Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The antisynthetase syndromes (ASSD) are characterized by the presence of anti-aminoacyl transfer RNA synthetase (ARS) autoantibodies and a clinical classic triad of myositis, arthritis, and interstitial lung disease (ILD). Two ASSD diagnosis criteria have been proposed; those from Connors, and the stricter from proposed by Solomon.
Regarding ARS detection, previous studies have shown differences in the specificity between different myositis immunoblots. Nevertheless, an adequate clinical correlation and the ARS positivity in another monospecific-assays or HEp-2 indirect immunofluorescence assay (IIFA), can safeguard a high specificity of myositis-specific autoantibodies in the immunoblots.
Objective:
To evaluate the performance of IIFA patterns in the ASSD diagnosis in patients with ARS positivity and adequate ASSD or IIM clinical suspicion.
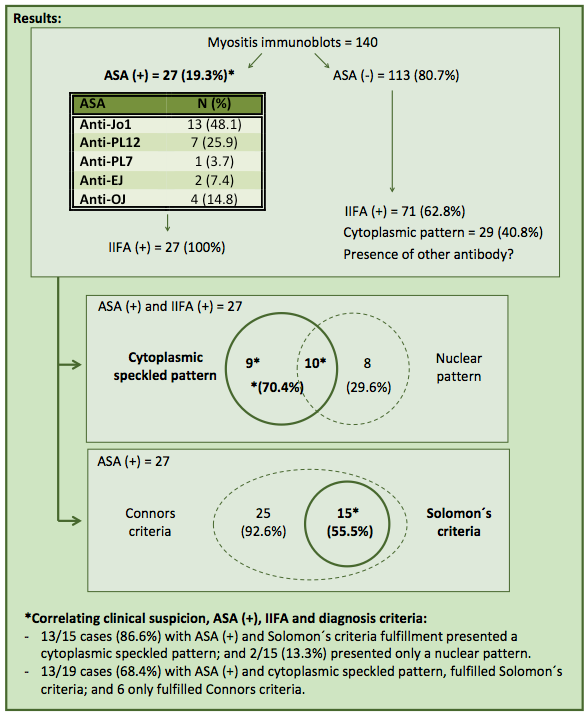
Methods: We analyzed data from one center (period 06/2008-06/2018). We searched all the myositis immunoblots (Euroimmun assay) requested by Rheumatologists under suspicion of ASSD or myositis and assessed: 1) the rate of cases with positive ARS; 2) the rate of cases with Connor´s or Solomon´s diagnosis criteria fulfillment; and 3) their relation with the IIFA patterns (Hep-2 cells; ≥1/80).
Results: A total of 140 myositis immunoblots were searched. Twenty-seven cases (19.3%) presented positive ARS: anti-Jo1 (n=13), anti-PL-12 (n=7), anti-PL-7 (n=1), anti-EJ (n=2), and anti-OJ (n=4). Twenty-five of these (92.6%) fulfilled Connors´ criteria, and 15 (55.5%) also met Solomon´s criteria. Additionally, all cases with positive ARS presented positive IIFA: 19 (70.4%) showed a cytoplasmic speckled pattern (10 of them with an associated nuclear pattern) and 8 cases (29.6%) presented only a nuclear pattern.
Correlating, 13 of 27 cases with clinical suspicion of IIM or ASSD and positive ARS (48.1%) presented a cytoplasmic speckled IIFA pattern and also fulfilled Solomon´s criteria; representing the 68.4% of the cases with these IIFA patterns and the 86.6% of those that met Solomon´s criteria.
On the other hand, 71 of the 113 cases (62.8%) with negative ARS presented positive IIF: 29 of them (40.8%) showed a cytoplasmic pattern (21 with an associated nuclear pattern) and 42 cases (59.2%) presented only a nuclear pattern.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that in patients evaluated by a Rheumatologist, with an adequate clinical suspicion of ASSD or IIM and with ARS positivity, the probability of fulfilling Solomon´s criteria is higher when the IIFA presents a cytoplasmic speckled pattern than when only a nuclear pattern is observed.
Additionally, the high rate of positive IIFA in patients without positive ARS, suggests the presence of other positive antibodies and is in favor of good clinical judgment of the Rheumatologists when requesting the tests and of the autoimmunity expert when accepted them. This highlights the importance of the International Autoantibody Standardization (IAS) and the International Consensus on Antinuclear antibodies Patterns (ICAP) initiatives; whose implementation clinical laboratories could facilitate the harmonization of these tests and consequently the development of multicenter studies.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Greco M, García De Yébenes M, Alarcón I, Rua Figueroa I, Loza E, Rodriguez-Lozano C, Brandy-Garcia A, Carmona L. Antisynthetase Syndromes: Correlation of Indirect Immunofluorescence Patterns with Diagnosis Criteria Fulfillment [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/antisynthetase-syndromes-correlation-of-indirect-immunofluorescence-patterns-with-diagnosis-criteria-fulfillment/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/antisynthetase-syndromes-correlation-of-indirect-immunofluorescence-patterns-with-diagnosis-criteria-fulfillment/