Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: There is still a debate concerning the concept of non-radiographic (nr-axSpA) axial Spondyloarthritis (e.g. to consider it as a distinct entity from r-axSpA (Ankylosing Spondylitis) or to consider it as the same disease with different phenotypical presentations). This study aims to compare clinical manifestations and burden of disease between r-axSpA and nr-axSpA over 5 years of follow-up in the DESIR cohort.
Methods: Patients from the DESIR cohort with x-ray sacroiliac joints available at baseline and who did not abandon the study because of different diagnosis than axSpA were included. A unilateral rating of “obvious sacroiliitis” according to the local reader (either a radiologist or a rheumatologist) was considered sufficient to be classified as r-axSpA. The incidence of a new episode of peripheral and extra-rheumatological manifestations between r-axSpA vs. nr-axSpA was assessed using incidence/100 person-years, incidence rate ratio and cox regressions adjusted for sex, age and TNF blockers (TNFb) intake. Mean values of c-reactive protein (CRP), patient reported outcomes (PROs) and days of sick leave over 5 years of follow-up were assessed using mixed models with random effects adjusted for sex, age, TNFb intake and baseline values. Disease-modifying drugs (DMARDs) initiation were also evaluated adjusted for CRP mean levels.
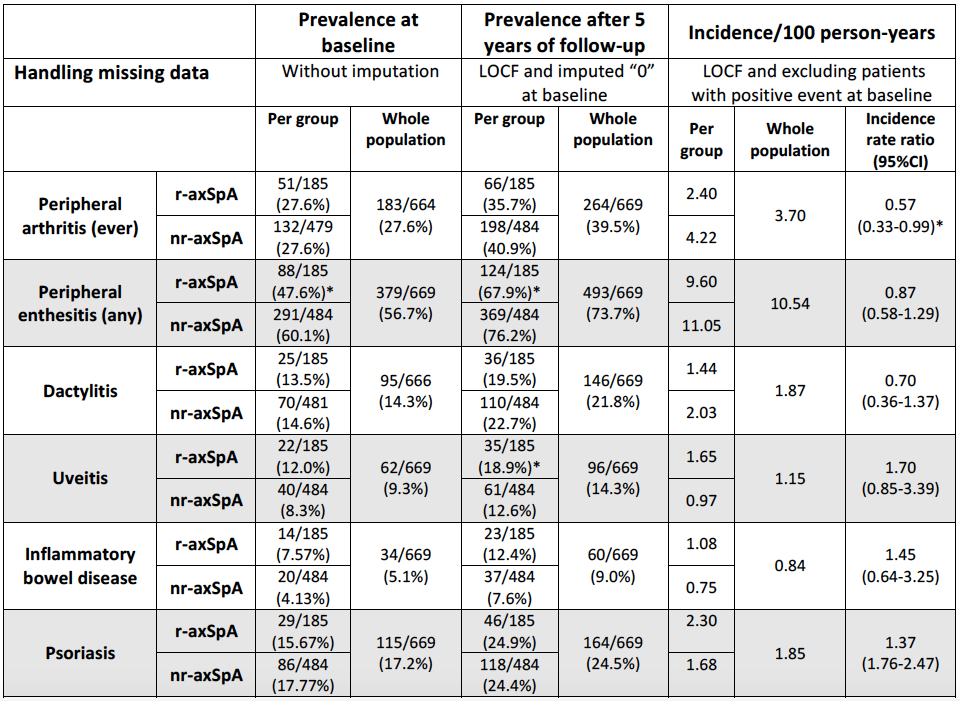
Results: In total 669 patients were included, of whom 185 (27.7%) and 484 (72.3%) were classified as r-axSpA and nr-axSpA, respectively. At baseline, r-axSpA patients showed significant higher prevalence of males (59.5% vs. 41.7%), smokers (44.0% vs. 34.2%), lower prevalence of peripheral enthesitis (47.6% vs. 60.1%) and lower mean age (31.3±8.9 vs. 34.5±8.4 years) than nr-axSpA. Table 1 shows baseline and 5 years-follow up prevalence, as well as the incidence of new cases of peripheral and extra-rheumatological manifestations. Only peripheral arthritis showed significant lower incidence among r-axSpA patients (2.40 vs. 4.22 new cases/100 person-years, incidence rate ratio 0.57 (95%CI 0.33-0.99)). However, adjusting for age, sex and TFNb intake, cox regressions did not show significant differences in the development of peripheral and extra-rheumatological manifestations between the two groups. Crude mixed models (Table 2) showed significant higher disease activity (BASDAI), poorer quality of life (SF-36 questionnaire) and higher mean days of sick leave over time among nr-axSpA patients. However, these differences disappeared when adjusting for confounders (see Table 2). r-axSpA group showed significant higher incidence of TNFb initiation (14.77 vs. 9.26 new first prescriptions/100 person-years) than nr-axSpA group, with a HR of 1.56 (95%CI 1.17-2.06) adjusted for sex, age and CRP mean levels.
Conclusion: r-axSpA and nr-axSpA patients showed minor differences at baseline. However, they seem to behave similarly over time, since the incidence of peripheral and extra-rheumatological manifestations as well as the burden of disease development remained similar when adjusted for confounders. Only peripheral arthritis seemed to be more incident among nr-axSpA group, while TNFb was most frequently used by r-axSpA patients.
*p-value <0.05 between r-axSpA and nr-axSpA
Mean -SD- represent the mean value over 5 years of follow-up.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
López-Medina C, Moltó A, Claudepierre P, Dougados M. Baseline Characteristics and Natural History of Radiographic versus Non-radiographic Axial Spondyloarthritis: 5 Years Follow-up of the Desir Cohort [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baseline-characteristics-and-natural-history-of-radiographic-versus-non-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-5-years-follow-up-of-the-desir-cohort/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/baseline-characteristics-and-natural-history-of-radiographic-versus-non-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-5-years-follow-up-of-the-desir-cohort/