Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I: Patient Reported Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The multi-dimensional health assessment questionnaire (MDHAQ) is a patient-reported outcome that is commonly used in clinical practice in the US and comprises of 10 items. Although the validated Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQDI) measures similar constructs as the MDHAQ, is less commonly used and has 16 items. Therefore, the objective of this study is to assess if the MDHAQ (divided by 3.33 to transform to the same scale as HAQDI) can substitute for the HAQDI in ACR20 assessment and cohort studies.
Methods: Between 2016-2019, patients with PsA were enrolled in the Psoriatic Arthritis Research Consortium (PARC), a longitudinal observational cohort at four United States institutions: University of Pennsylvania, Cleveland Clinic, New York University, and University of Utah. Baseline patient characteristics were descriptively reported. A priori we hypothesized that the MDHAQ and HAQDI would have high correlation at baseline ( >0.8) and among the change scores ( >0.8) and that responsiveness would be similar. Correlations were calculated among the total scores using Spearman’s correlation coefficients at baseline and follow-up visit. Change scores (e.g., score at visit 1 minus score at visit 2) and standardized mean responses were calculated. Sensitivity analyses excluding patients with low disease activity were calculated. We additionally examined agreement with the 20% improvement cut-off to determine the potential effect of using MDHAQ in the ACR20 criteria in place of HAQDI.
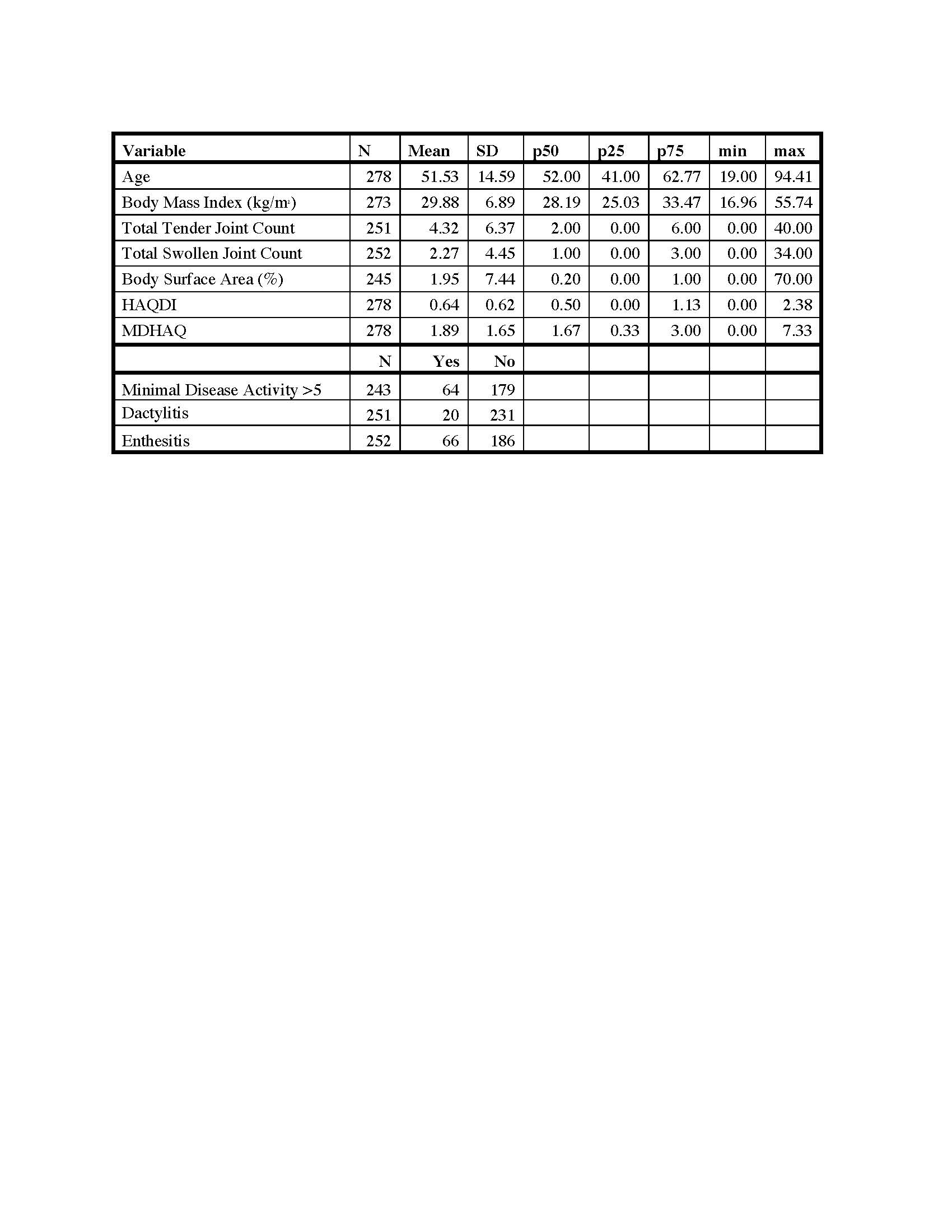
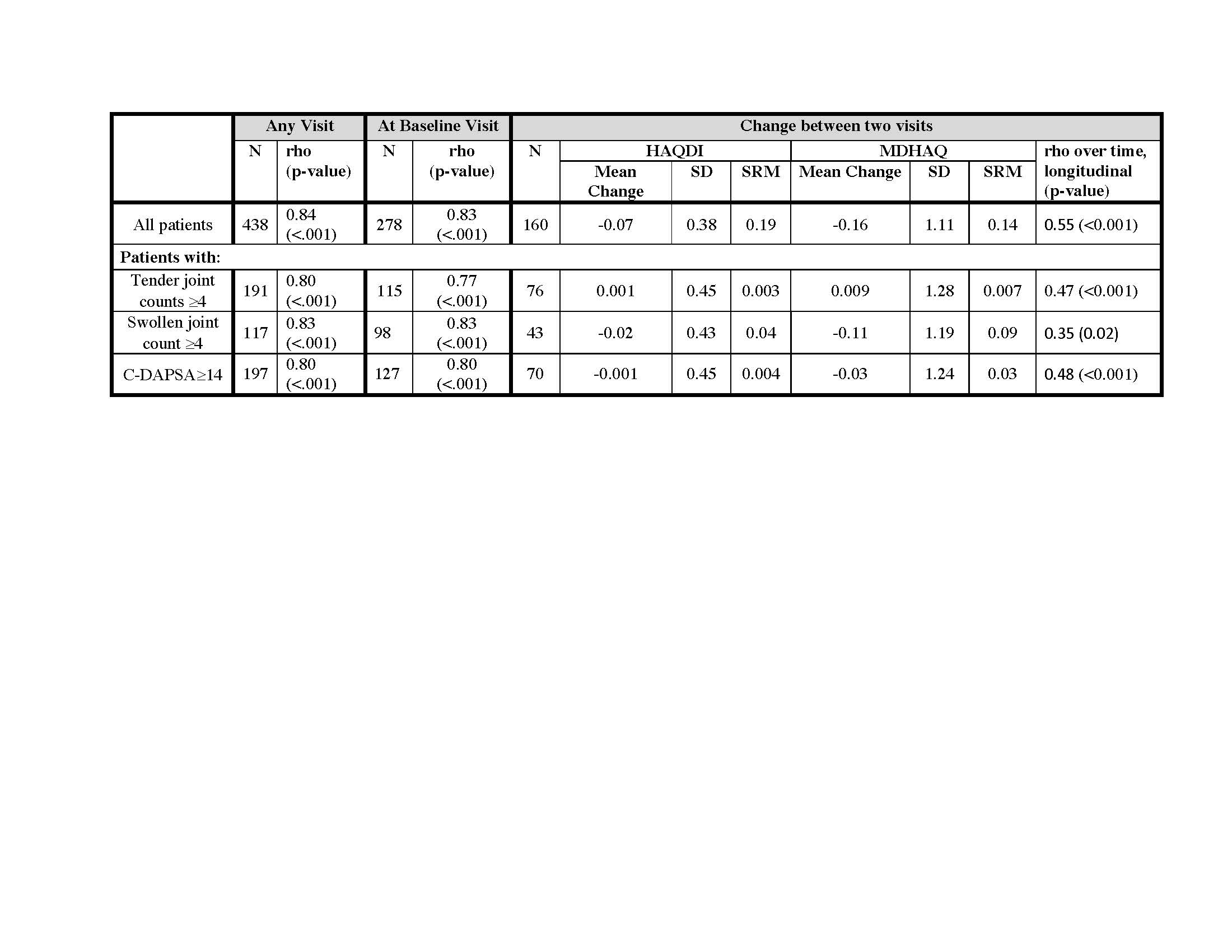
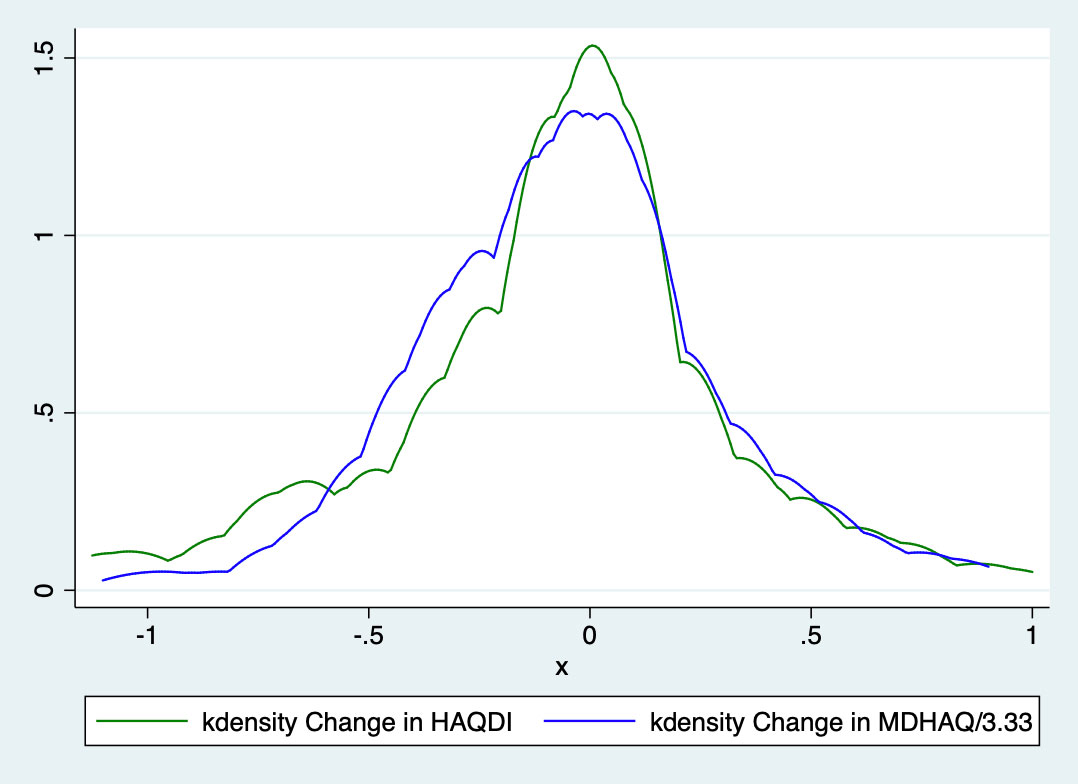
Results: HAQDI and MDHAQ data were available in 438 visits in which both questionnaires were completed and 161 patients with HAQDI and MDHAQ at two time points. The mean age was 51.5 ± 14.6 years old, 53% were male, and most had low disease activity with mean swollen (66) and tender (68) joint counts 2.3 ± 4.4 and 4.3 ± 6.4, respectively. At baseline, the mean HAQDI was 0.64 ± 0.62 (range 0-3) and the mean MDHAQ was 1.9 ± 1.7 (range 0-10; Table 1). Dividing the MDHAQ by 3.33 to transform it to the same scale as the HAQDI resulted in a transformed MDHAQ mean of 0.56 ± 0.48 with a mean excursion from the HAQDI score of 0.07 ± 0.35 (Figure 1). Among all time points, the Spearman’s correlation coefficient between the two instruments was 0.84 and among the first visit only, the coefficient was 0.83. The mean change over two visits in the HAQDI was -0.07 ± 0.4, with a standardized response mean (SRM) of 0.19 and mean change in the MDHAQ was -0.16 ± 1.1 with an SRM of 0.14. The Spearman’s correlation coefficient among the two change variables was 0.55 (Table 2). Using the 20% criteria for the ACR20, the agreement among use of HAQ-DI and MDHAQ is 74%. When excluding patients with a clinical Disease Activity index for Psoriatic Arthritis (c-DAPSA) score < 14 (i.e., low disease activity), the correlation coefficients were similar.
Conclusion: Although the HAQDI consists of more questions than the MDHAQ, the total scores correlated well when analyzed cross-sectionally. However, the correlation was moderate between the change over time. Using the 20% improvement cut-off, most were correctly classified with MDHAQ but MDHAQ cannot directly replace HAQDI for the ACR20 criteria.
Acknowledgement: Funded by NIH/NIAMS R01 AR072363
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wan M, Walsh J, Husni M, Scher J, Reddy S, Ogdie A. Longitudinal Construct Validity and Responsiveness of MDHAQ and HAQDI in PsA: Can MDHAQ Replace HAQDI? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/longitudinal-construct-validity-and-responsiveness-of-mdhaq-and-haqdi-in-psa-can-mdhaq-replace-haqdi/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/longitudinal-construct-validity-and-responsiveness-of-mdhaq-and-haqdi-in-psa-can-mdhaq-replace-haqdi/