Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I: Patient Reported Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Axial spondyloarthritis (axSpA) can be associated with significant burden and impaired work activity. In Chile, several barriers impede adequate treatment, such as insufficient access to specialists and biologic treatment. Furthermore, there is an important lack of insight into the local situation. This hampers the development of adequate national treatment standards and financial support.
The objectives were to (1) evaluate the disease burden, quality of life, work participation and treatment status in Chilean axSpA patients and (2) to assess the influence of gender.
Methods: A cross sectional online survey among Chilean axSpA patients, recruited via the Chilean SpA Patient Foundation (“Espondilitis Chile”) between July and October 2018. The survey requested information on gender, age, disease characteristics (diagnosis, disease duration, treatment), disease burden (BASDAI and BASFI), quality of life (ASAS Health Index) and work participation (WPAI). The association between BASDAI, quality of life or work participation (presenteeism, absenteeism) and subgroups (gender, biologics) was assessed through univariable and multivariable regression analyses, correcting for age, disease duration and concomitant treatment (NSAIDs, opiates).
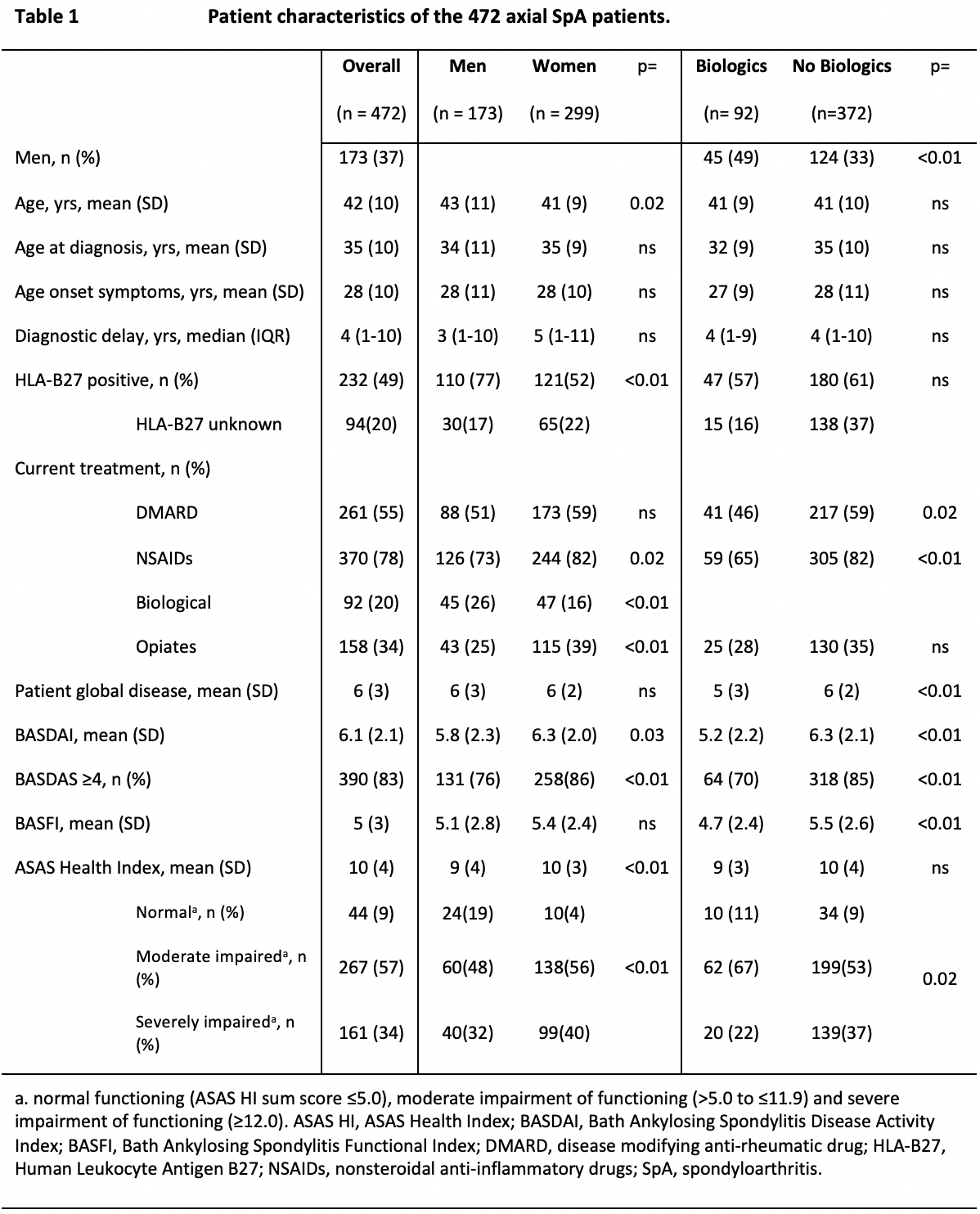
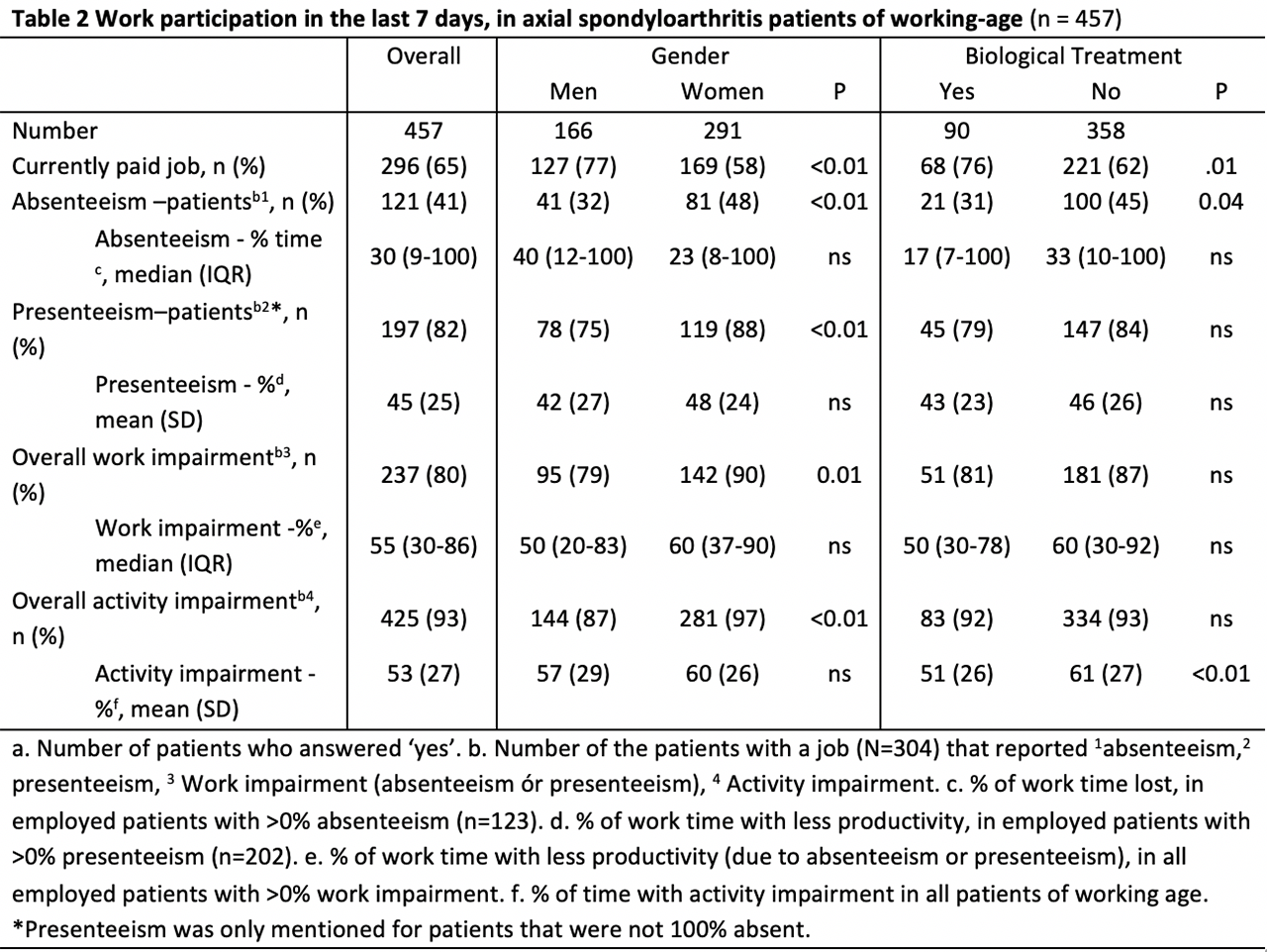
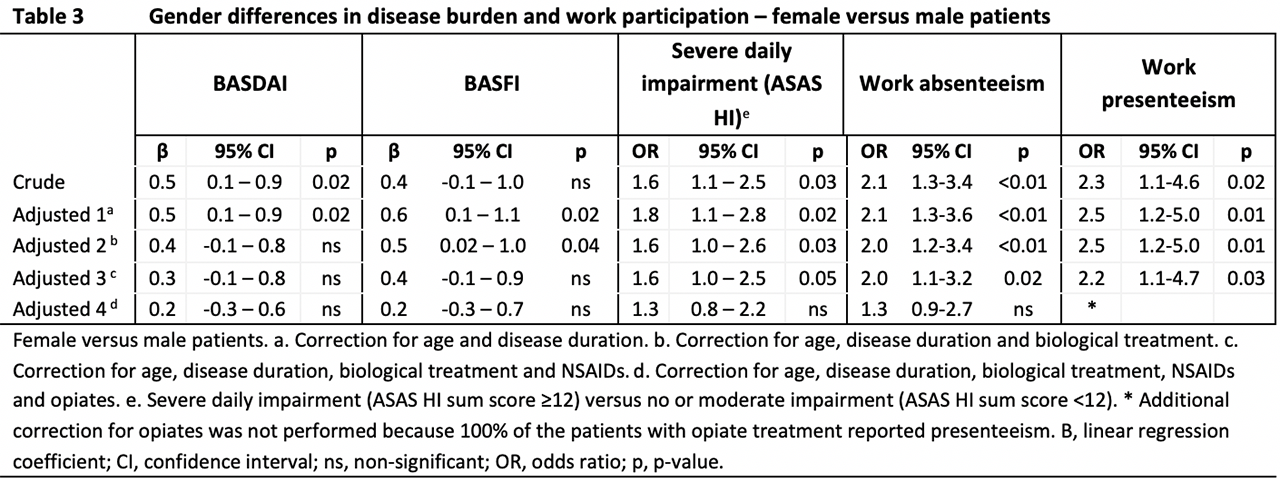
Results: AxSpA was reported by 472 participants (91% radiographic, 63% women, mean age 42+10 years), and the levels of disease activity (BASDAI ≥4: 83%; ASAS HI ≥moderately impaired: 91%; table 1) and work disability (absenteeism: 41%; presenteeism 82%; table 2) were high. Thirty-four percent used opiates. Biologics use was very low (20%) but significantly associated with lower BASDAI, BASFI, ASAS HI, and risk of absenteeism. Females had significantly higher BASDAI, BASFI and ASAS HI, although were less likely to receive biologics (26% versus 16%, p< 0.01). After correction for treatment, these gender differences were not significant anymore (table 3).
Conclusion: This web survey strongly suggest a high disease burden and work impairment in Chilean axSpA patients. The use of biologics is low, while the use of opiates was alarmingly high. Women used significantly less biologics despite reporting a worse disease state and work disability, which could be due to treatment inequity. This is the first large web survey on axSpA patients in Latin America and the first to describe labor participation and gender differences in disease activity and treatment in Chilean axSpA patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ibanez S, van Bentum R, Valenzuela O, van der Horst-Bruinsma I. Axial Spondyloarthritis Patients Report Important Impairments in Daily Life and Work Ability – a Web Survey in 472 Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/axial-spondyloarthritis-patients-report-important-impairments-in-daily-life-and-work-ability-a-web-survey-in-472-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/axial-spondyloarthritis-patients-report-important-impairments-in-daily-life-and-work-ability-a-web-survey-in-472-patients/