Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The management of fibromyalgia is difficult, combining pharmacological and non-drug treatments, including massage. Its pathophysiology, still poorly understood, is complex, including muscle anomalies with reduced ATP and microcirculation. To date, only superficial massages have been tested in fibromyalgia. Deep haptic massage, used in athletes, have an action on muscle structures by reaching the free nerve endings present in the muscle and to ensure a “gate control” of the pain. The purpose of this pilot study was to evaluate the effects of deep haptic massage in fibromyalgia.
Methods: Preliminary monocentric open ended prospective study from october 2015 to november 2017.
Inclusion criteria : women, 18 to 65 years, fibromyalgia by ACR criteria, with a White Spread Index (WPI) ≥ 7 and severity score (SS) ≥ 5 or WPI between 3 and 6 and SS ≥ 9, with stable treatment for 1 month without modification expected within the next 6 months.
Non inclusion criteria : pregnant women, chronic inflammatory rheumatism, infection disease, individualized psychiatric pathology, severe visceral impairment, non-drug combination therapy, skin lesions contraindicating massages.
Intervention : 2 sessions of deep haptic massage of 30 minutes per week for 6 weeks.
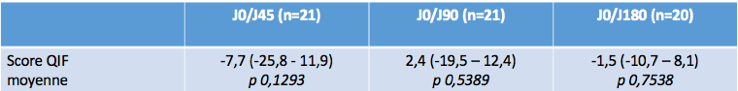
Evaluation at week 0 (S0), S6, S12 and S24. Main evaluation criteria at S6 : fibromyalgia Impact Questionnaire (FIQ). Secondary criteria FIQ to S12 and S24 and sub-items from FIQ to S6, S12 and S24. EVA patient and physician satisfaction at S6, S12 and S24. The analysis of the evolution of the FIQ score carried out using a T Test for a sample.
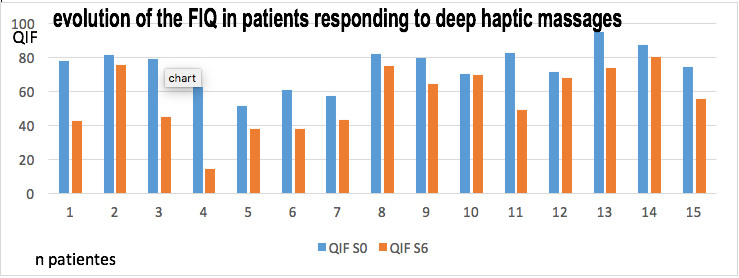
Results: 21 patients were included (1 study discharge at 3 months), including an age median of 53 (47-57), medians WPI 15 (13-18) and SS 9 (8-11). The average FIQ was from 68.8±16.1 to S0, 60.1±16à S6, 65.7±18.8 à S12 and 68.4±14.5 to 6 months. An average variation between S0 and S6 of -8 percent (ns). No change in subitems of the FIQ is not significant. The medians of EVA satisfaction at S6 for the patient and physician were similar, respectively 7,5/10 and 6/10. At 3 and 6 months from the massage, EVA satisfaction decreases in a similar way in patients and doctors (5/10 and 4.5/10 respectively). In a subgroup of 14 patients “deep haptic massage reponders”, there is an average variation between S0 and S6 of -26 percents (FIQ means : S0 : 74.03±12.8; S6 : 55.37±19.7).
Conclusion: In our study, deep haptic massage does not appear to be effective in the management of fibromyalgia. Nevertheless, positive effects in a subgroup representing more than 50 percents of patients encourage further investigation on a larger scale.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
FELCE a, aubrun a, allam y, Choplin A, Euller Ziegler L, Breuil V. Effects of Deep Haptic Massage in Fibromyalgia (pilot Study) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-deep-haptic-massage-in-fibromyalgia-pilot-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/effects-of-deep-haptic-massage-in-fibromyalgia-pilot-study/