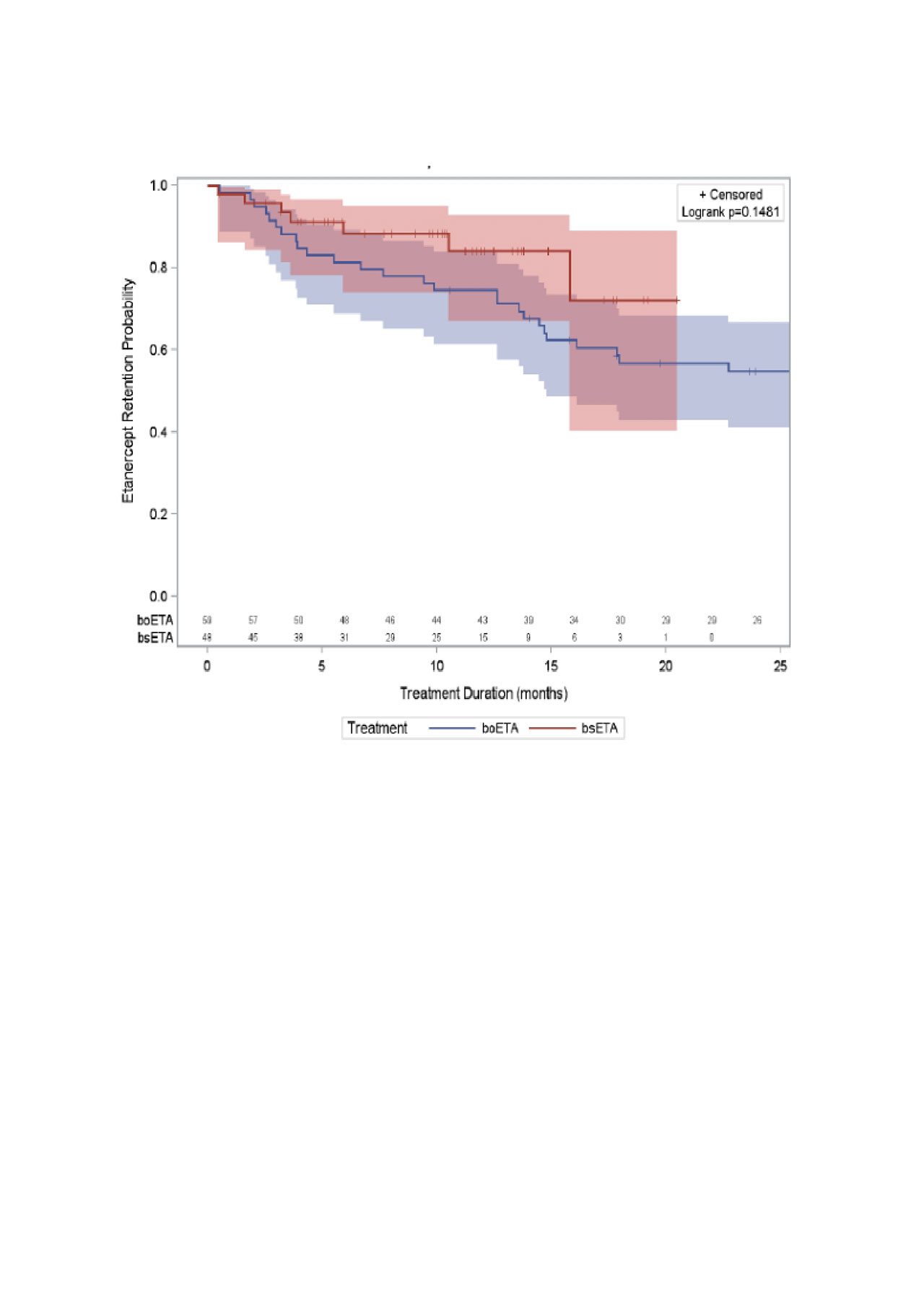
Results: We studied 48 patients initiating bsETA (including 37 etanercept-naïve patients) and 59 patients initiating boETA. Sex distribution, age, comorbidities and disease duration (at etanercept initiation) were similar between groups (Table 1). Use of MTX and/or other conventional synthetic DMARD (csDMARDs) at etanercept initiation was also similar between groups; however, patients in the boETA group started with a significant higher dose of MTX (22.0 ± 3.5mg) when compared to bsETA users (19.0 ± 5.2mg, p=0.011). Persistence on therapy was similar in both groups (Figure 1): after 12 months, 75% of originator etanercept versus 84% of biosimilar etanercept initiators remained on their initial treatment. Adjusting for baseline age, sex, disease duration, methotrexate dose at baseline, and comorbidities, the adjusted HR for therapy persistence in biosimilar etanercept versus originator etanercept group was 2.05 (95% CI 0.83, 5.04).
Conclusion: Patients initiating bsETA or boETA were similar in terms of age, disease duration, disease activity, and comorbidities. We were unable to identify clear differences in treatment persistence between the two groups; a strong trend for greater persistence with biosimilar versus originator may be related to residual confounding (e.g.: disease activity). Further work is ongoing to study outcomes in a larger, multicentre group of patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Moura C, Choquette D, Coupal L, Bessette L, Bernatsky S. Biosimilar Etanercept Use in Rheumatoid Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, and Psoriatic Arthritis: The RHUMADATA® Registry Experience [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biosimilar-etanercept-use-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-ankylosing-spondylitis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-the-rhumadata-registry-experience/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biosimilar-etanercept-use-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-ankylosing-spondylitis-and-psoriatic-arthritis-the-rhumadata-registry-experience/