Session Information
Date: Wednesday, October 24, 2018
Title: 6W018 ACR Abstract: Epidemiology & Pub Health IV: Determinants & Consequences of Tx (2952–2957)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 11:00AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: While efficacy of triple therapy [methotrexate (MTX), sulfasalazine (HCQ), and sulfasalazine (SSZ)] and TNF inhibitor (TNFi) plus MTX was similar in a previous clinical trial, use of triple therapy is infrequent in the US. We aimed to examine geographical and clinical factors associated with the two treatment strategies for RA.
Methods: We used Truven MarketScan data (2003-2014) to conduct a cohort study among RA patients ≥18 years old with MTX prescription. Triple therapy was defined as adding on both HCQ and SSZ, and TNFi therapy was defined as adding a TNFi to MTX. Index date was the first dispensing date of the last drug to complete triple therapy, or TNFi. Exclusion criteria included malignancy, renal dialysis, HIV, nursing home stay, or hospitalized infection, and any prior use of study drugs except MTX 180 days before the index date. We assessed geographic patterns and baseline covariates including demographics, comorbidities, medications, and health care utilizations associated with starting TNFi or triple therapy using multivariable logistic regression.
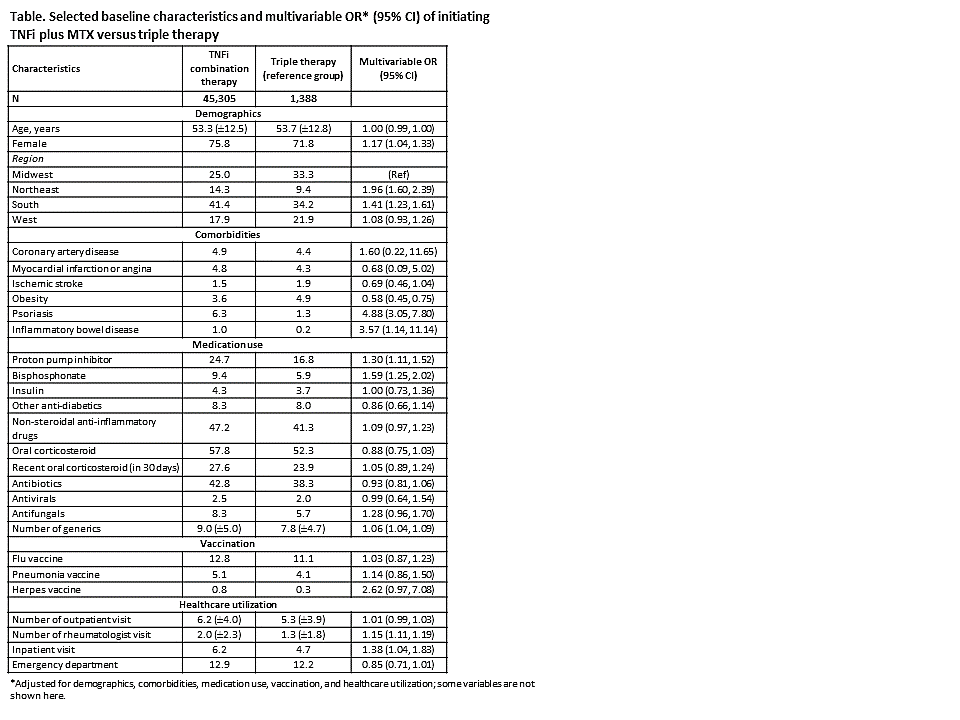
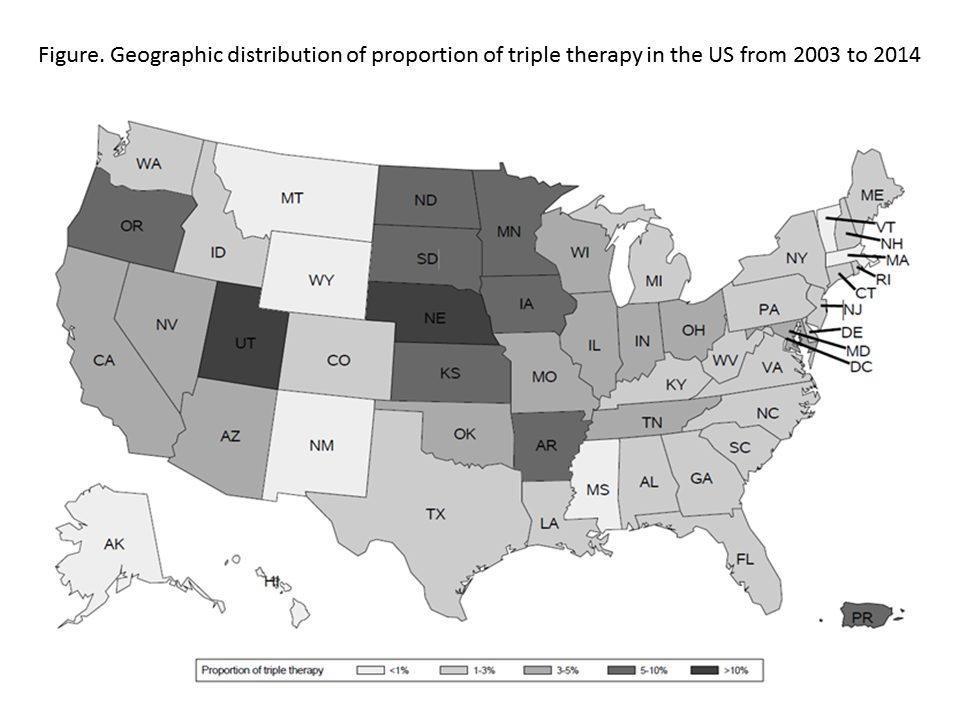
Results: We identified a total of 46,693 patients (45,305 (97.0%) TNFi plus MTX and 1,388 (3.0%) triple therapy initiators). Females were more likely to receive TNFi therapy (OR, 95% CI =1.17, 1.04-1.33, Table). We noted a significant geographical pattern with regard to initiation of triple therapy (Figure). Patients were most likely to receive triple therapy in Midwest (Table, Figure). Specifically, Nebraska had the highest rate of receiving triple therapy, followed by its adjacent states. We did not find any association between underlying cardiovascular diseases and either of two treatment groups. However, obese patients were 42% more likely to be started on triple therapy. Baseline psoriasis and inflammatory bowel disease increased odds of receiving TNFi (OR, 95% CI = 4.88, 3.05-7.80 and 3.57, 1.14-11.14). Generally, TNFi initiators used more medications and had rheumatologist or inpatient visit more frequently than those on triple therapy.
Conclusion: In this large nationwide cohort of RA patients, triple therapy use was infrequent. Geographical and certain clinical factors such as coexisting psoriasis or inflammatory bowel disease, use of bisphosphonates, proton pump inhibitors, frequency of rheumatologists visit, and inpatient visit were associated with choosing TNFi versus triple therapy.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jin Y, Kang EH, Tong A, Desai RJ, Kim SC. Factors Related to Initiation of TNF Inhibitor Versus Triple Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-related-to-initiation-of-tnf-inhibitor-versus-triple-therapy-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/factors-related-to-initiation-of-tnf-inhibitor-versus-triple-therapy-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients/