Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is characterized by thromboses and/or obstetric complications in presence of antiphospholipid antibodies (aPL). Extracellular vesicles have been suggested to play a role in the pathogenesis of APS (1,2), however no data till now has been provided for exosomes, representing small (< 100nm), secreted vesicles of endosomal origin. Recent advances show exosomes to be involved in autoimmune cell-cell communication (3). We hypothesize that markers involved in coagulation, hemostasis and the immune system are enriched on exosomes isolated from APS patients and we aimed to determine their surface marker profiles.
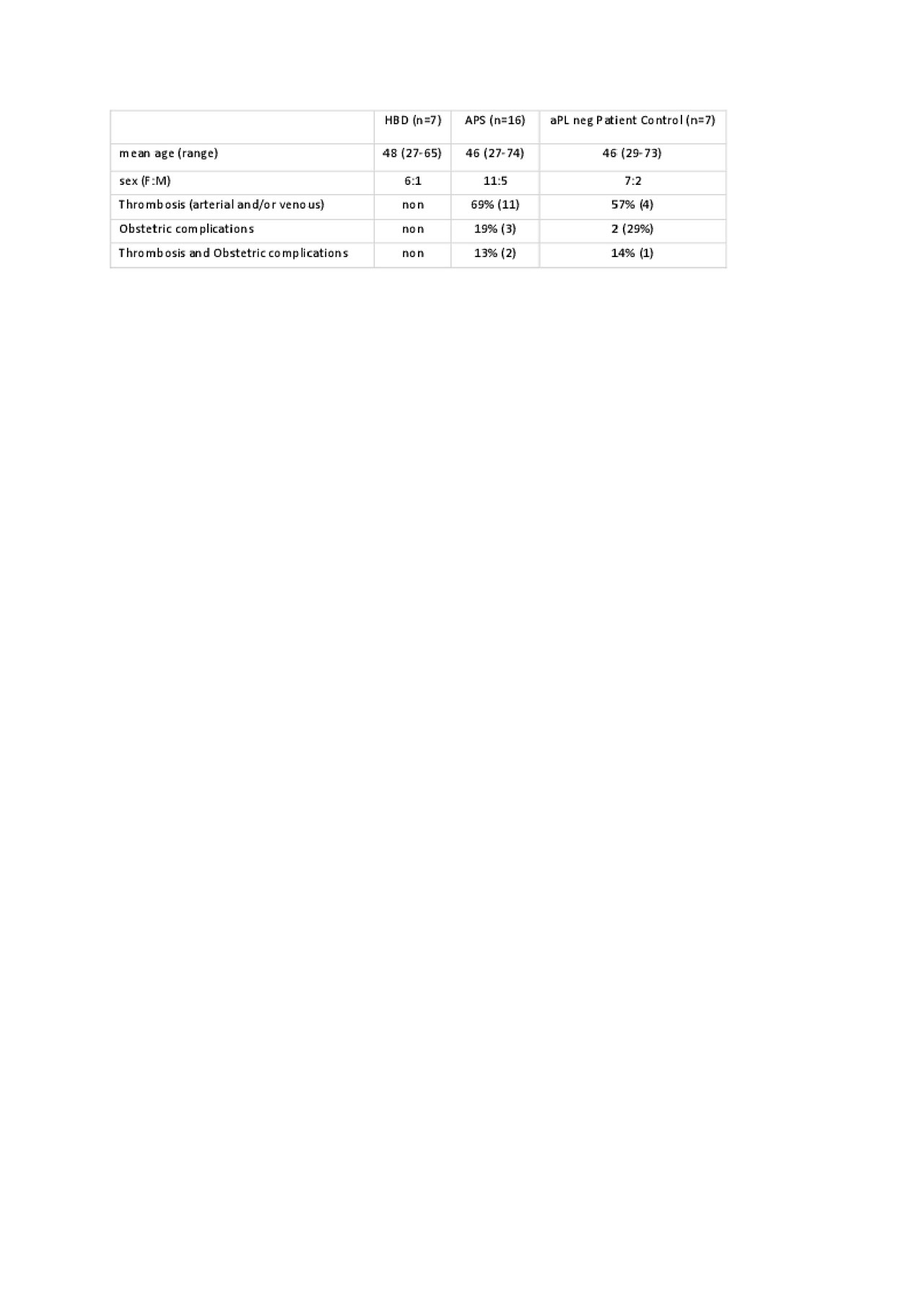
Methods: Platelet poor plasma was collected from 16 APS patients and 14 aPL negative controls, (7 healthy blood donors (HBDs) and 7 patient controls (PC)) (Table 1). The groups were sex- and age-matched. LA was determined by clotting tests, aCL, anti-β2GPI, aPS/PT were measured with in-house ELISAs (4). Exosomes were isolated using CD63-labelled magnetic beads and surface protein profile studied with MACSPlex Exosome kit (both from Miltenyi Biotec), for 37 markers (CD1c, CD2, CD3, CD4, CD8, CD9, CD11c, CD14, CD19, CD20, CD24, CD25, CD29, CD31, CD40, CD41b, CD42a, CD44, CD45, CD49e, CD56, CD62P, CD63, CD69, CD81, CD86, CD105, CD146, CD209, CD326, CD133/1, CD142, MCSP, SSEA-4, ROR1, HLA-ABC and HLA-DRDPDQ). All results were normalized against expression of tetraspanin surface proteins e.g. CD9/81/63. Student t-test and χ2 test were calculated to compare APC median signal intensities between the groups. The database of known and predicted protein interactions STRING 10.5 was used for analysis of interactions between markers.
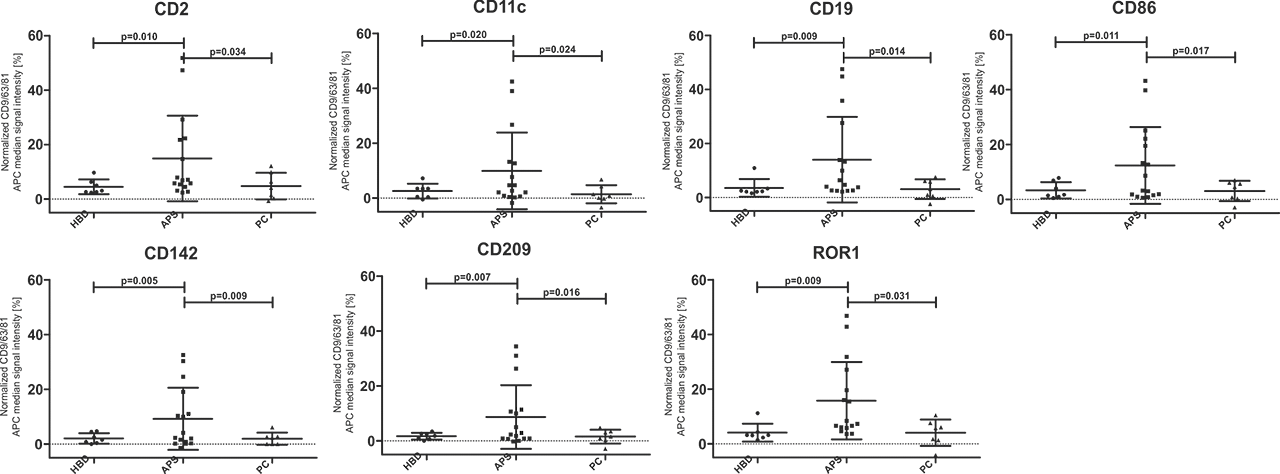
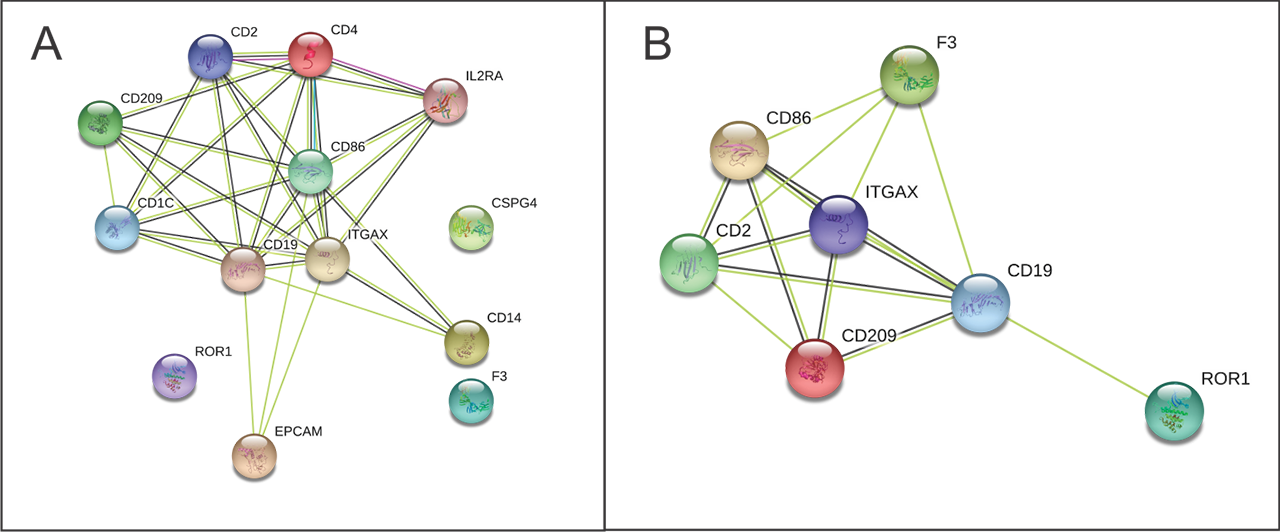
Results: 7/37 surface markers (CD2, CD11c, CD19, CD86, CD142, CD209 and ROR1) exhibited significantly higher expression in APS patients vs. both control groups (Fig 1). Specifically, CD86+, CD142+ (TF), ROR+ exosomes were found in 44% (7/16), CD2, CD19+, CD209+ in 38% (6/16) and CD11c+ in 31% (5/16) of APS patients, while there was no positive HBD or PC (p< 0.05). Using STRING analysis (Fig 2A), we found strongest GO term assigned to analytes APS vs. HBD, to be cell surface receptor signaling pathway, the immune system process, while weaker association was found for regulation of T cell activation. In the KEGG pathway, the strongest association was shown for hematopoietic cell lineage, and less strong for cell adhesion molecules and complement/coagulation cascades. When comparing APS to both control groups (Fig 2B) in the KEGG pathway the association for complement/coagulation cascades was stronger.
Conclusion: Significant differences in exosomal surface markers of APS patients vs. HBD and PC indicate the involvement of the immune system, surface receptor signaling, cell adhesion molecules and complement/coagulation cascades. Profiles of exosomes thus show activated status of immune cells and coagulation cascade in aPL positive patients. Our study also demonstrates that MACSPlex facilitates sensitive multiparametric phenotyping of exosomes in patient plasma.
- Chaturvedi S, Semin Thromb Hemost, 2018
- Lackner KJ, Exp Rev Clin Immunol, 2018
- Tan L, Autoimmunity, 2016
- Zigon P, Clinical and Developmental Immunology, 2013
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Štok U, blokar E, Ambrožič A, Tomsic M, Sodin-Semrl S, Čučnik S, Žigon P. Surface Proteins on Exosomes Derived from Plasma of APS Patients Indicate an Altered Immune, Cell Adhesion and Coagulation Profile [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/surface-proteins-on-exosomes-derived-from-plasma-of-aps-patients-indicate-an-altered-immune-cell-adhesion-and-coagulation-profile/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/surface-proteins-on-exosomes-derived-from-plasma-of-aps-patients-indicate-an-altered-immune-cell-adhesion-and-coagulation-profile/