Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In 2018 an international task force published a recommended Treat to Target (T2T) approach to juvenile idiopathic arthritis (JIA) treatment. In February 2019, 17 centers participating in the Pediatric Rheumatology Care and Outcomes Improvement Network (PR-COIN) began a collaborative improvement project using quality improvement (QI) methods to test and implement T2T interventions. Based upon published literature and one center pilot experience, PR-COIN designed an approach to introduce interventions to support successful and reliable deployment of three T2T component processes: standardized disease activity assessment, setting a treatment target with patient/family, and use of polyarticular JIA (Poly-JIA) clinical decision support (CDS). Our objective is to implement T2T with high reliability in 80% of PR-COIN centers by October 2019.
Methods: With patient/family partners, PR-COIN co-produced educational materials to train providers on implementation of T2T and to introduce families to the concept. The network adapted an evidence and consensus-based treatment algorithm, and designed a step-by-step implementation plan to support local implementation with a data submission platform to evaluate the interventions. Interactive monthly webinars feature best practices and performance reports, and QI/T2T process coaching. The interventions are being implemented in three steps: 1) standardized assessment and review of components of the clinical juvenile arthritis disease activity score (cJADAS10), including the physician global assessment, active joint count, patient assessment, 2) use shared decision making (SDM) concepts to select treatment target with the family and compare it to current disease activity and 3) use of CDS. Sites progress to the next step once reliable process implementation ( >80%) is demonstrated in a representative sample of patients with Poly-JIA.
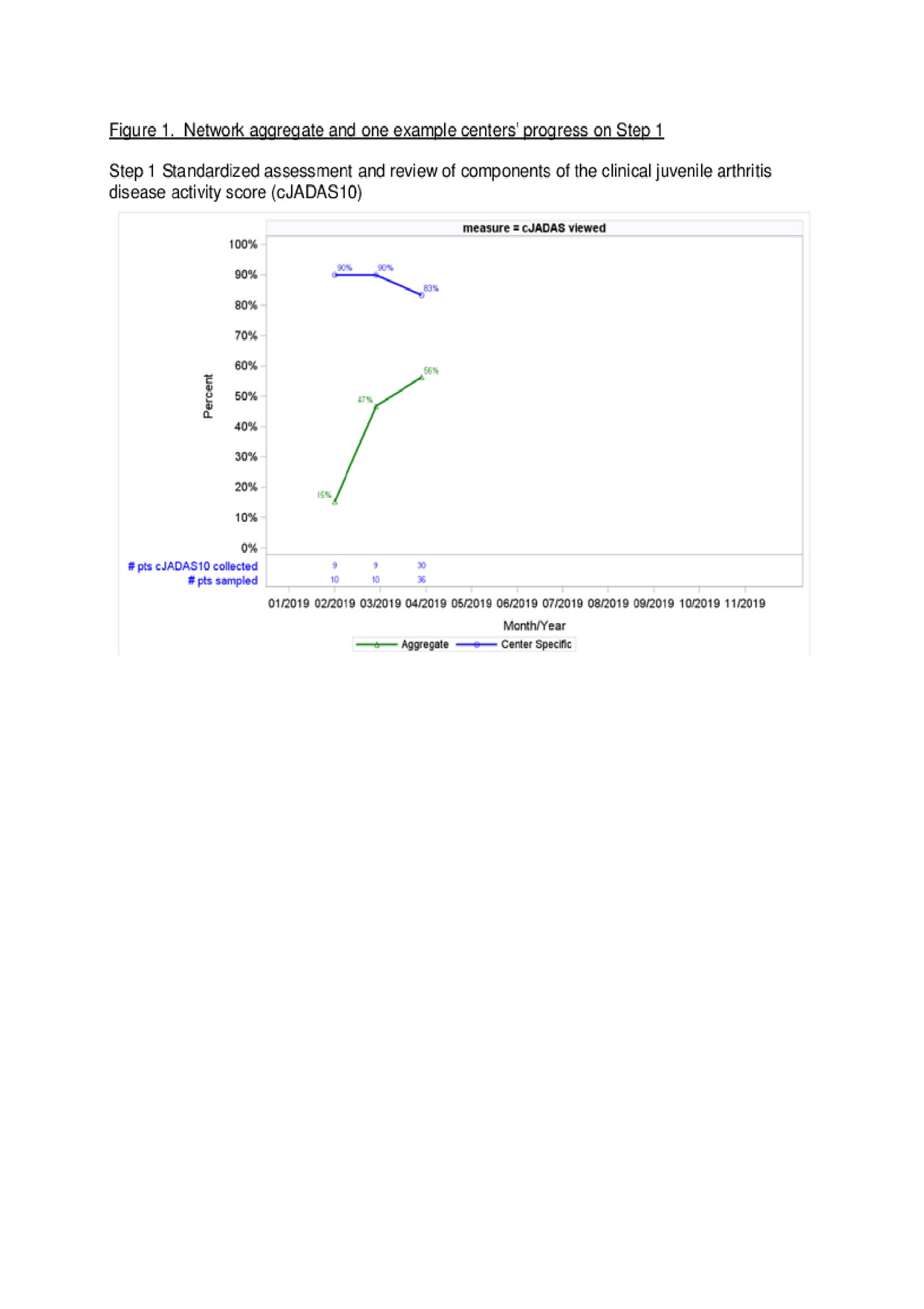
Results: As of April 2019, 16 centers are participating. All centers completed on-site training, 9/16 (56%) submitted at least one QI tool, and 11/16 (69%) eligible centers submitted performance data. A sample of patient-level data indicate 157/279 (56%) of patients are receiving Step 1 activities (Figure 1). Four of the sixteen centers (25%) are performing Step 1 activities with high reliability and have progressed to Step 2, with 4 / 35 (13%) of sampled patients engaged in SDM to set treatment targets (Figure 2). Figures show aggregate data alongside an example single center performance. Centers are demonstrating progressive improvement over time towards the reliability criteria to full implementation of T2T and performance goals.
Conclusion: Introduction of novel interventions required for fidelity of T2T implementation in pediatric rheumatology clinical practice requires a tiered approach with demonstrated commitment from trained providers, buy-in from leadership, and an identified QI lead. Co-producing support materials with families, infrastructure to support QI, and reliable data submission are key to success. We predict that center-level cJADAS10 improvement will correlate with reliability of the implementation of interventions.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Morgan E, Taylor J, Qiu T, Griffin N, Paul A, Bingham C, Bullock D, Ferraro K, Goh Y, Gilbert M, Halyabar O, Jones K, Kohlheim M, Lovell D, MacDonald D, Smitherman E, Vago A, Weiss J, Yildirim-Toruner C, Young A, Batthish M, Gottlieb B, Harris J, Hazen M, Laxer R, Lee T, Mannion M, Olson J, Shishov M, Vora S, Burnham J. Designing and Testing Treat to Target as a New Care Model in JIA Across a Network of Pediatric Rheumatology Centers [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/designing-and-testing-treat-to-target-as-a-new-care-model-in-jia-across-a-network-of-pediatric-rheumatology-centers/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/designing-and-testing-treat-to-target-as-a-new-care-model-in-jia-across-a-network-of-pediatric-rheumatology-centers/