Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, & Attitudes Poster I: Patient Reported Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: With many disease domains affected in PsA, clinical and patient-reported outcome (PRO) measures are important to assess disease improvement following treatment. Rapid, meaningful improvements in disease activity are a priority for physicians and patients (pts). Tofacitinib is an oral Janus kinase inhibitor for the treatment of PsA. Higher proportions of pts achieved responses in PROs and clinical measures when treated with tofacitinib for 3 months vs placebo (PBO).1-5 Proportions of responders were also similar between tofacitinib and adalimumab (ADA) after 3, 6, and 12 months.2,3,5 We aimed to determine the time to initial response using responder definitions for selected PROs and clinical endpoints in pts with active PsA treated with tofacitinib, ADA, or PBO switching to tofacitinib.
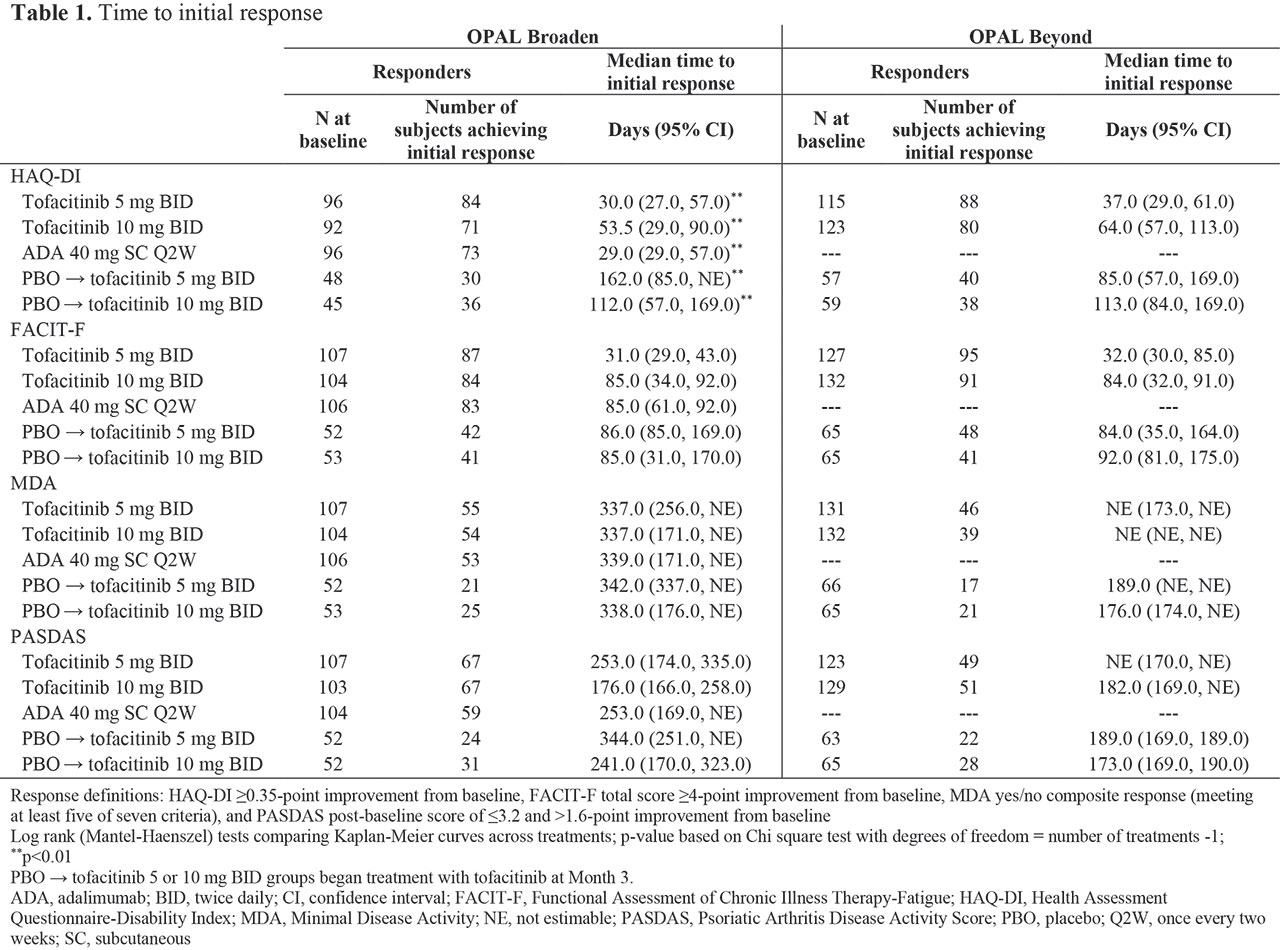
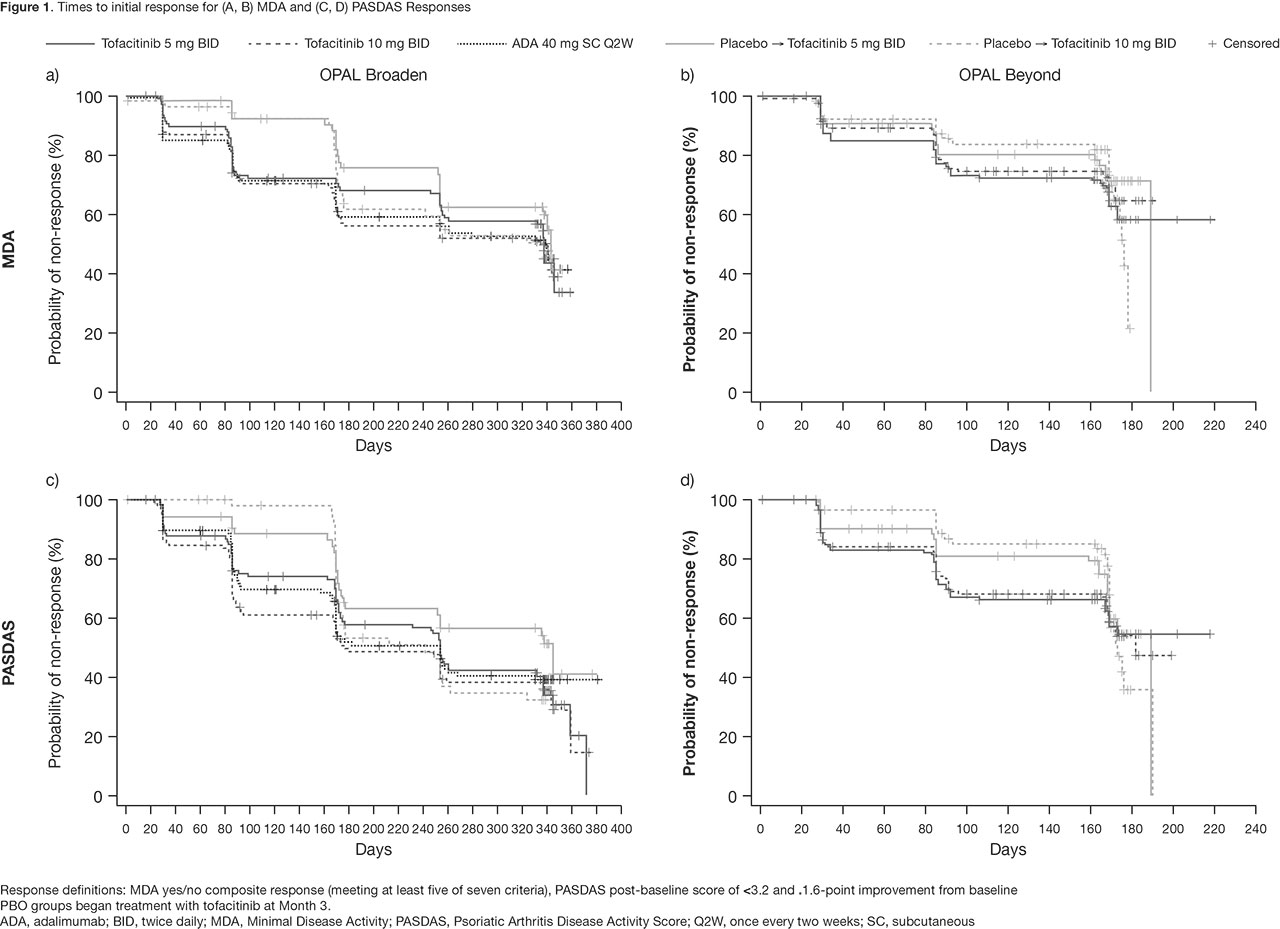
Methods: In this post hoc analysis, data were collected from two Phase 3 studies (OPAL Broaden [12 months; NCT01877668]; OPAL Beyond [6 months; NCT01882439]).3,4 Pts receiving tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg twice daily (BID), subcutaneous ADA 40 mg once every two weeks (Q2W; OPAL Broaden only), or PBO, switching to tofacitinib 5 or 10 mg BID at Month (M)3, were included. Responder definitions included: HAQ-DI ≥ 0.35-point improvement from baseline (BL), Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue (FACIT-F) total score ≥ 4-point improvement from BL, Minimal Disease Activity (MDA) yes/no composite response (meeting at least 5/7 criteria), and PsA Disease Activity Score (PASDAS) post-BL score of ≤ 3.2 and > 1.6-point improvement from BL. First post-BL data were collected at Week 2 (eg for HAQ-DI) or M1. Time-to-event analyses were performed using the Kaplan-Meier (KM) method, with pts censored at last observed visit. Log-rank tests compared time to initial response across treatment groups.
Results: KM analyses show days to initial response (Table 1, Figure 1). Time to initial HAQ-DI responses was significantly different between treatment groups in OPAL Broaden (p < 0.01): faster in pts receiving tofacitinib 5 mg BID, tofacitinib 10 mg BID, and ADA, vs pts who switched from PBO to tofacitinib at M3. A similar, but not significant (ns) trend was observed for HAQ-DI responses in OPAL Beyond. Generally, initial FACIT-F responses were achieved faster in pts receiving tofacitinib 5 mg BID vs other treatment groups in both studies (ns). Times to initial MDA and PASDAS responses were similar between tofacitinib and ADA treatment groups.
Conclusion: Times to initial response in functional ability and disease activity were similar in pts treated with either tofacitinib or ADA. Time to initial response prior to first post-BL observation (Week 2 or M1) was not estimable in this analysis. These results may help physicians better understand the time frame for a meaningful response in pts receiving tofacitinib.
- Strand V et al. RMD Open 2019;5:e000808.
- Strand V et al. RMD Open 2019;5:e000806.
- Mease P et al. N Engl J Med 2017;377:1537–50.
- Gladman D et al. N Engl J Med 2017;377:1525–36.
- Helliwell P et al. Arthritis Res Ther 2018;20:242.
Acknowledgments: Study sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Medical writing support was provided by Eric Comeau of CMC Connect and funded by Pfizer Inc.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gladman D, Coates L, Wu J, Fallon L, Hsu M, Bushmakin A, Bacci E, Cappelleri J, Helliwell P. Time to Response for Clinical and Patient-Reported Outcomes in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis Treated with Tofacitinib, Adalimumab, or Placebo [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/time-to-response-for-clinical-and-patient-reported-outcomes-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-treated-with-tofacitinib-adalimumab-or-placebo/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/time-to-response-for-clinical-and-patient-reported-outcomes-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-treated-with-tofacitinib-adalimumab-or-placebo/