Session Information
Date: Monday, November 11, 2019
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Delayed diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis (PsA) can lead to poor clinical outcomes. A large proportion of PsA patients remain undiagnosed due to a lack of robust biomarkers. Gene expression analysis at single peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) resolution may help to identify novel cells and RNA signatures present in PsA compared to psoriasis patients without arthritis (PsC).
Methods: PBMCs were isolated from 3 patients with early PsA (< 2 years) and 3 PsC patients matched for age, sex, and psoriasis duration. All patients were treatment naïve. Single cells were isolated using the droplet-based Chromium platform (10X Genomics) and cDNA libraries were sequenced on an Illumina HiSeq 4000. Data were processed in CELLRANGER and secondary analysis performed using R packages. Poor quality cells were filtered out based on high percentage of mitochondrial content, number of genes expressed and library size. Data were normalized by scran normalization and unsupervised graph-based clustering of cells was performed using a K-nearest neighbor algorithm. Cell types were inferred using immune marker genes and computed cluster markers.
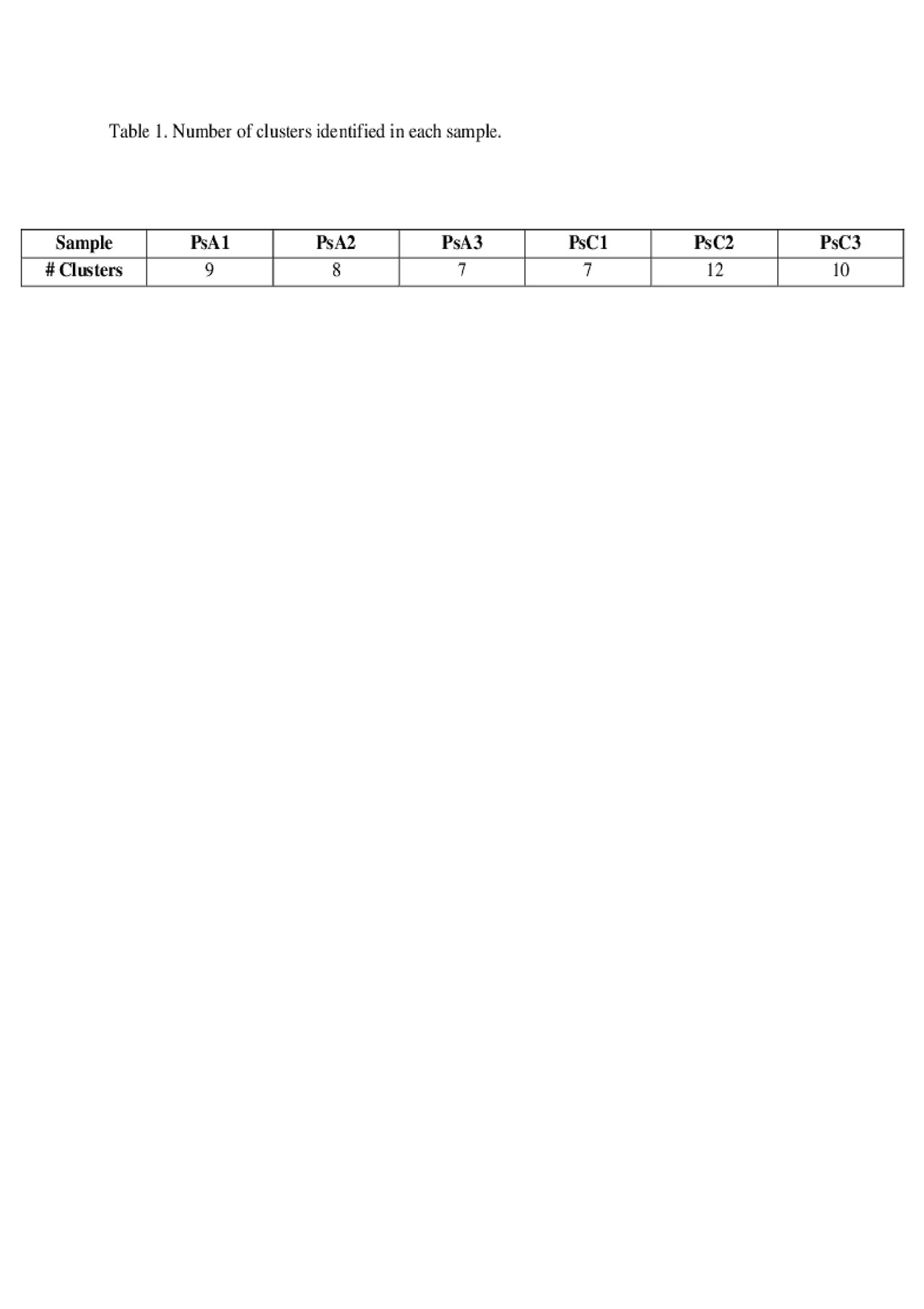
Results: PsA patients were 2/3 male, median age 65 (range 53-75) years, median active joint count 3 (0-7), and median psoriasis area and severity index (PASI) score of 1.4 (0.4-3.1). PsC patients were 2/3 male, age 64 (56-75) years, PASI score 2.8 (0.3-8.7). After quality control and filtering, high quality expression profiles were obtained from 7350 and 7022 cells from PsA and PsC patients, respectively. The number of clusters identified in each sample is shown in Table 1. Sample PsA2 had unique clusters of monocytes and CD34+ cells, whereas PsC2 had a unique cluster of plasmacytoid dendritic cells. The remaining clusters were evident in all patients and consisted of T cells, B cells, macrophages, NK cells and myeloid dendritic cells. Differential expression analysis of PsA compared to PsC patients revealed several differences (shown in Table 2). In myeloid dendritic cells significant upregulation of genes such as JUP (junction plakoglobin/gamma catenin, fold change[FC]=1.36, adj.p=6.8×10-47) and LYZ (lysozyme, FC=1.23, adj.p=2.9×10-39) was found. T cells showed significant downregulation of IL32 (interleukin 32, FC=0.66, adj.p=5.0×10-35), ERAP2 (endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 2, FC=0.77, adj.p=3.0×10-16), and upregulation of HLA-C (human leukocyte antigen C, FC=1.28, adj.p=3.2×10-33). FCGR3A+ monocytes showed a significant upregulation of IFITM3 (interferon induced transmembrane protein 3, FC=1.56, adj.p=3.5×10-11) and LILRA6 (leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor A6, FC=1.23, adj.p=1.8×10-5). Cytotoxic T cells showed upregulation of TRBV4-2 (T cell receptor beta variable 4-2, FC=3.02, adj.p=7.3×10-29) and TNFAIP3 (TNF alpha induced protein 3, FC=1.35, adj.p=3.8×10-6). Natural killer cells and naïve T helper cells showed significant downregulation of several ribosomal proteins in PsA compared to PsC patients.
Conclusion: The data show novel insights into gene expression differences in different cell populations that might help in differentiating PsA from PsC.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Machhar R, Liang K, Pollock R, Gladman D. Single Cell RNA Sequencing of Patients with Psoriatic Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/single-cell-rna-sequencing-of-patients-with-psoriatic-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/single-cell-rna-sequencing-of-patients-with-psoriatic-disease/